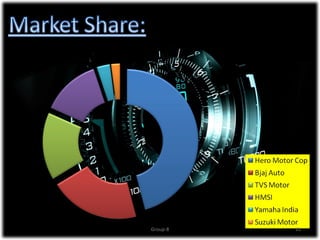
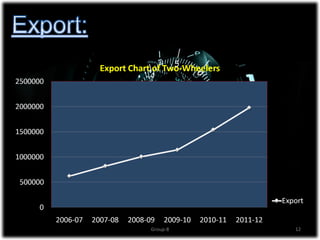
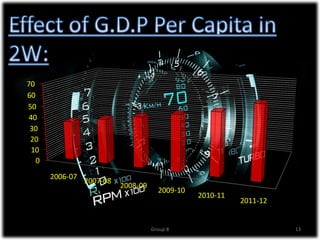
The document discusses the significant growth of India's two-wheeler industry, which is the second largest in the world and contributes 6% to the country's GDP. It highlights key market trends, including a shift towards scooters, the impact of economic factors such as inflation, and government initiatives to promote the automotive sector. The industry is expected to maintain a robust growth rate, with projections of increasing sales volumes over the coming years.