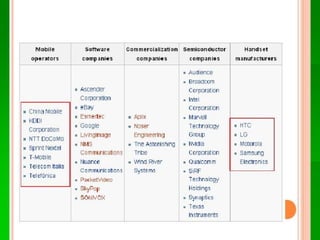
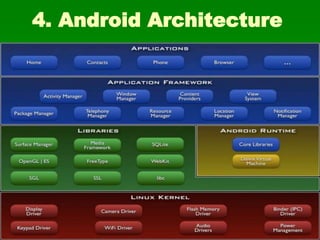
Android is an open-source operating system developed by Google and the Open Handset Alliance. It was created to provide a full software stack for mobile devices including an OS, middleware and key apps. The Android architecture includes applications, framework, libraries and services built on a Linux kernel. Developers use Java to write Android apps which run in their own process using the Dalvik virtual machine. The Android SDK provides tools like Eclipse IDE and emulators to help developers build apps for Android devices.