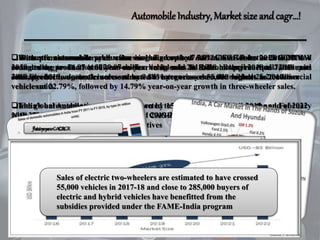
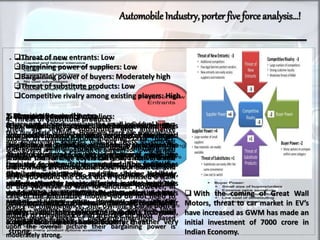
The document provides a comprehensive analysis of the automobile industry, detailing its economic significance, market growth projections, and government initiatives supporting foreign investment and electric vehicle adoption in India. It also includes a Porter’s Five Forces analysis, indicating low threats of new entrants and substitutes, high rivalry among existing players, and moderate buyer bargaining power. Key industry trends include a significant growth in domestic automobile sales and production, with projections for the global automotive market reaching USD 83 billion by 2022.