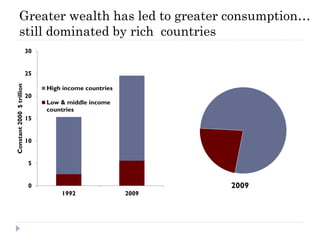
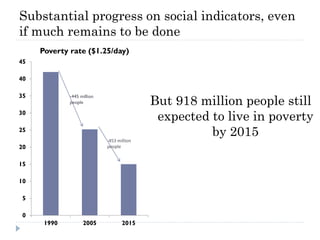
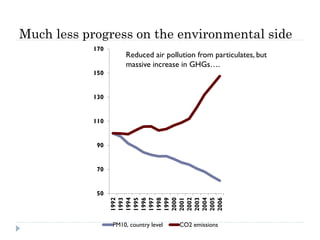
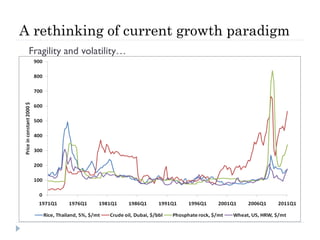
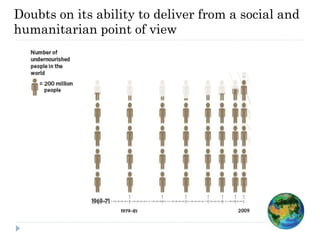
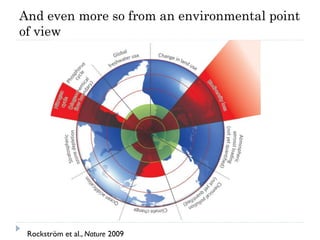
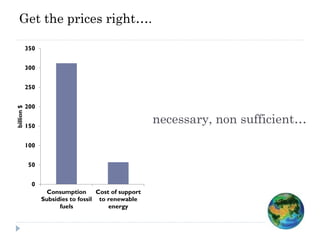
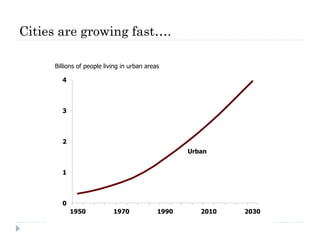
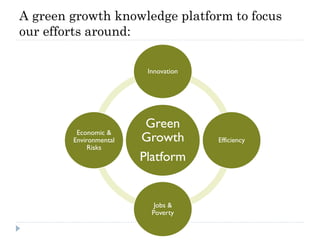
The document discusses the significant changes in global economic conditions since the early 1990s, highlighting increased wealth and consumption largely in developing countries. However, while social indicators have progressed, environmental issues remain critical, necessitating a rethinking of growth paradigms towards sustainable development and green growth. It emphasizes the importance of infrastructure transitions, innovative technology, and the role of urbanization in achieving these goals.