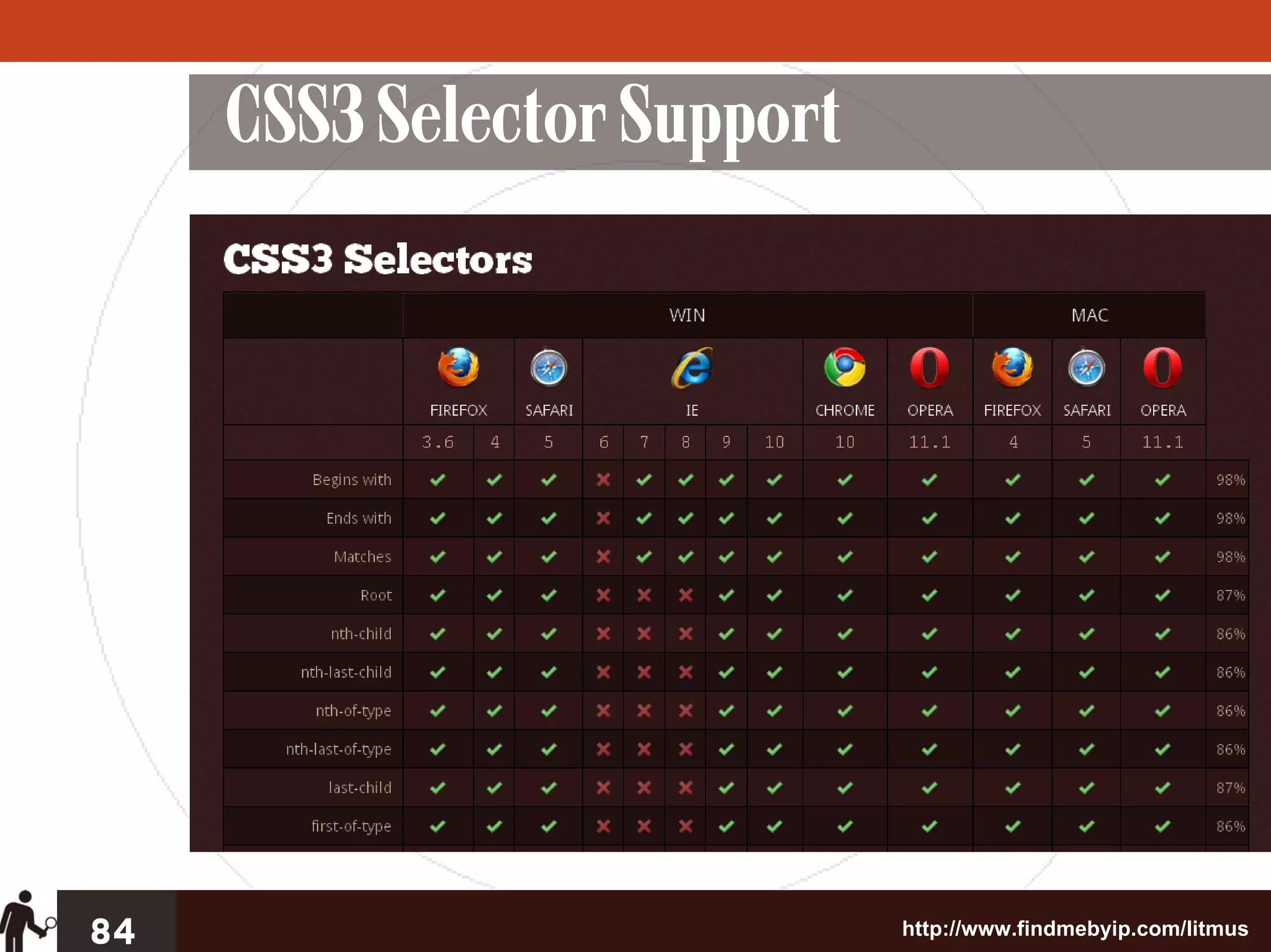
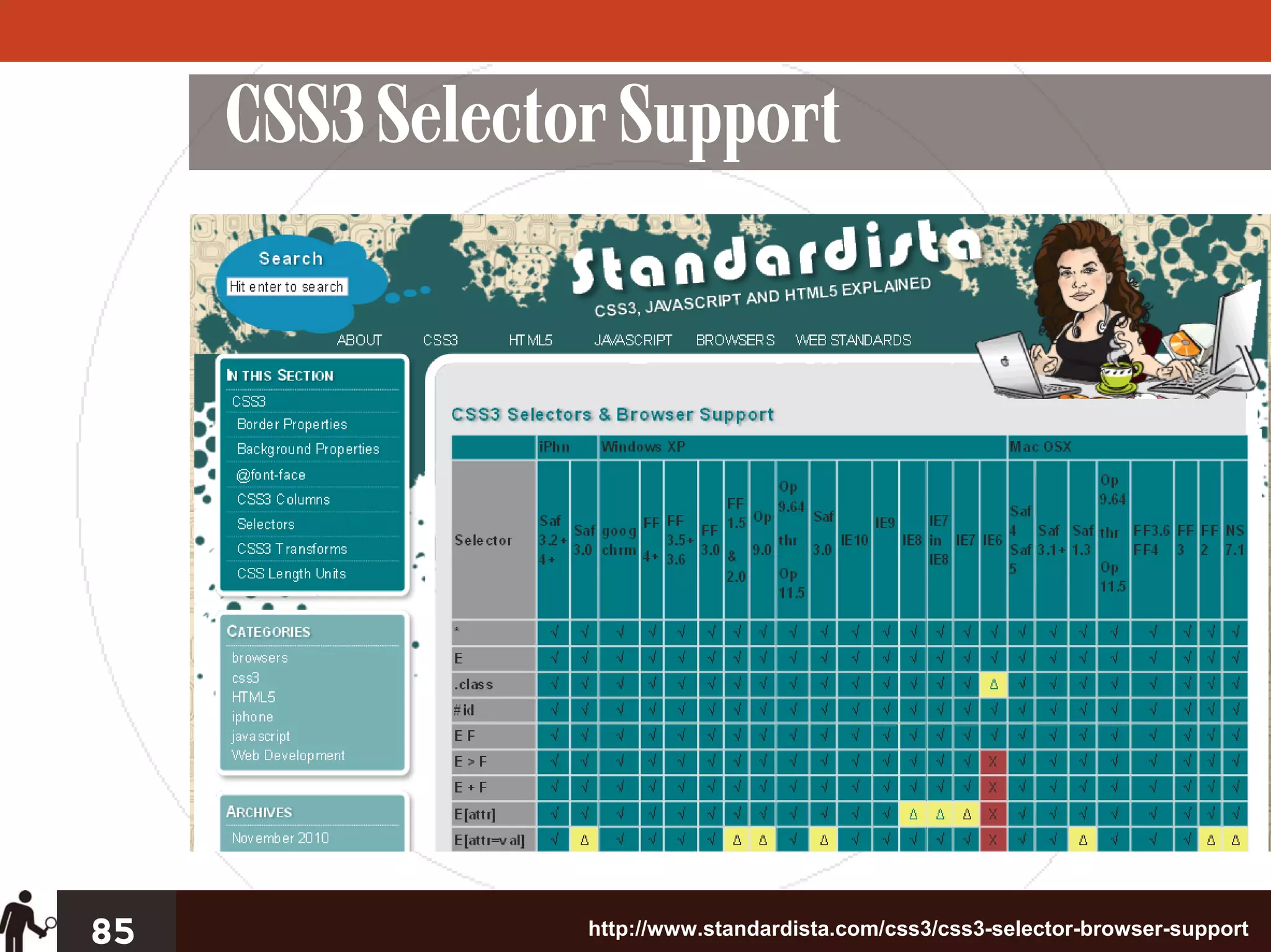
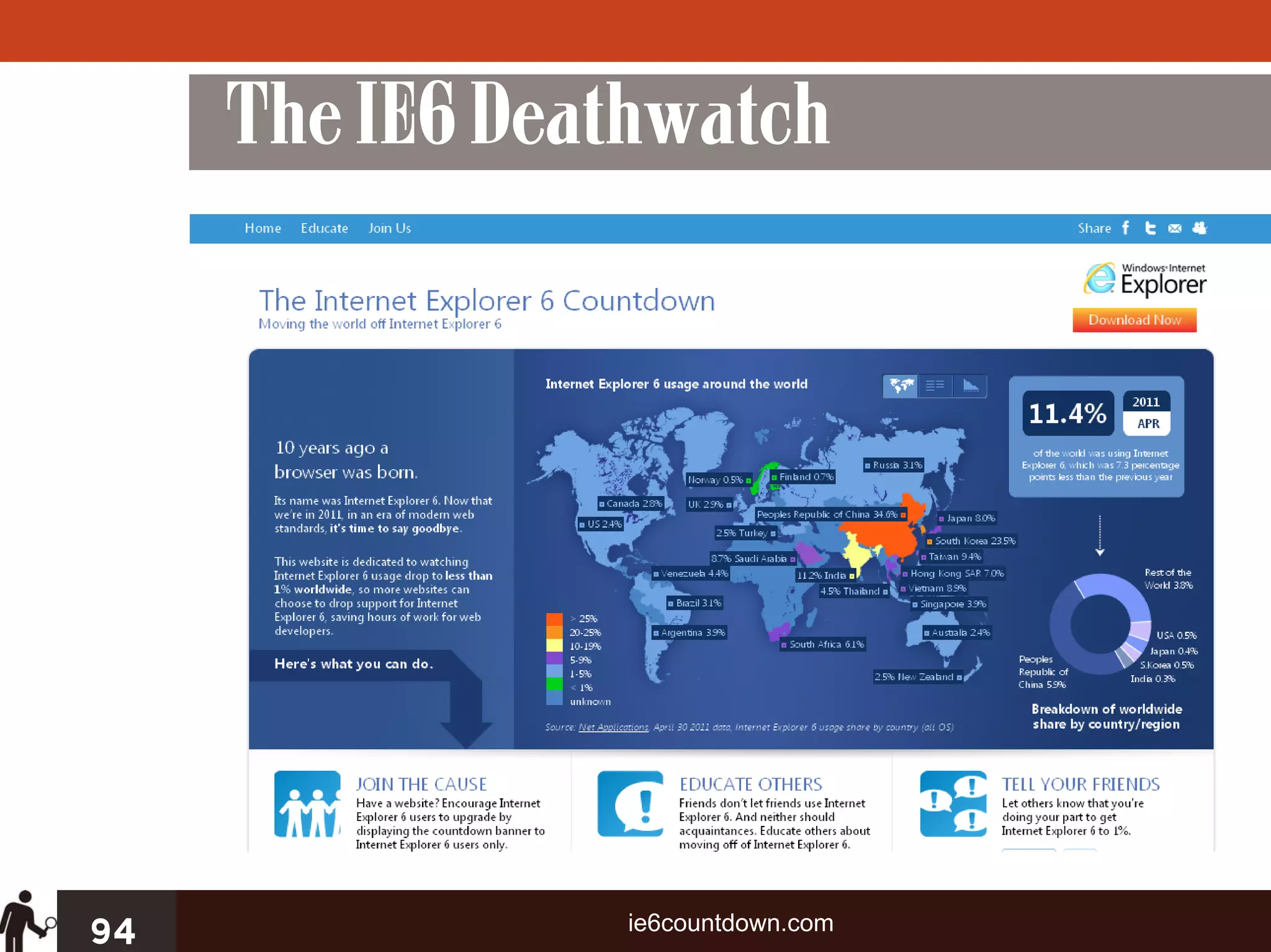
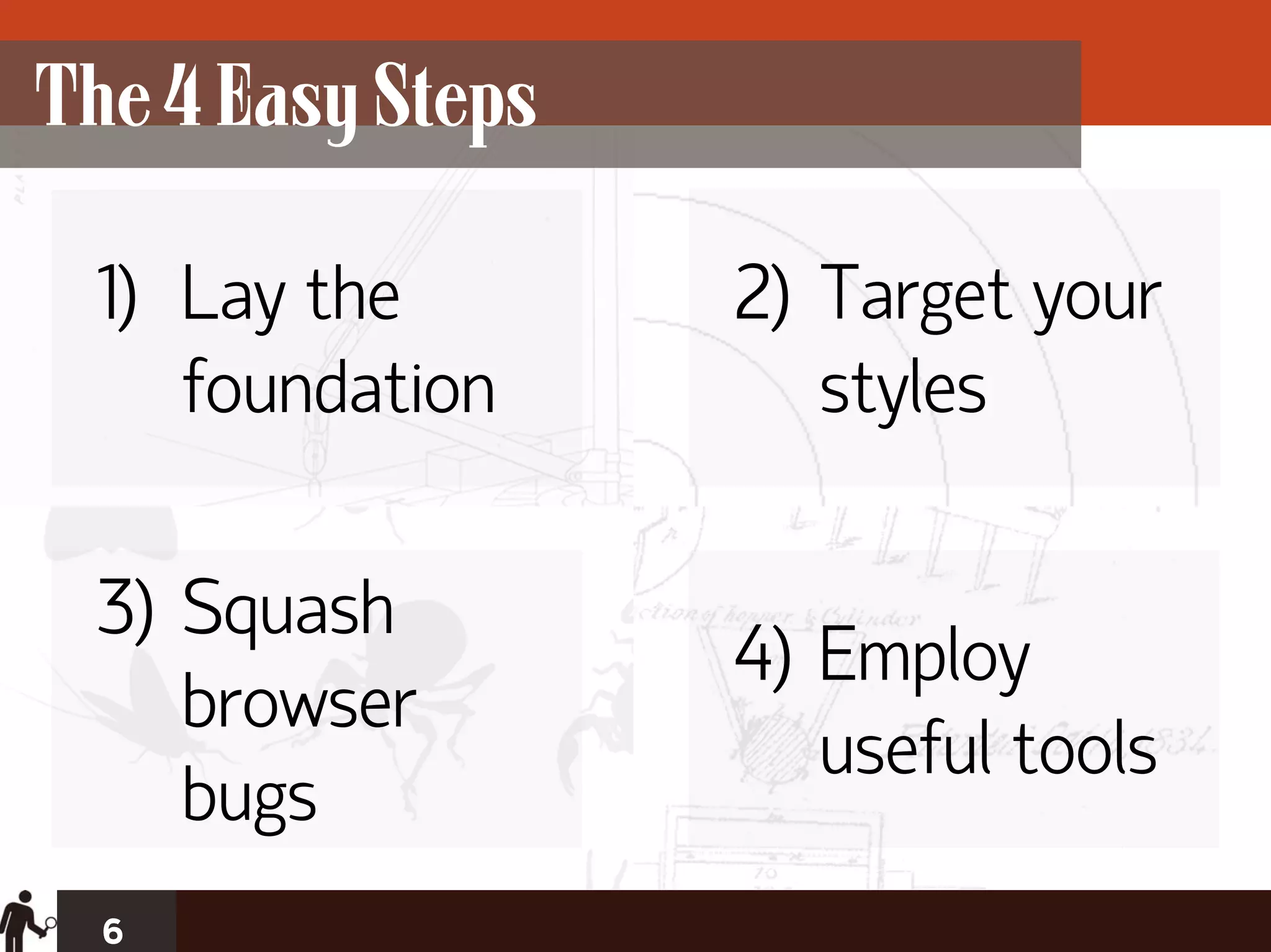
The document outlines four key steps for effective CSS troubleshooting and optimization: establishing a solid foundation, targeting styles effectively, and employing micro and macro optimization techniques. It emphasizes the importance of preventive coding, using best practices for cross-browser compatibility, and utilizing tools for problem identification. Additionally, it discusses strategies for organizing CSS code efficiently to enhance readability and maintainability.




































































![CSS 2.1 Selectors
• Universal * • Pseudo elements
– :before
• Child Combinator – :after
E>F
• State pseudo-classes
• Adjacent/Sibling Combinator – Dynamic
E+F • :hover
• :active
• Attribute E[~attribute] • :focus
• At Rules – Language
– @font-face • :lang
– @media
– @page – Structural
– @charset • :first-child
79](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationcsstroubleshootingrwx-111202145925-phpapp01/75/Advanced-CSS-Troubleshooting-Efficiency-79-2048.jpg)
![CSS2.1 Selectors & IE Support
• Universal * (ie7/8 – yes)
• Child: e > f (ie7/8 – yes)
• Sibling/Adjacent: e + f (ie7 no, ie8 – yes)
• Attribute: e[attribute] (ie7/8 – yes)
• Pseudo elements (ie7/8 – no)
– ::before
– ::after
• State pseudo-classes, v2.1
– :first-child (ie7/8 – yes)
– :hover (ie7/8 – yes)
– :active (ie7/8 – yes)
– :focus (ie7/8 – no)
– :lang (ie7/8 – no)
80](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationcsstroubleshootingrwx-111202145925-phpapp01/75/Advanced-CSS-Troubleshooting-Efficiency-80-2048.jpg)
![CSS3 Selectors
• General sibling • Pseudo-elements*
E~F
*all pseudo-elements indicated with
:: in CSS3
• Attribute presence
– a[attribute="value"]
– a[attribute~="value"]
– a[attribute|="value"]
• Attribute substrings
– a[attribute^="value"]
– a[attribute$="value"]
– a[attribute*="value"]
82](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationcsstroubleshootingrwx-111202145925-phpapp01/75/Advanced-CSS-Troubleshooting-Efficiency-82-2048.jpg)