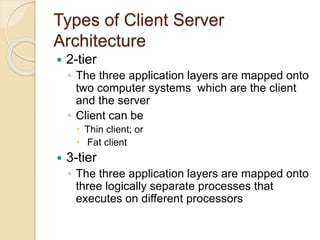
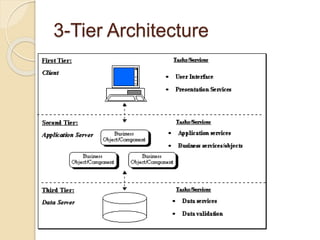
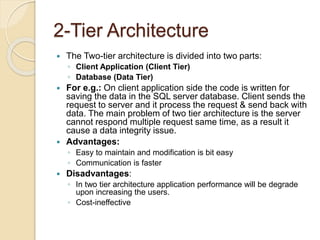
This document discusses client-server architecture. It defines clients as workstations that rely on servers for resources like files, devices, and processing power. Servers are dedicated computers that manage disk drives, printers, or network traffic. In a client-server model, applications are split into client and server components, with clients accessing services provided by servers. There are two main types: 2-tier, with clients and a single server, and 3-tier, with separate servers for the interface, logic, and data layers, allowing for better scalability. Thin clients rely fully on servers, while fat clients run some application logic locally.