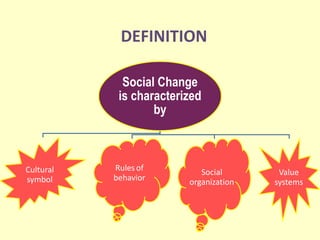
Social change is characterized by changes in cultural symbols, rules of behavior, social organization, and value systems over time. The document discusses the definition and history of social change, theories proposed by various theorists like Comte, Spencer, Spengler, Toynbee and Sorokin, types of social change, significance and impact on society, and social change in institutions. Key impacts include modernization, urbanization, technological changes, and changes to institutions like family, government, religion, and education to adapt to changing circumstances.