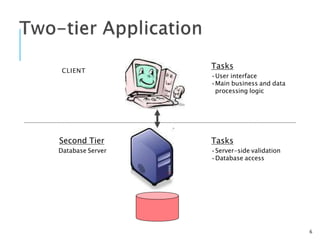
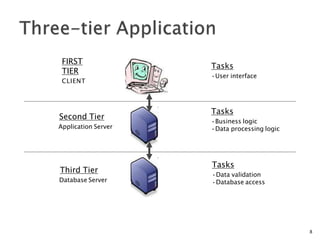
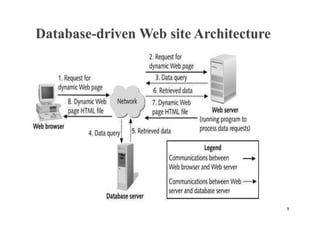
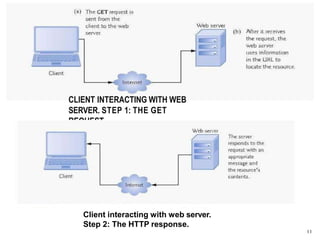
A web database allows storing and accessing data over the internet through a website. It uses a client-server model where the client interacts with a web server to make requests and receive responses with data from a database server. Web databases provide platform independence and allow businesses to provide customer access to account information anywhere online. Emerging technologies like NoSQL and Hadoop are leading to new database innovations while challenges remain around reliability, security, and scalability for large commercial websites.