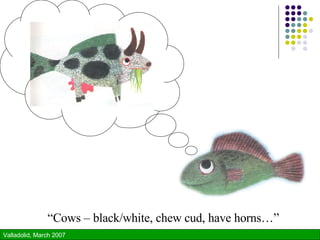
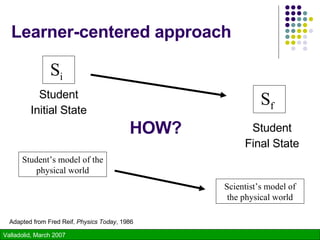
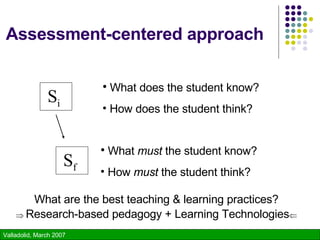
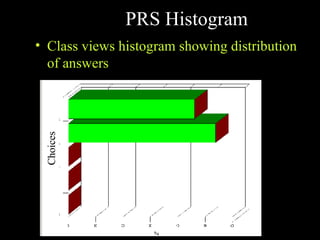
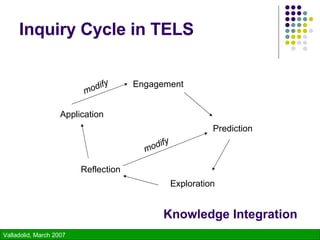
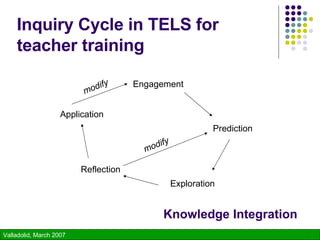
The document discusses using technology to enhance learning environments and science education. It describes a parable about a fish and frog that illustrates how direct experience is not always possible and technology can provide alternative experiences. It then discusses frameworks for learner-centered, knowledge-centered, assessment-centered, and community-centered education and how these converge with principles of constructivism. Specific technologies described include classroom response systems, virtual learning spaces, and GroupScribbles - an electronic collaborative whiteboard tool.
![Inquiry, Teaching & Technology S. Raj Chaudhury Christopher Newport University Newport News, Virginia, USA [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presntacinraj-1195153373421160-5/75/presntacionRaj-1-2048.jpg)