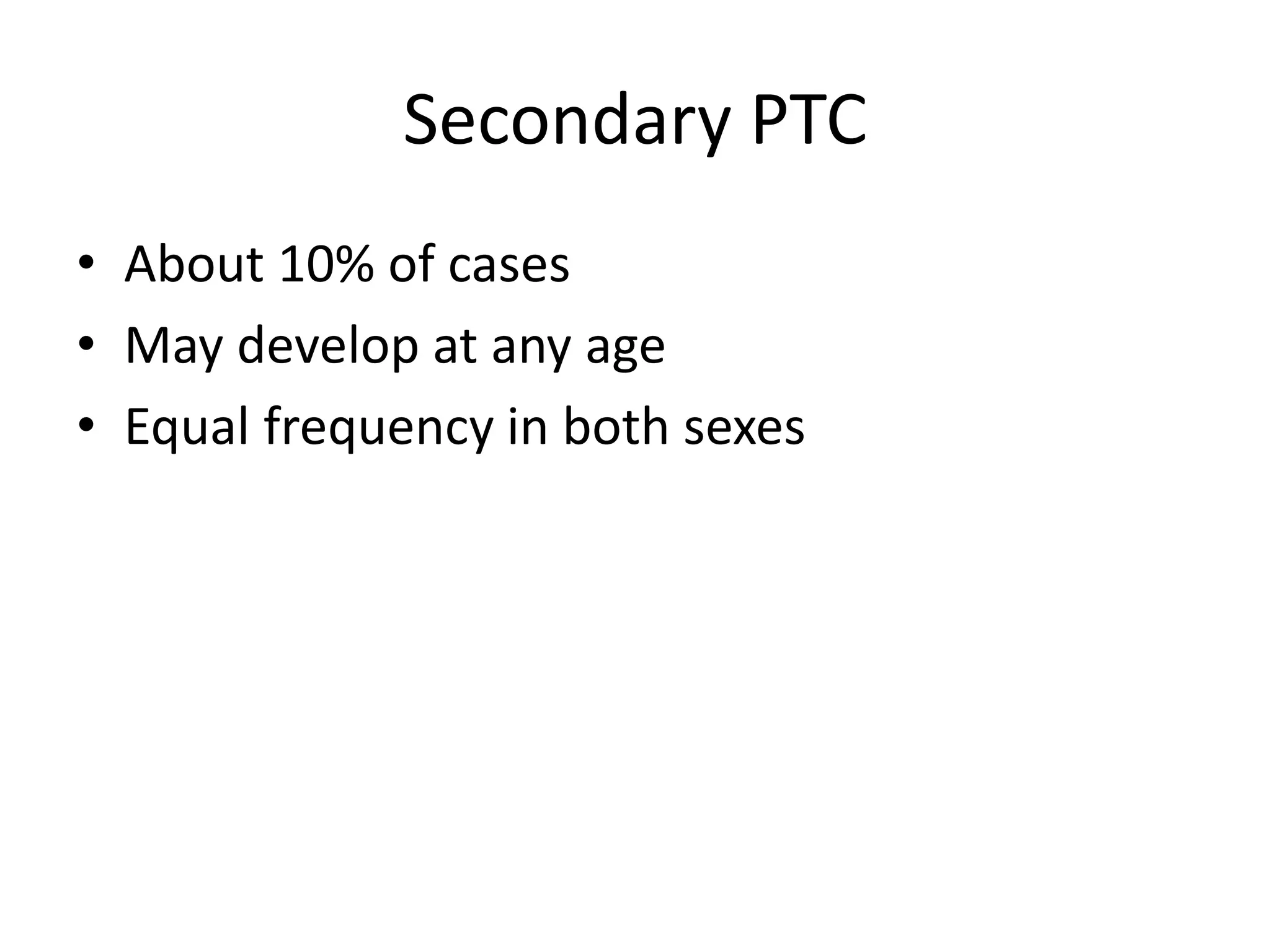
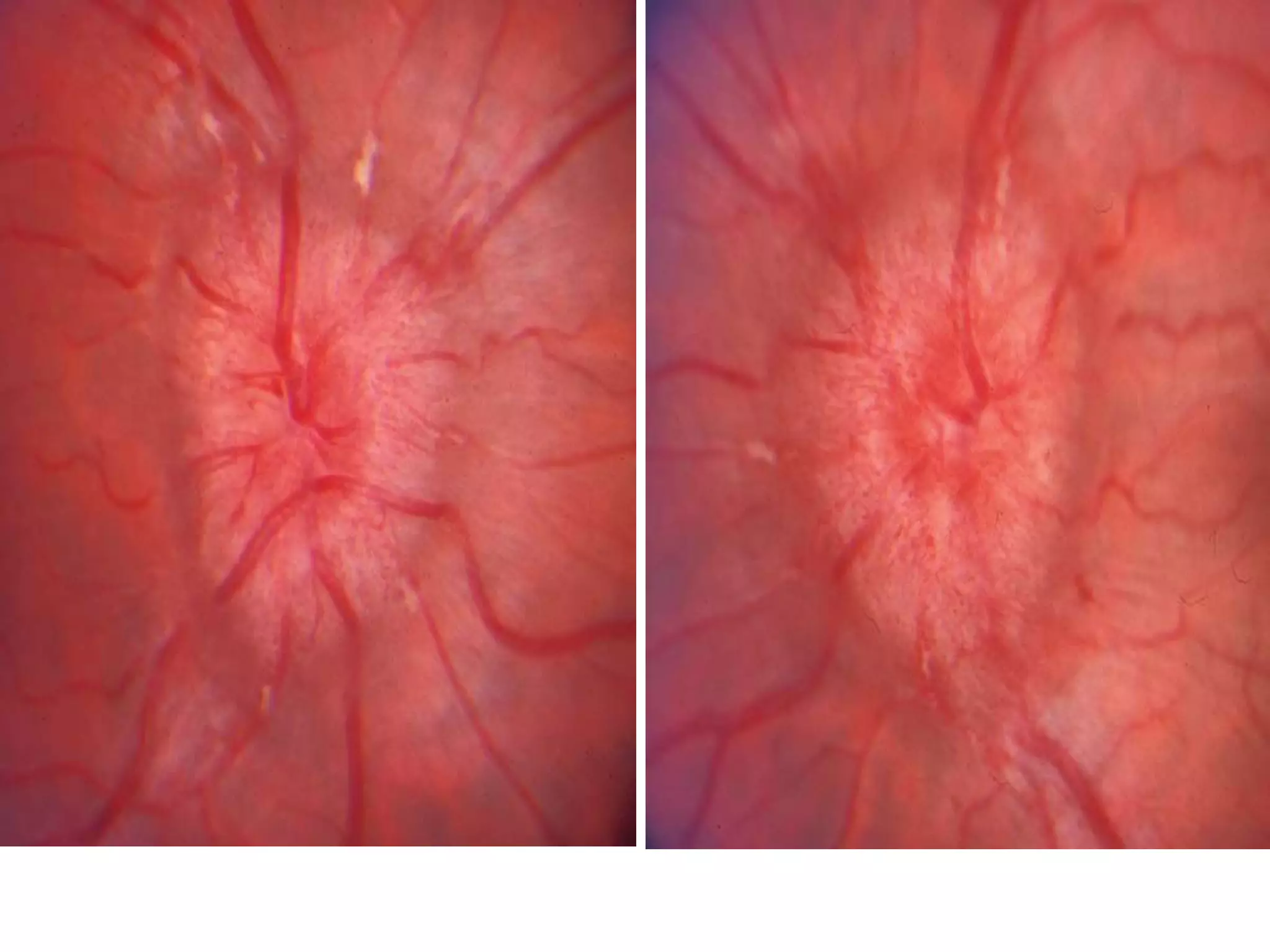
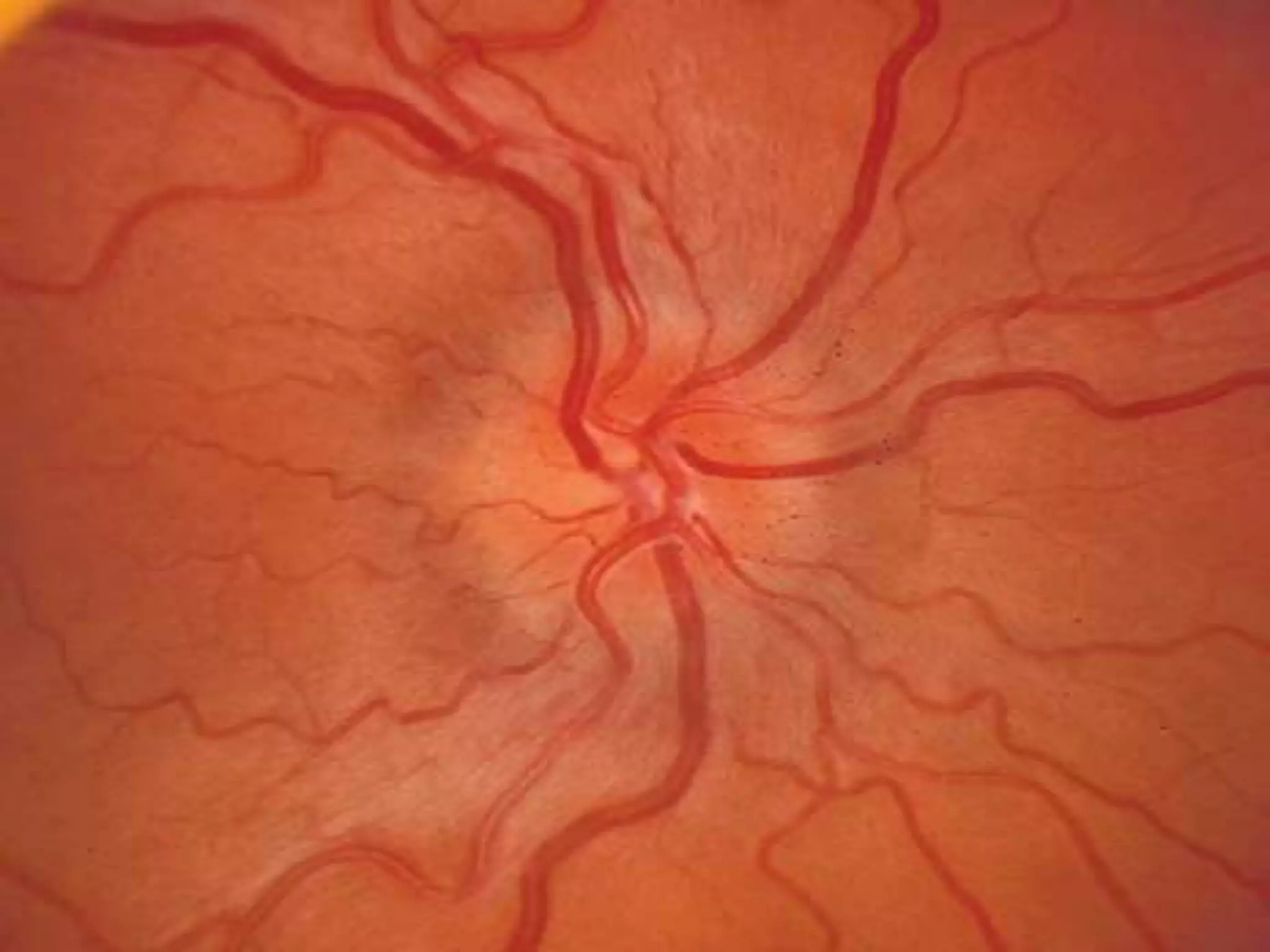
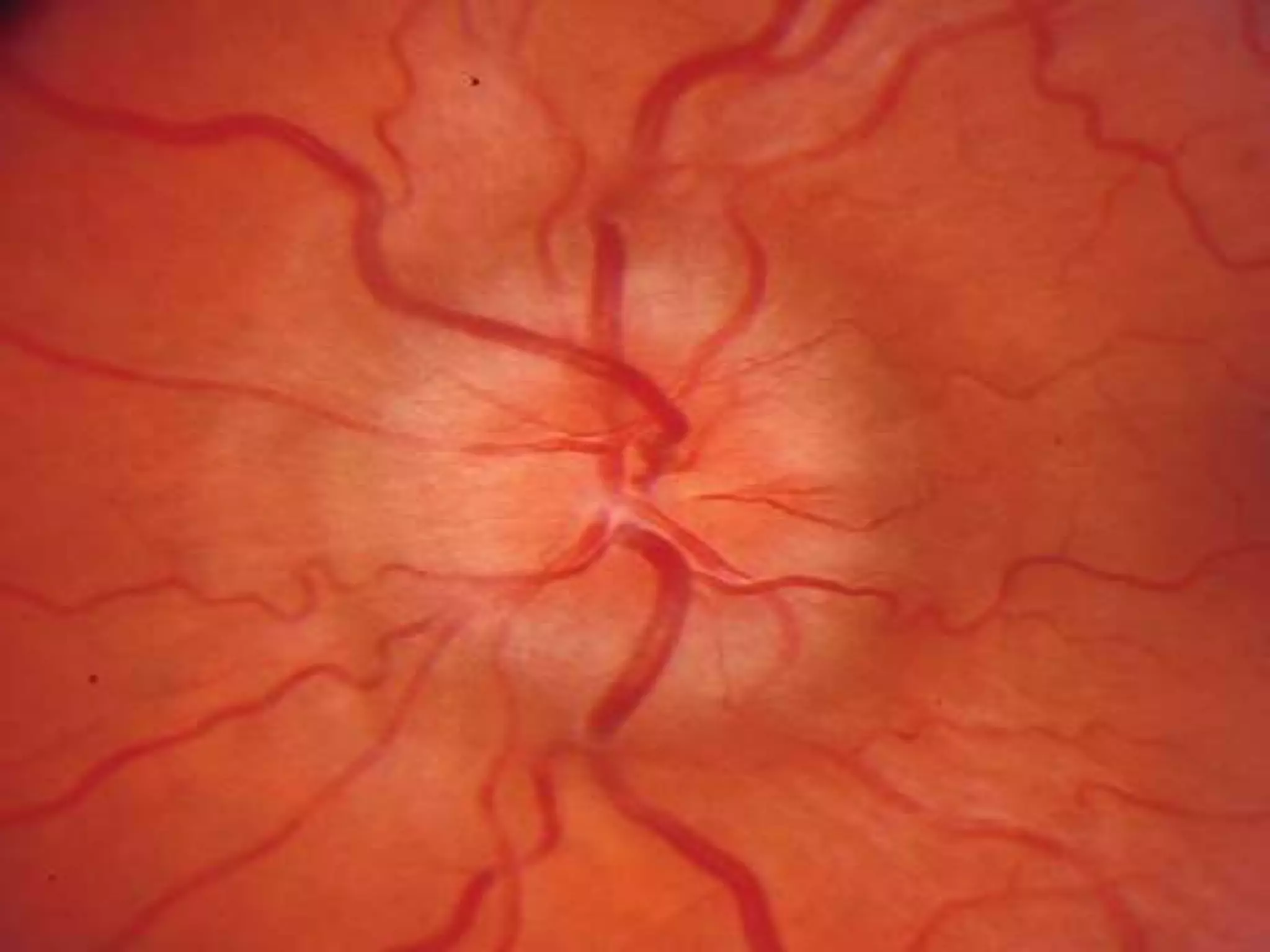
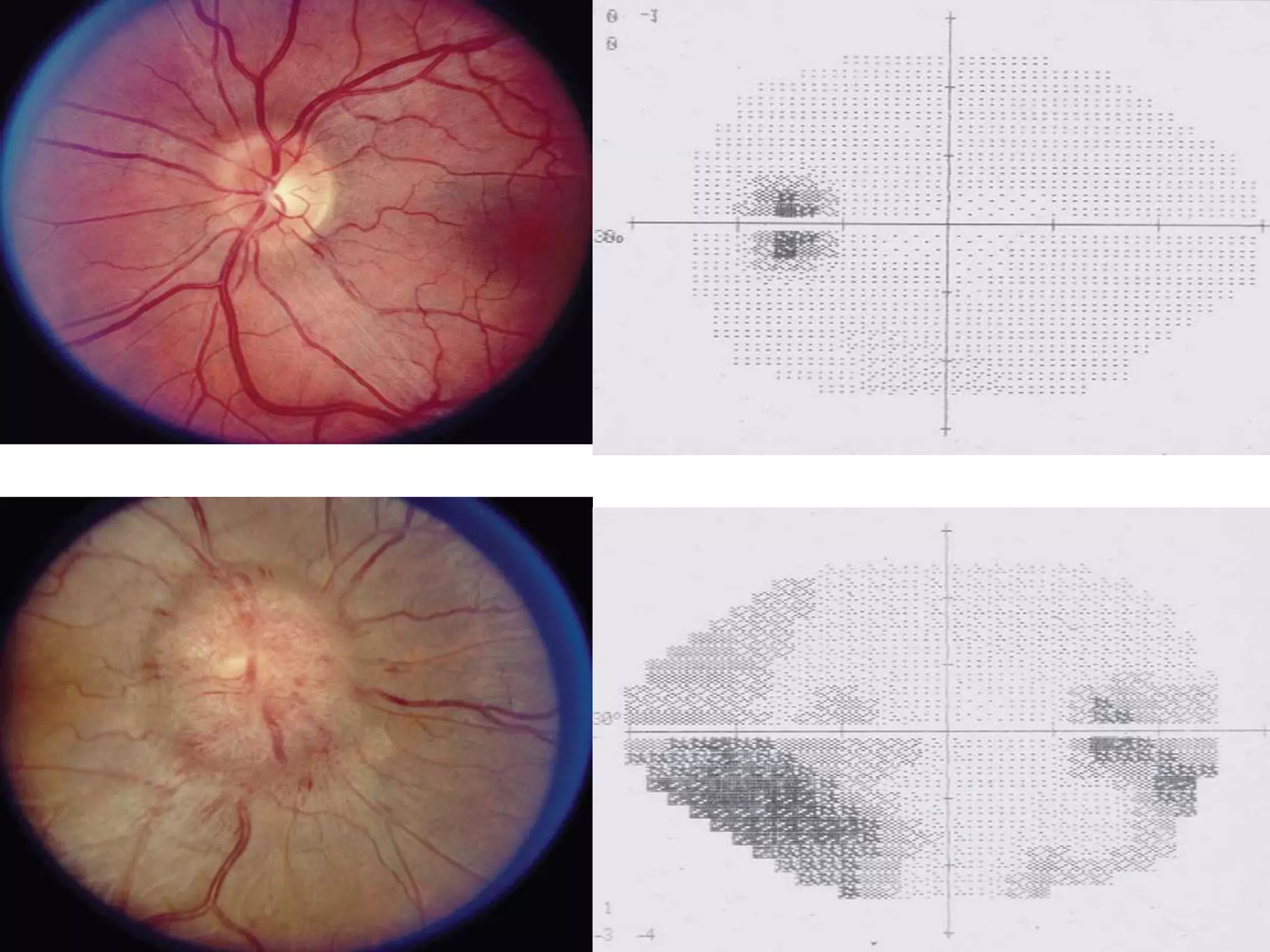
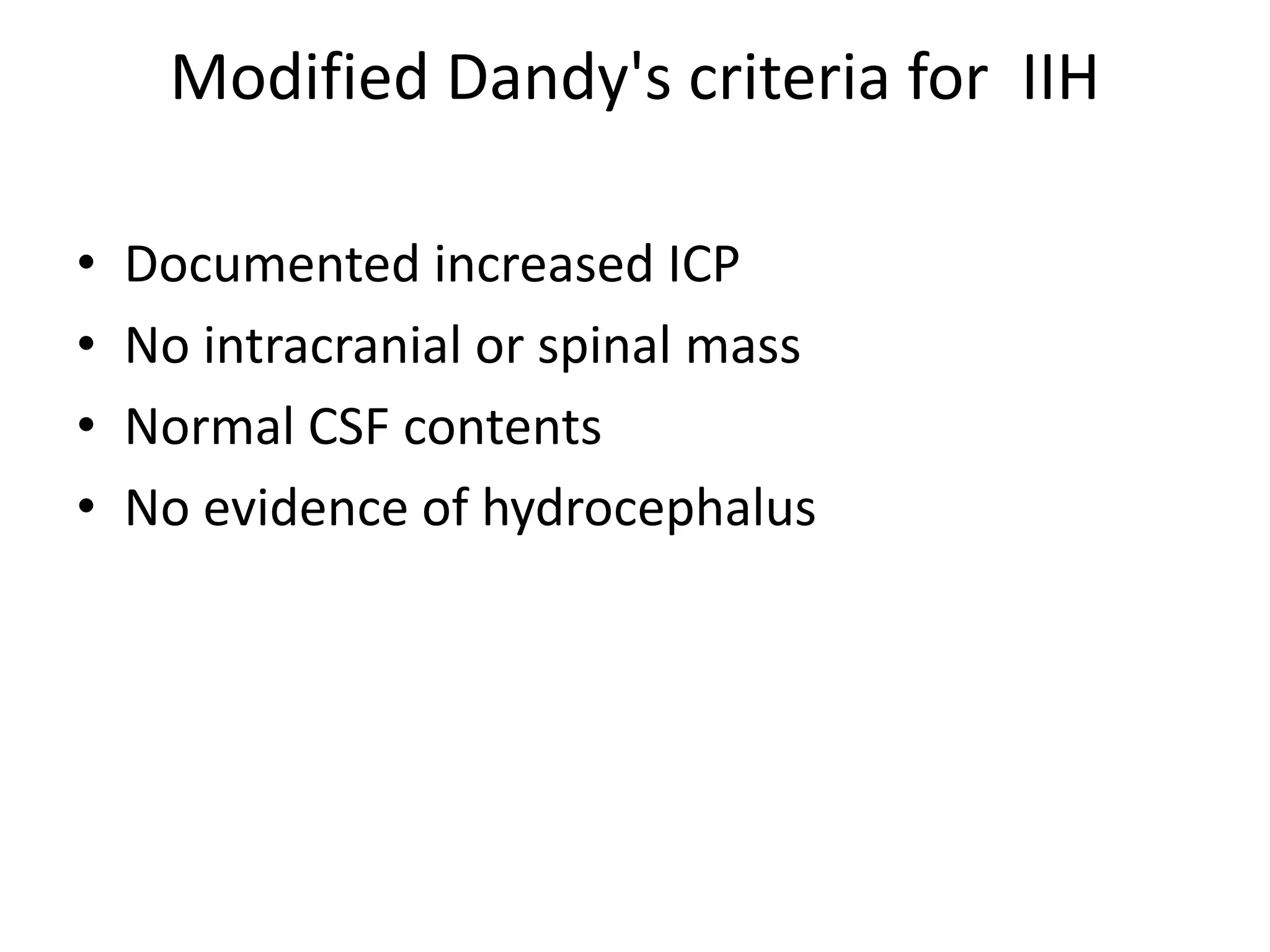
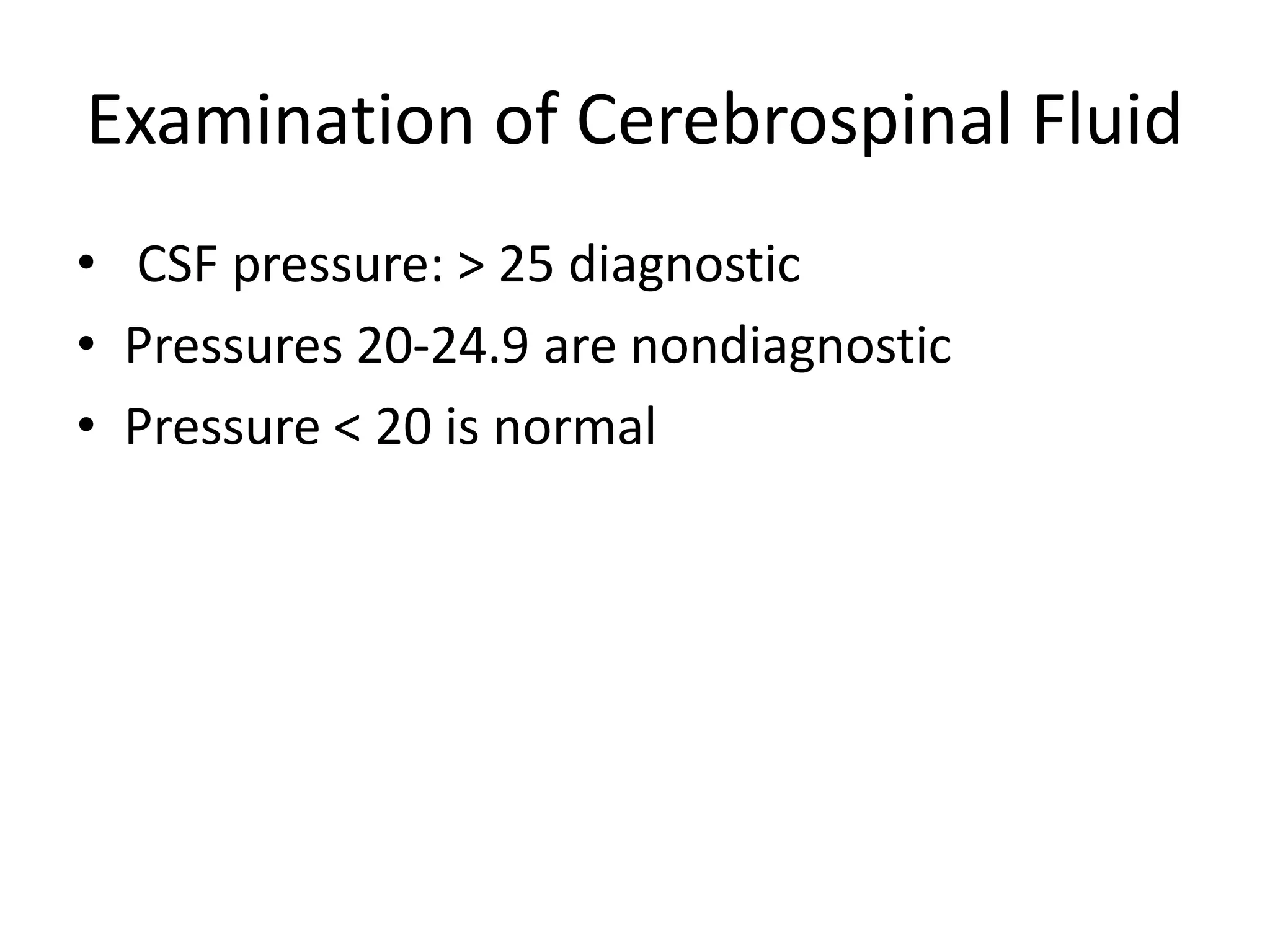
This document summarizes pseudotumor cerebri (PTC), also known as idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH). It describes a case of a 39-year-old obese female with PTC symptoms including headaches, visual issues, and papilledema. PTC is characterized by increased intracranial pressure without a tumor. Treatment involves weight loss, medications like acetazolamide, surgical procedures like optic nerve sheath fenestration or shunt placement, and managing any underlying causes. Complications can include permanent vision loss if not properly treated.