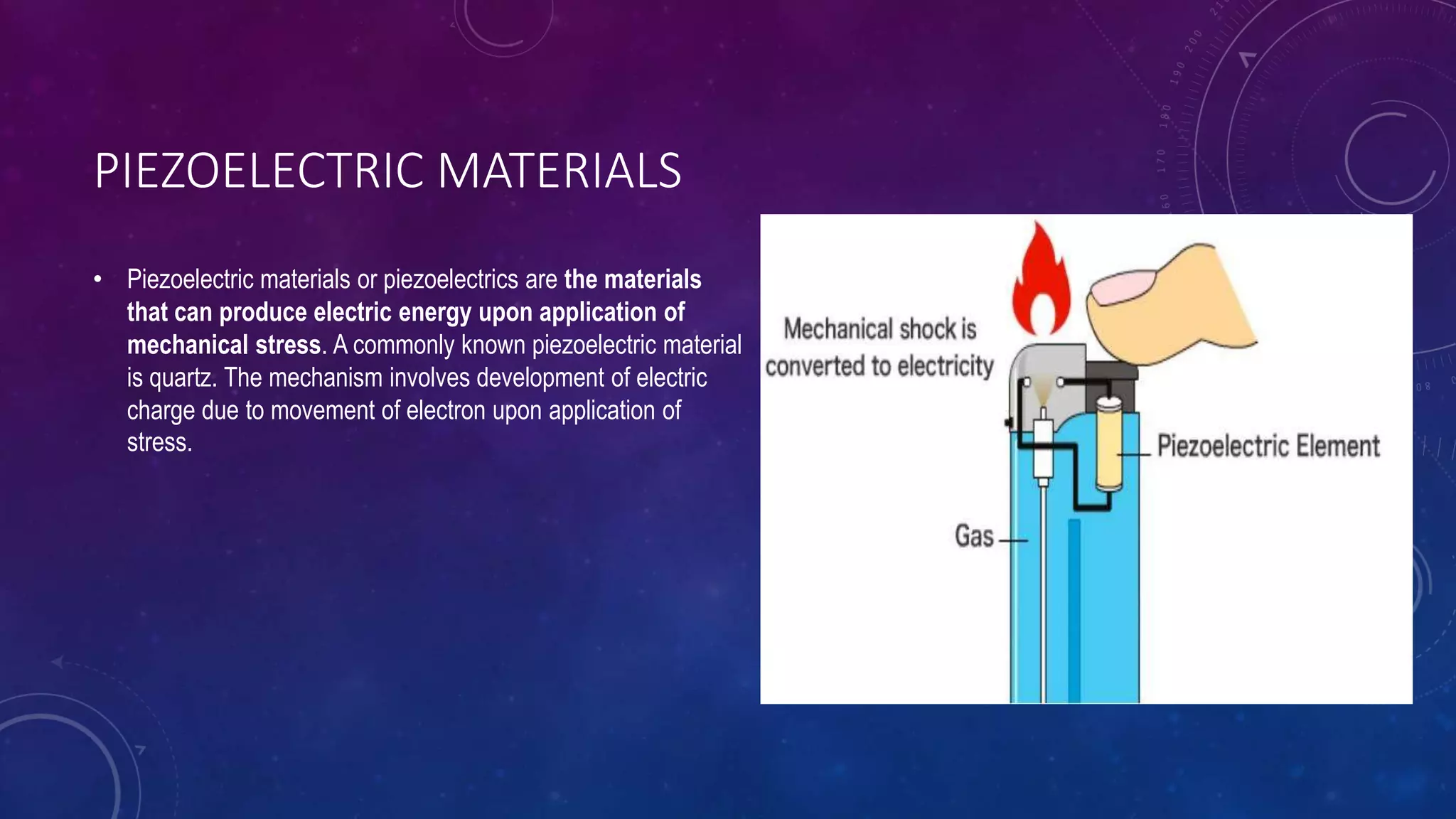
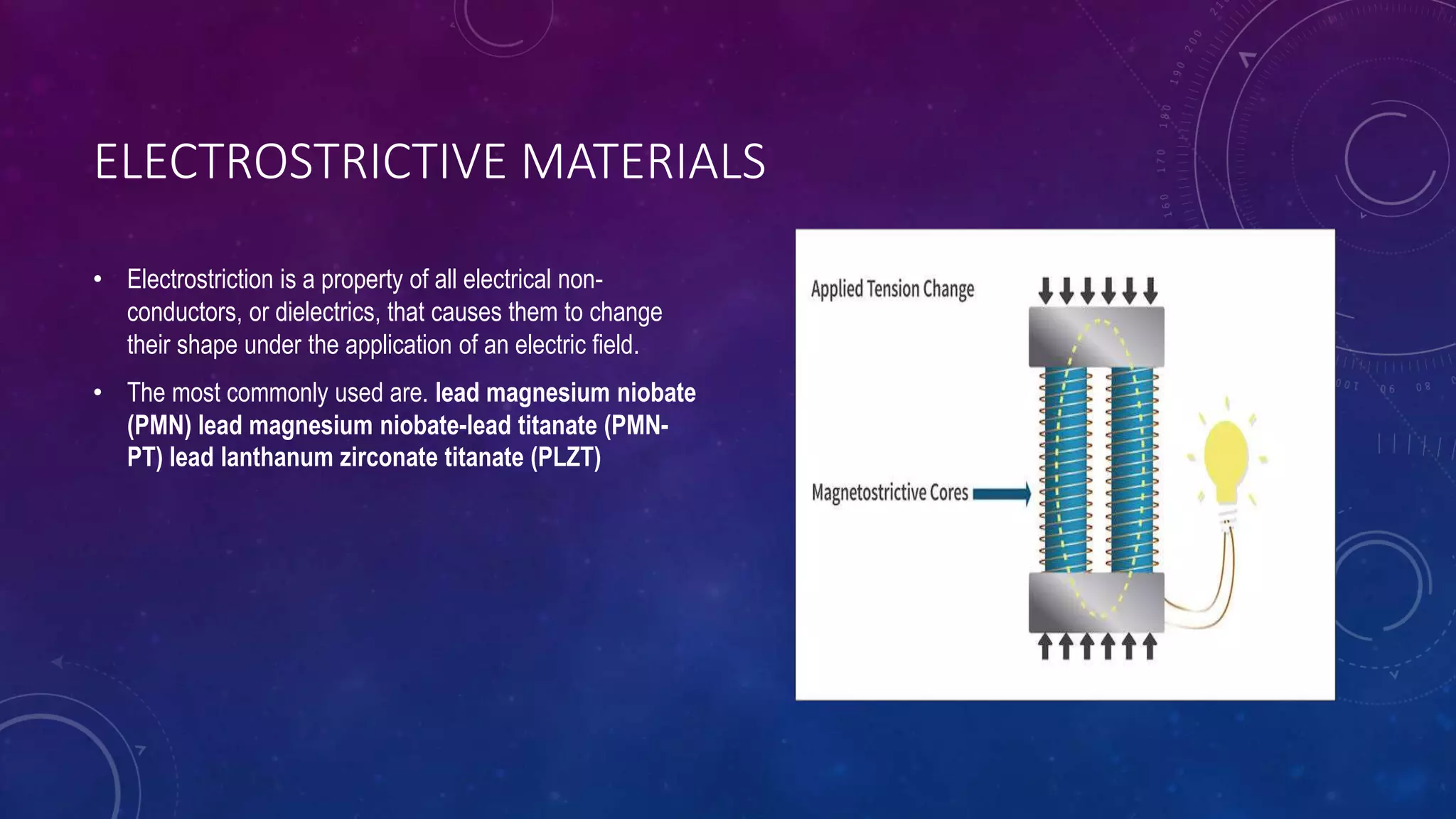
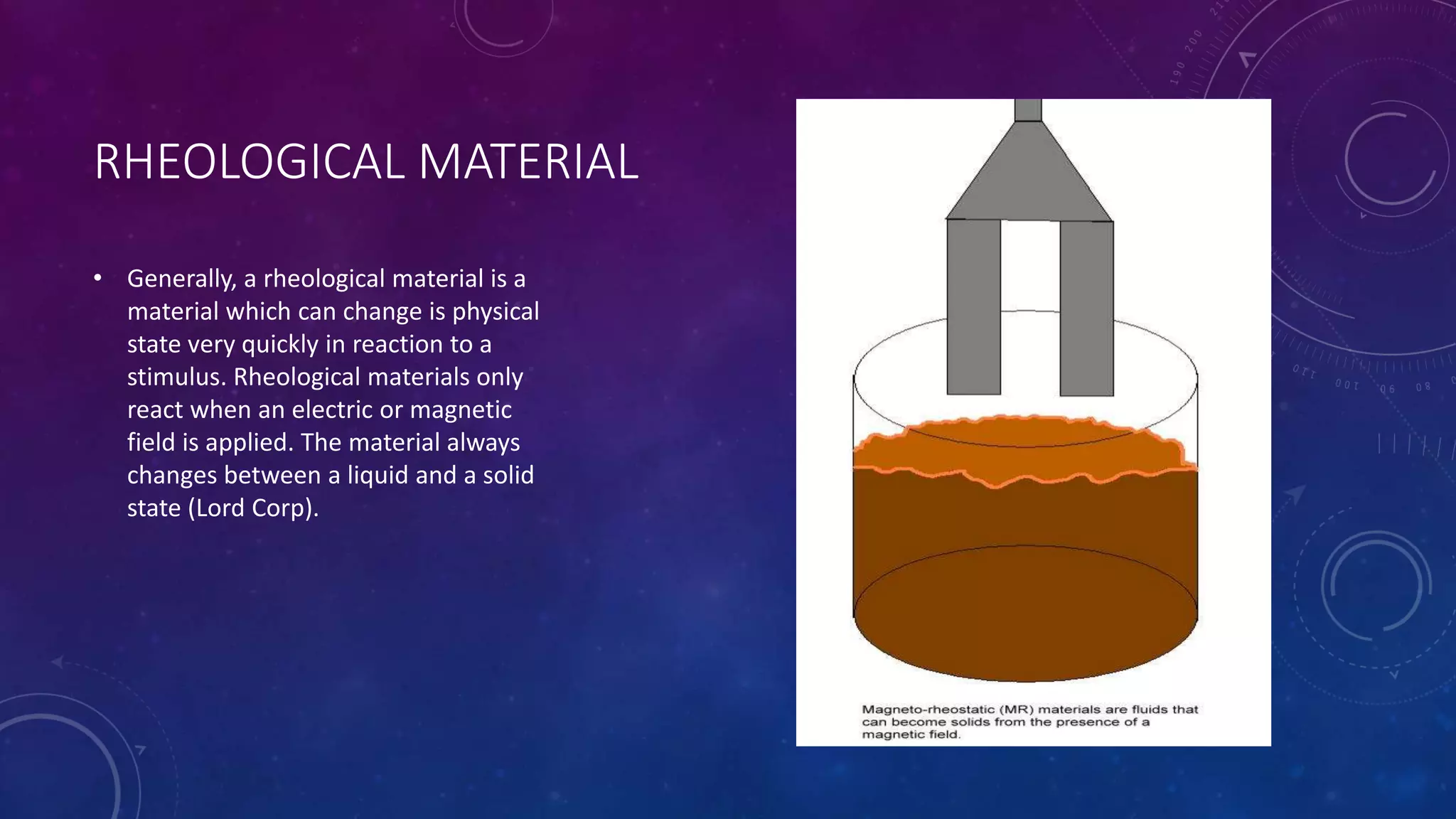
Smart materials are materials that can change their properties in a controlled, reversible manner in response to external stimuli like stress, temperature, or electric/magnetic fields. They can sense and respond to their environment in predictable ways, simplifying devices by reducing weight and chances of failure compared to conventional mechanisms. Some key smart materials include piezoelectric, magnetostrictive, electrostrictive, and thermoresponsive materials. Piezoelectric materials generate electric current when mechanically stressed while magnetostrictive materials convert between magnetic and elastic energy. Electrostrictive materials change shape with electric fields and thermoresponsive polymers change solubility with temperature. Advantages include new capabilities without sensors or electronics but overstimulation from