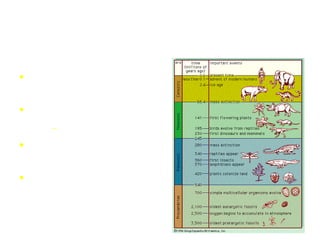
1) Scientists believe the Big Bang around 12-14 billion years ago formed galaxies, stars, and planets from the explosion of atomic particles.
2) A supernova 7 billion years ago from an early generation of giant stars produced a solar nebula of dust and gas that collapsed under gravity to form our sun and planets.
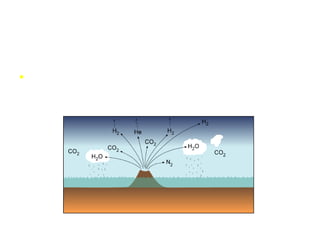
3) 4.6 billion years ago, Earth was a molten ball surrounded by an atmosphere of hydrogen and helium, which early volcanoes transformed with gases like carbon dioxide and water vapor, allowing early life to emerge.