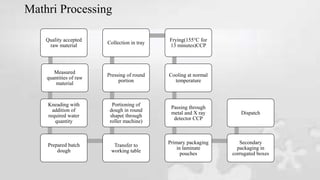
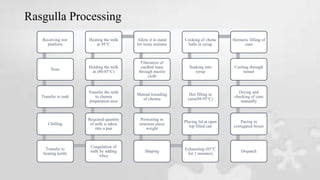
Haldiram's is a leading Indian snack food company known for sweets and savory snacks. The internship provided exposure to Haldiram's quality assurance processes, including chemical and microbiological testing of ingredients and products. Tests were conducted for milk, oils, moisture and more to ensure quality. The intern also observed the manufacturing process for popular items like mathri and rasgulla, involving steps from receiving ingredients to packaging. Regular audits were performed to maintain standards from the British Retail Consortium. The six month training gave valuable insight into a major food producer's operations.