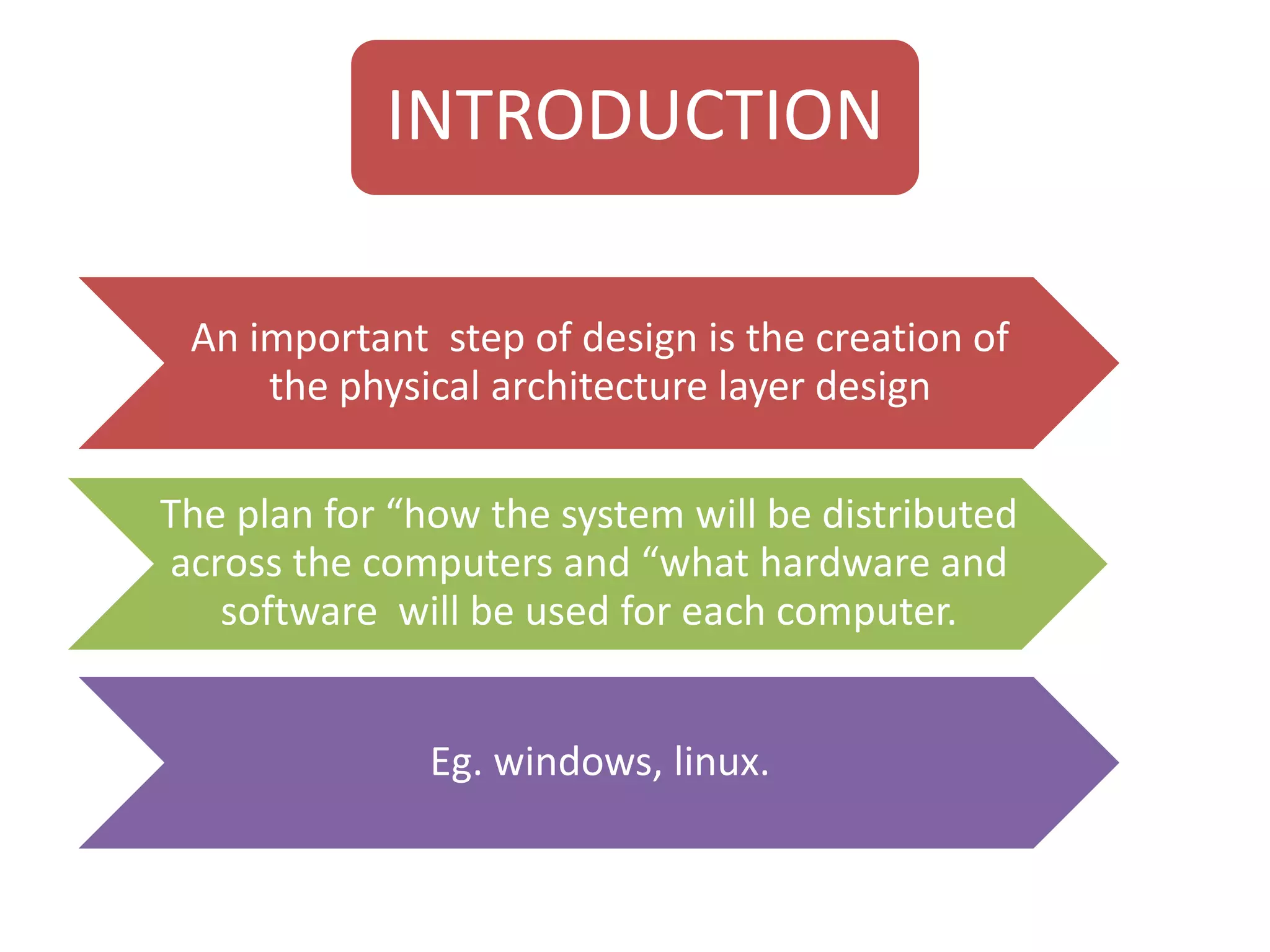
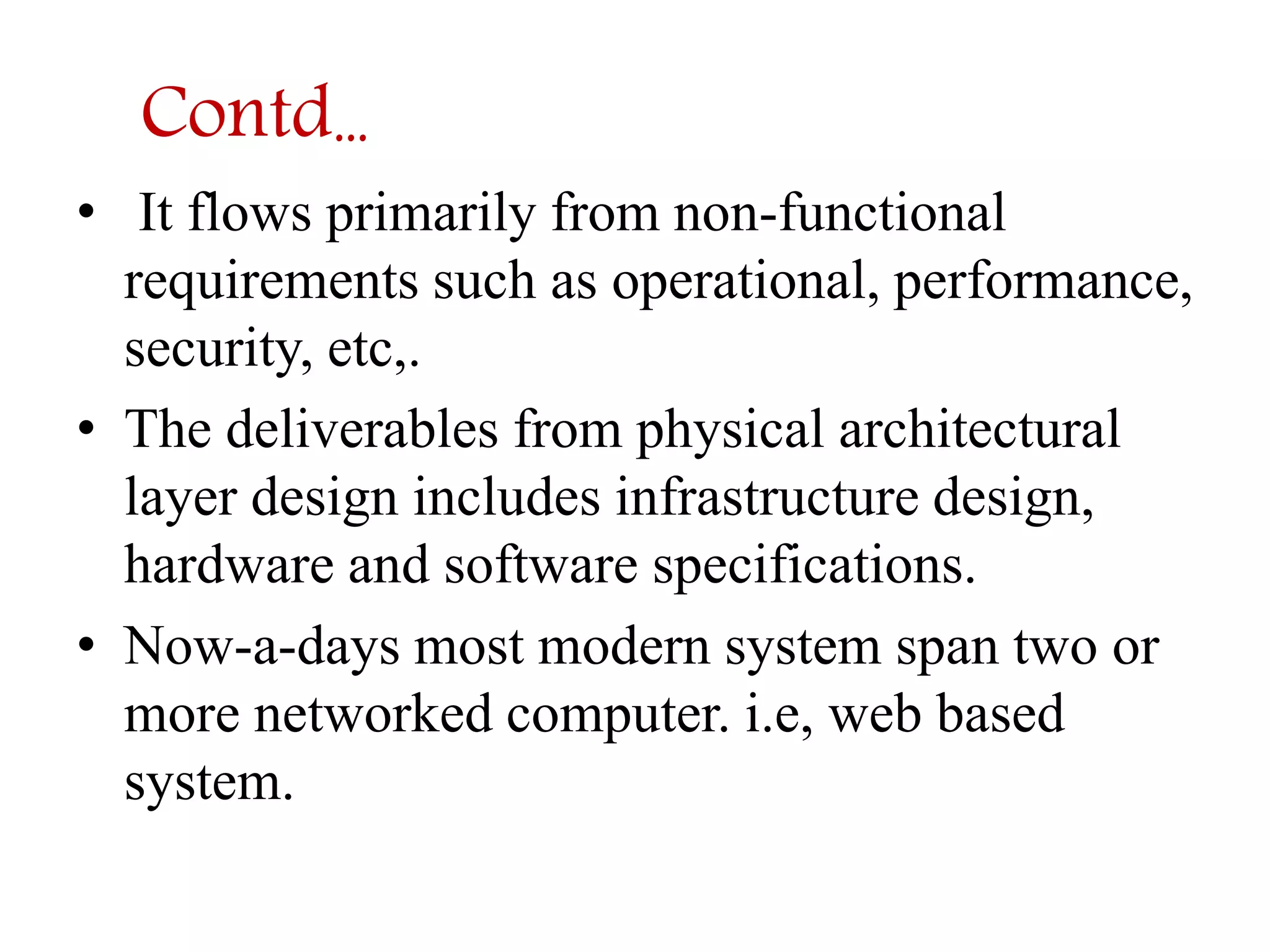
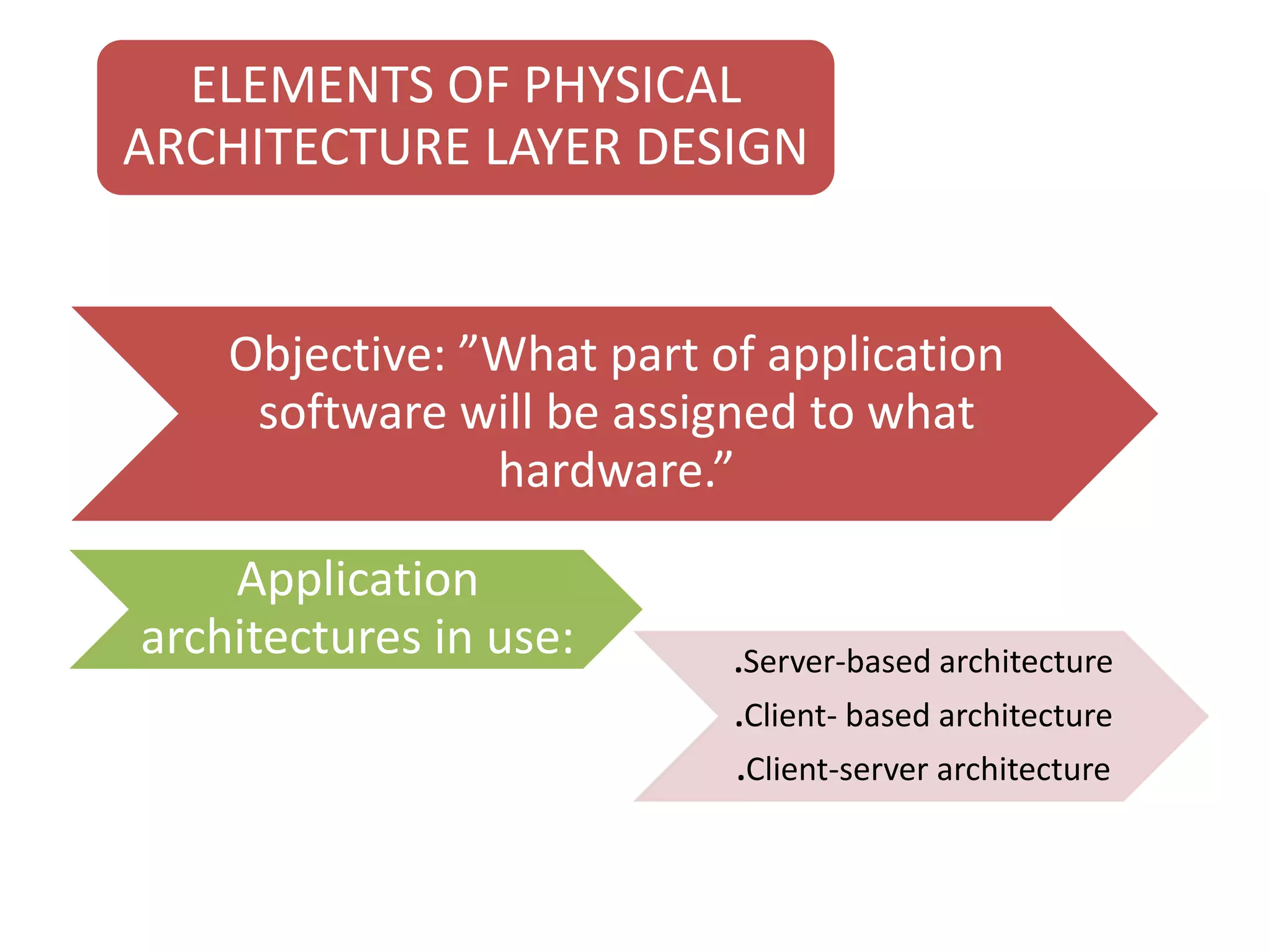
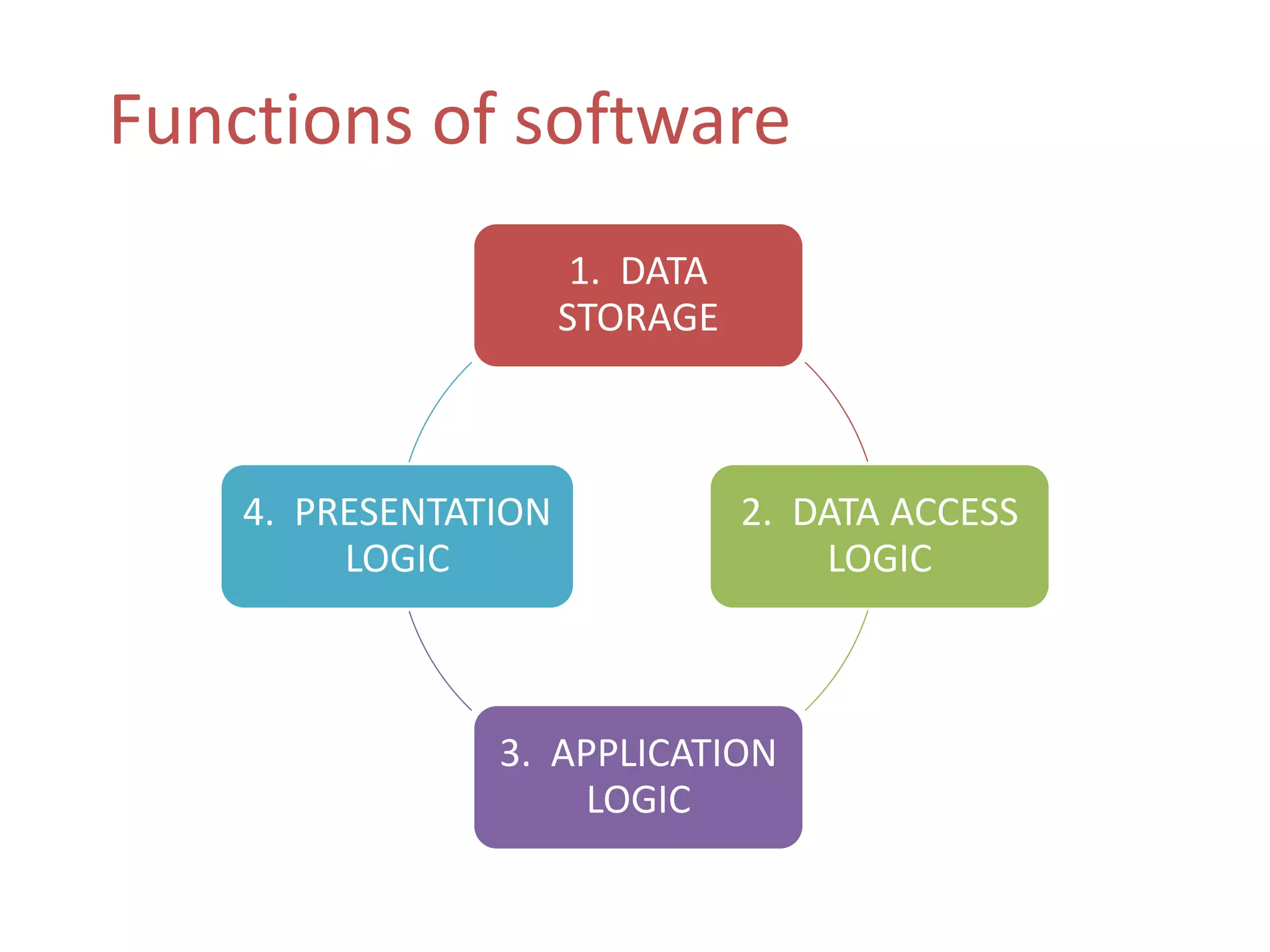
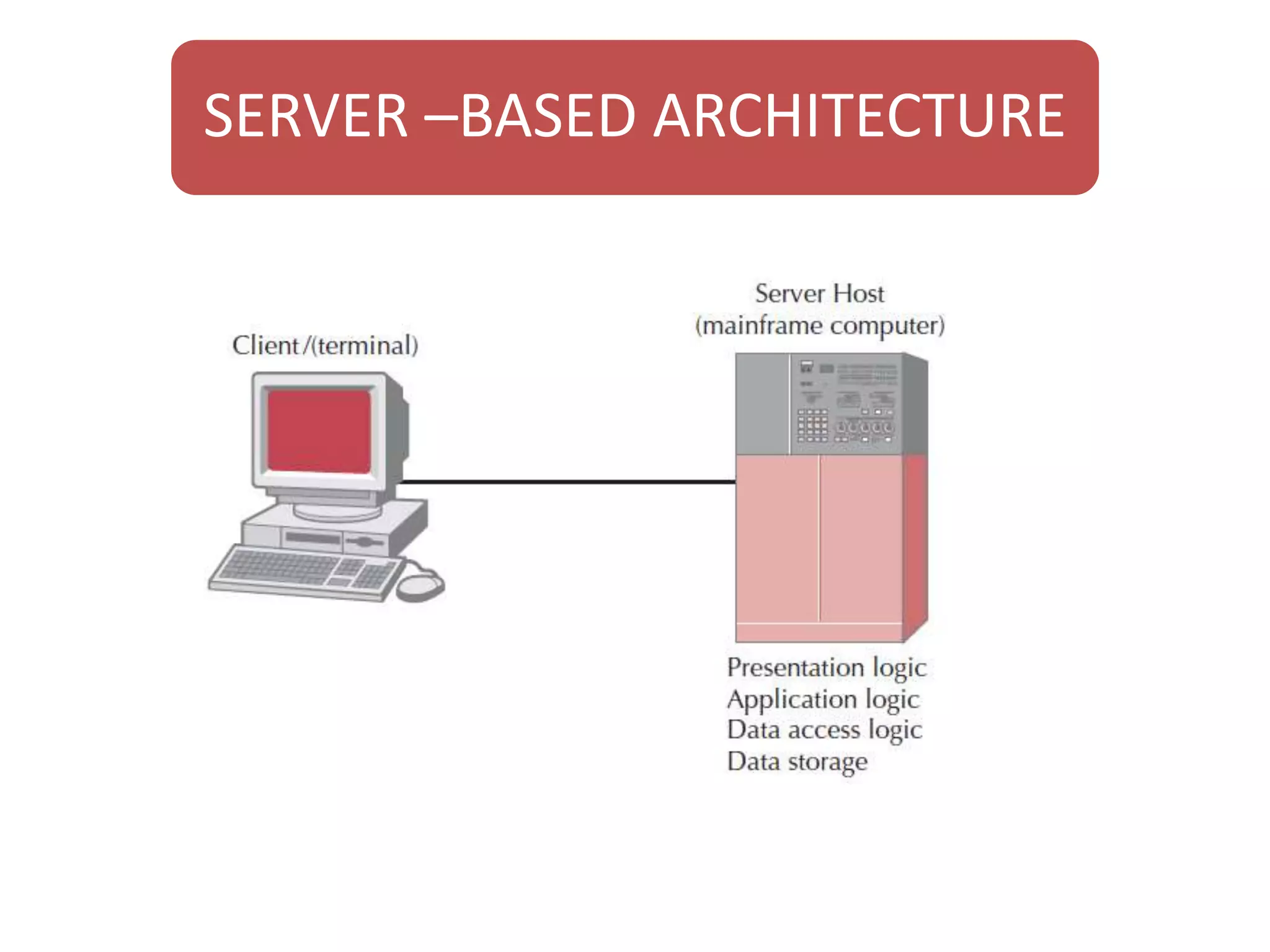
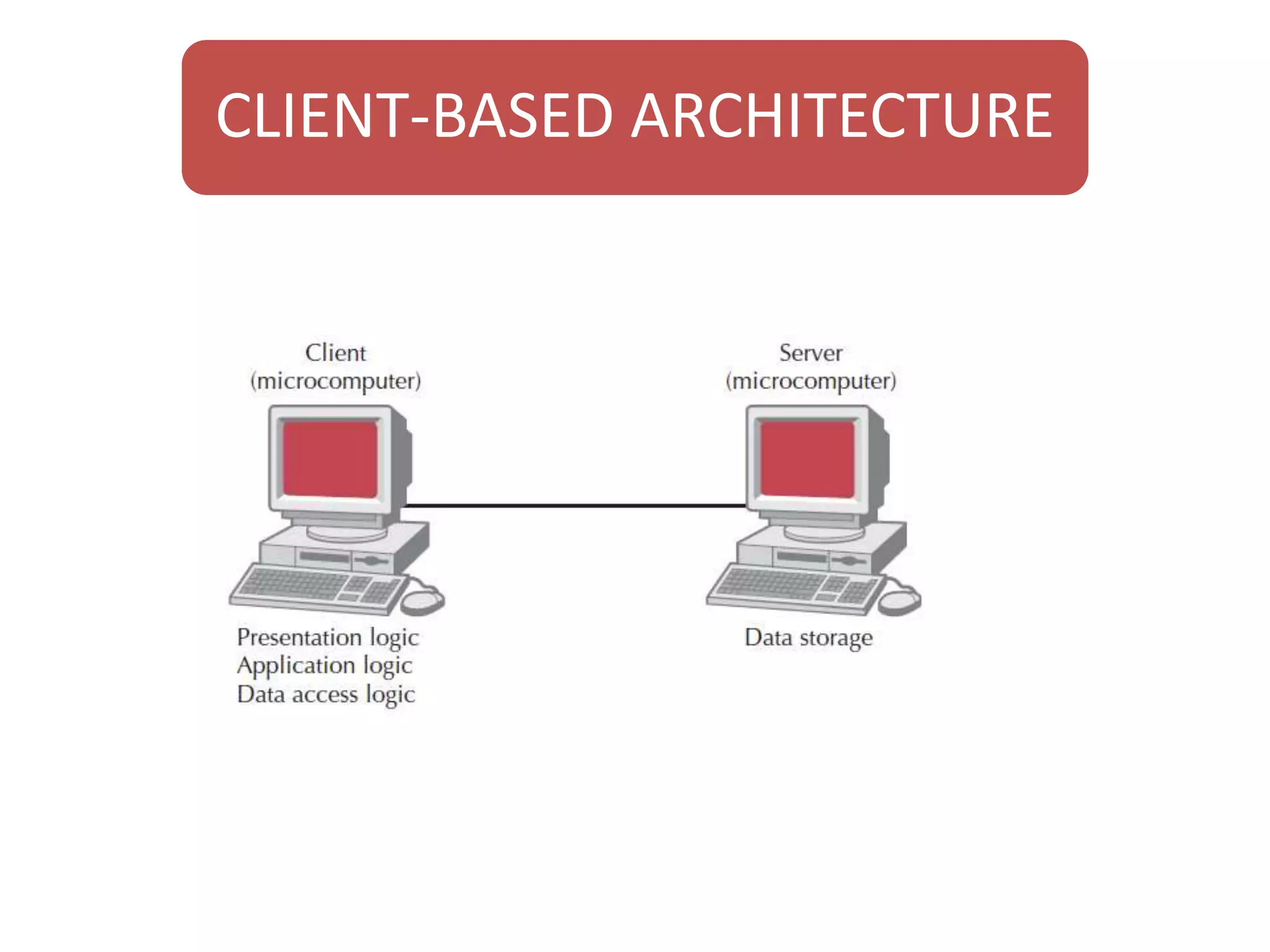
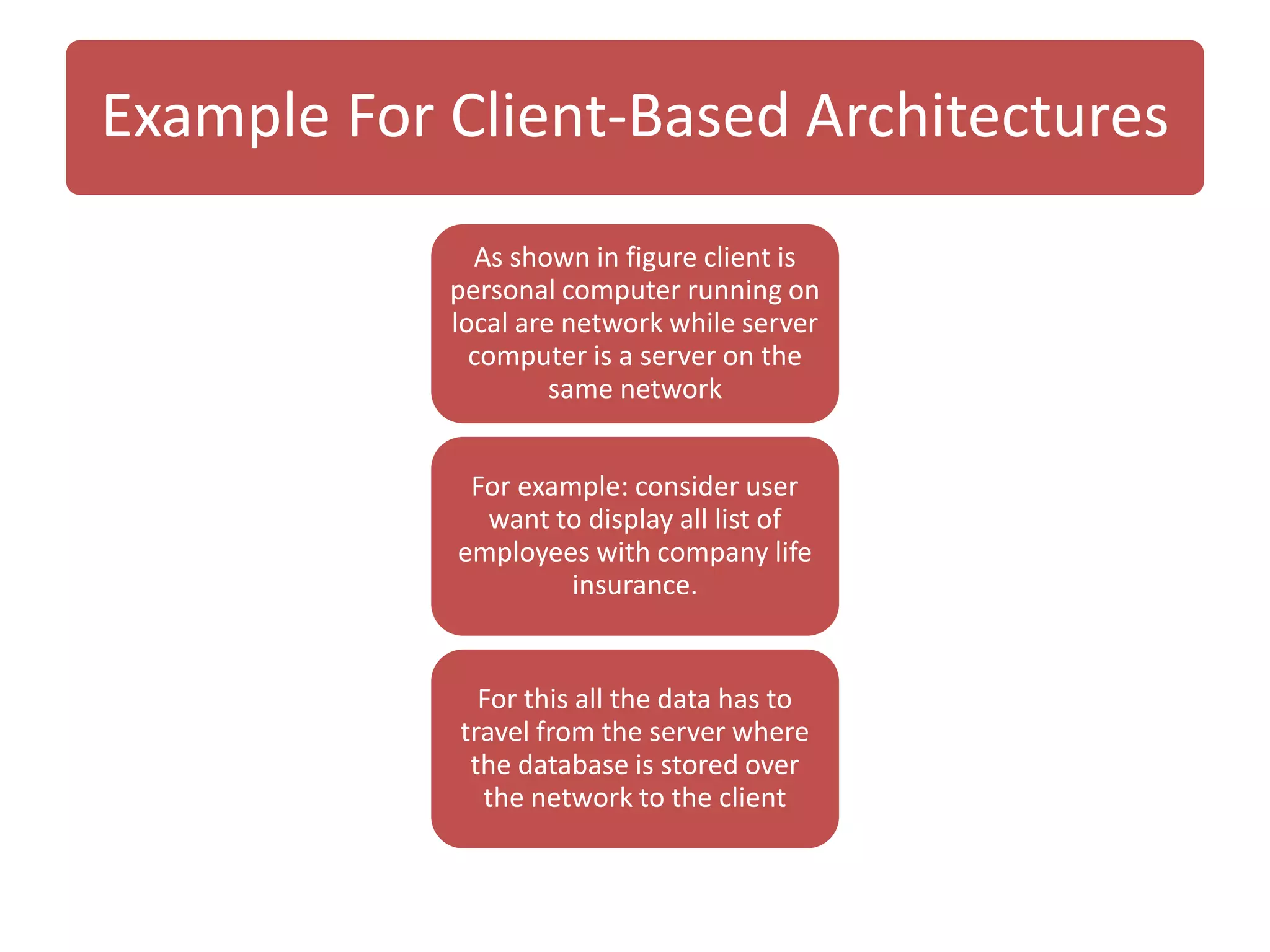
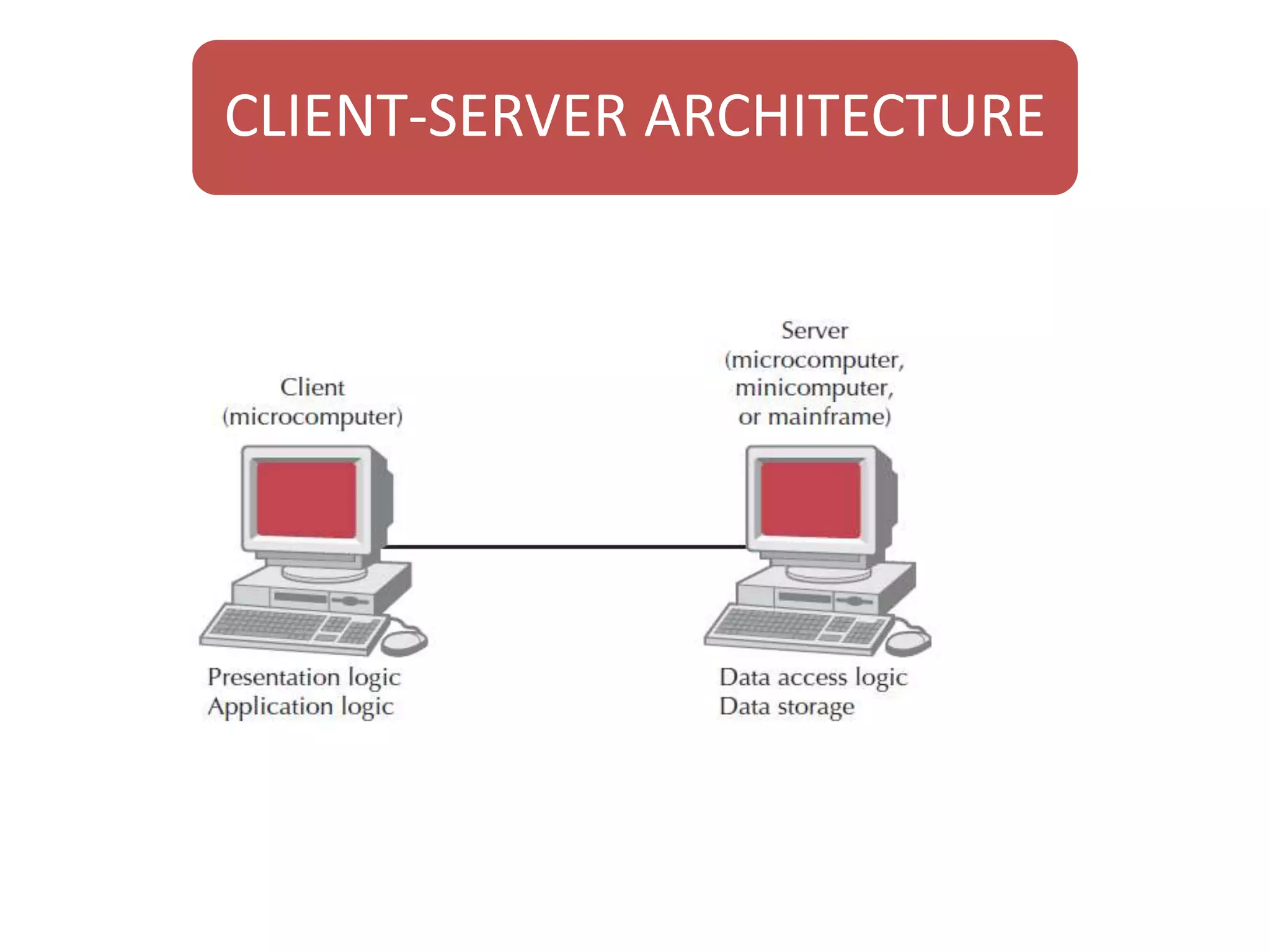
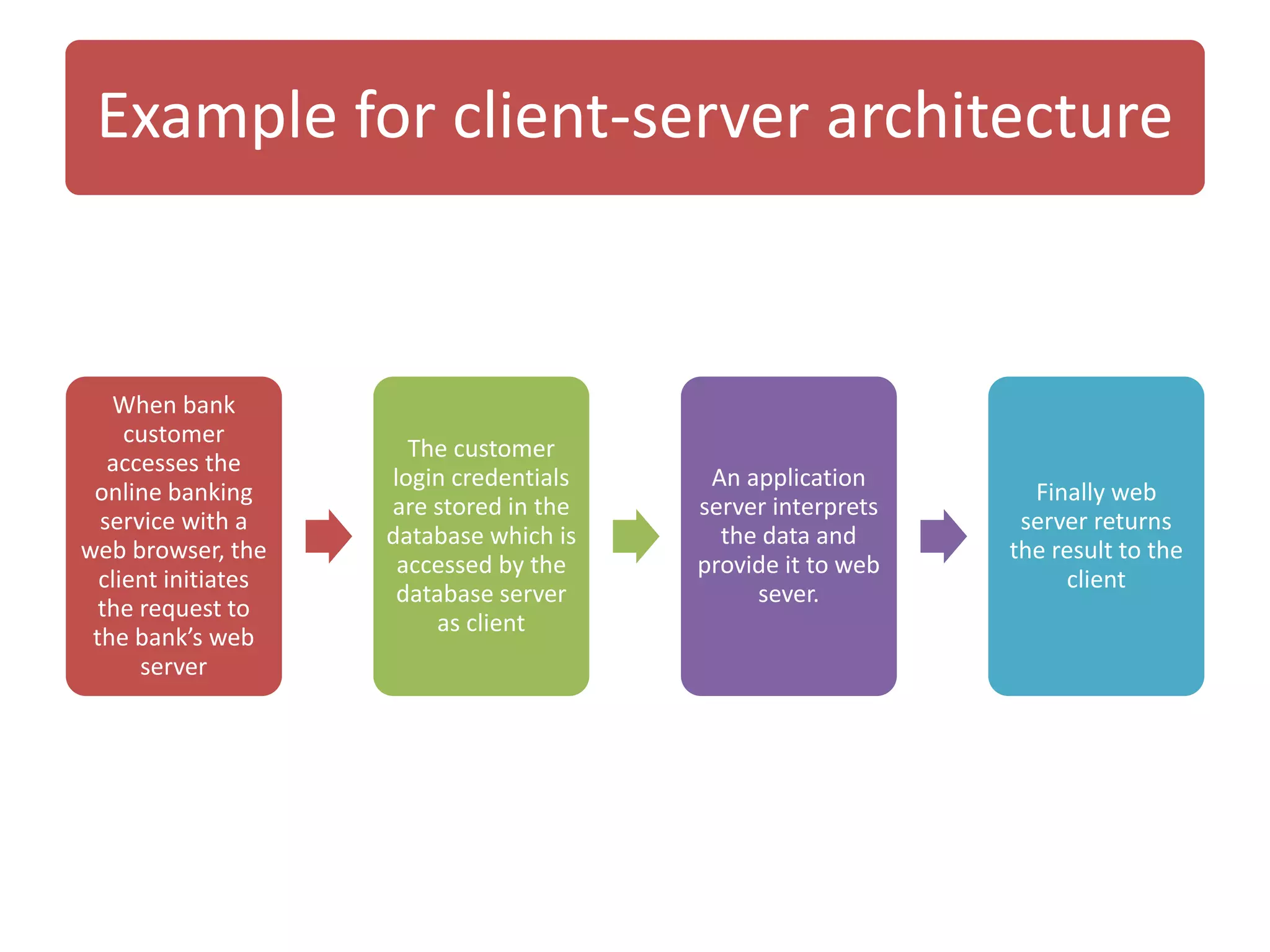
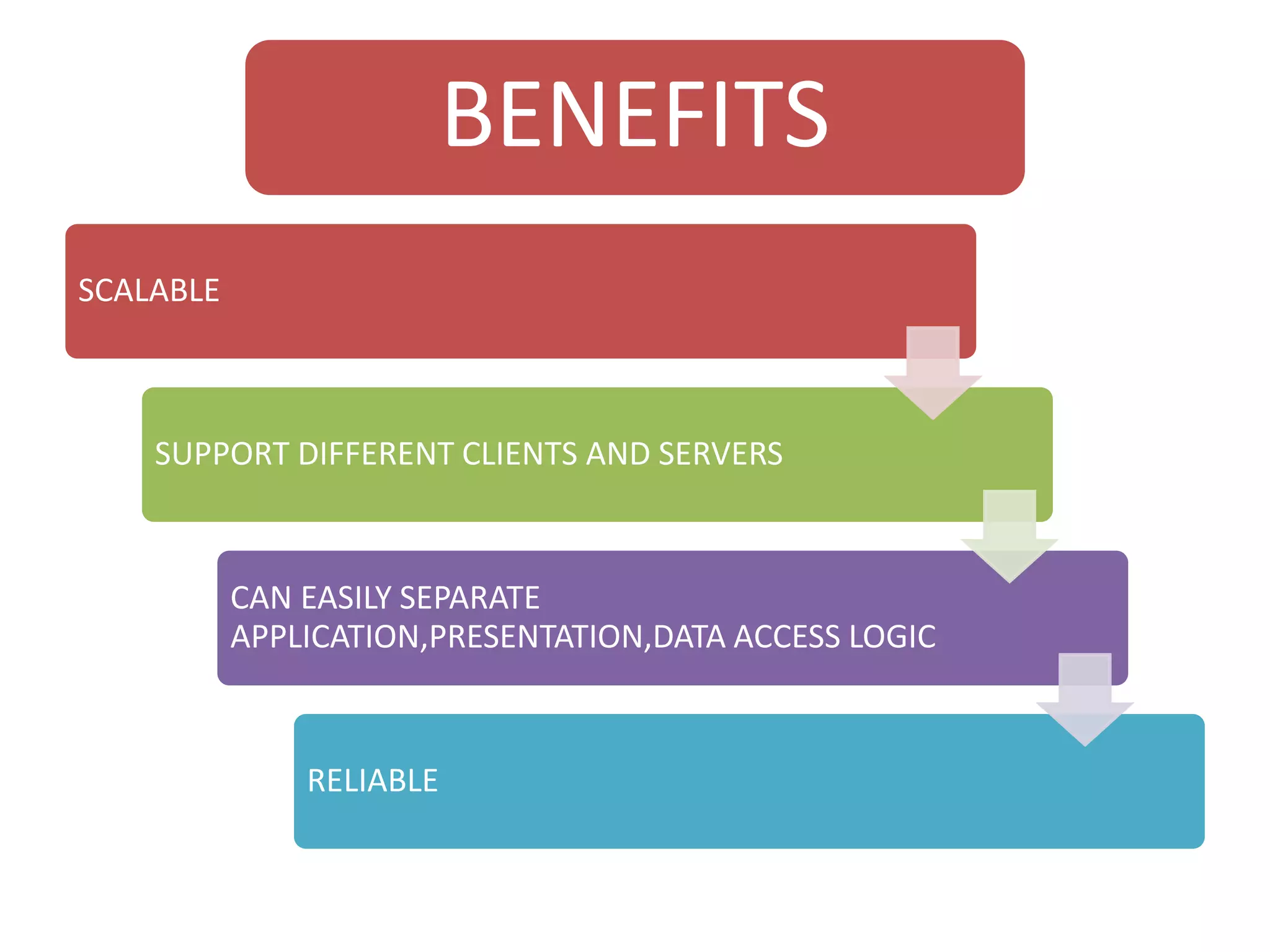
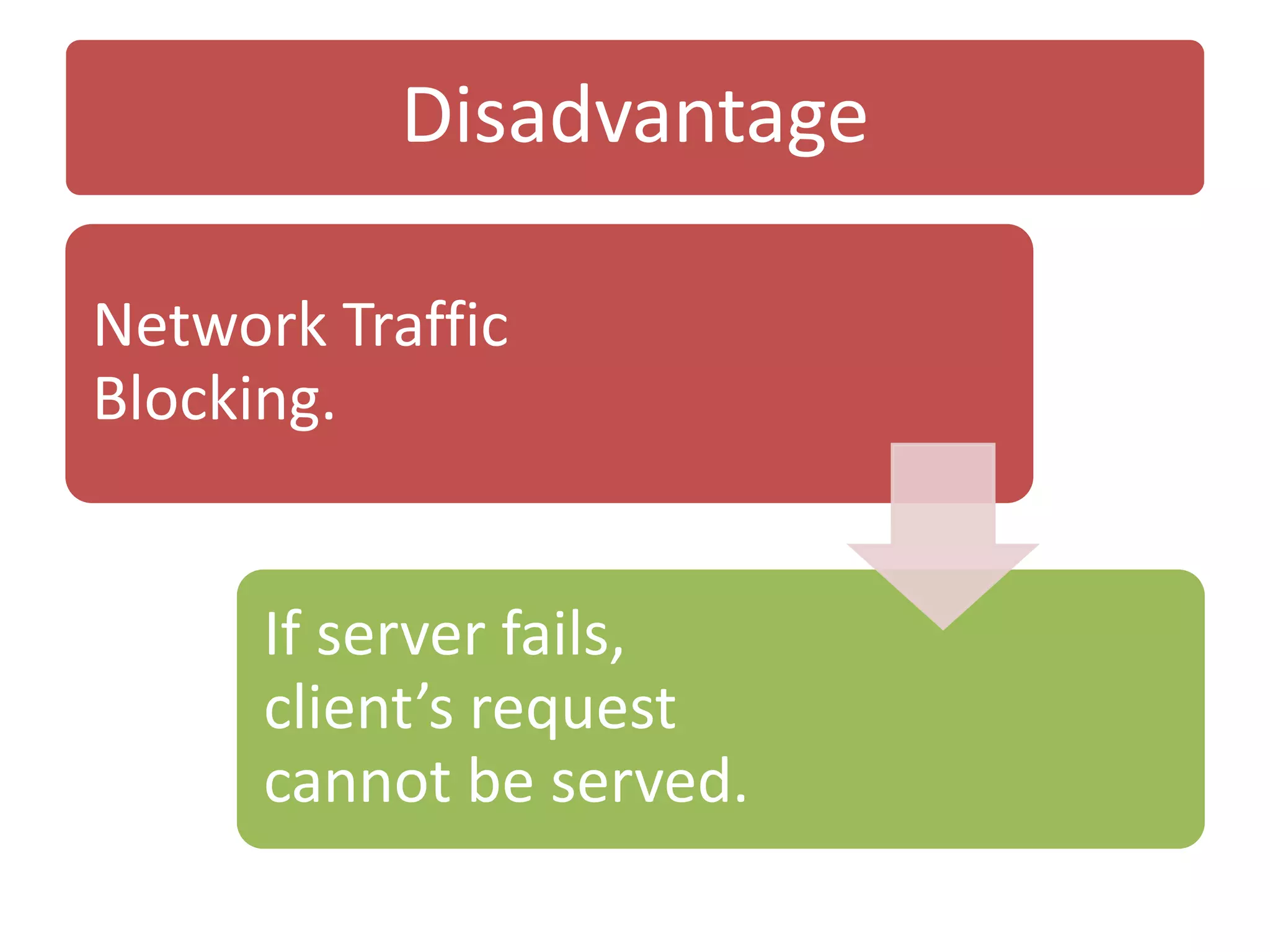
The document discusses physical architecture layer design, which involves determining how a system will be distributed across computers and the hardware and software that will be used. This includes infrastructure design, hardware specifications, and determining which application software components will run on which hardware. Common application architectures are server-based, client-based, and client-server. The physical architecture design flows from non-functional requirements and specifies the system's hardware and software components.