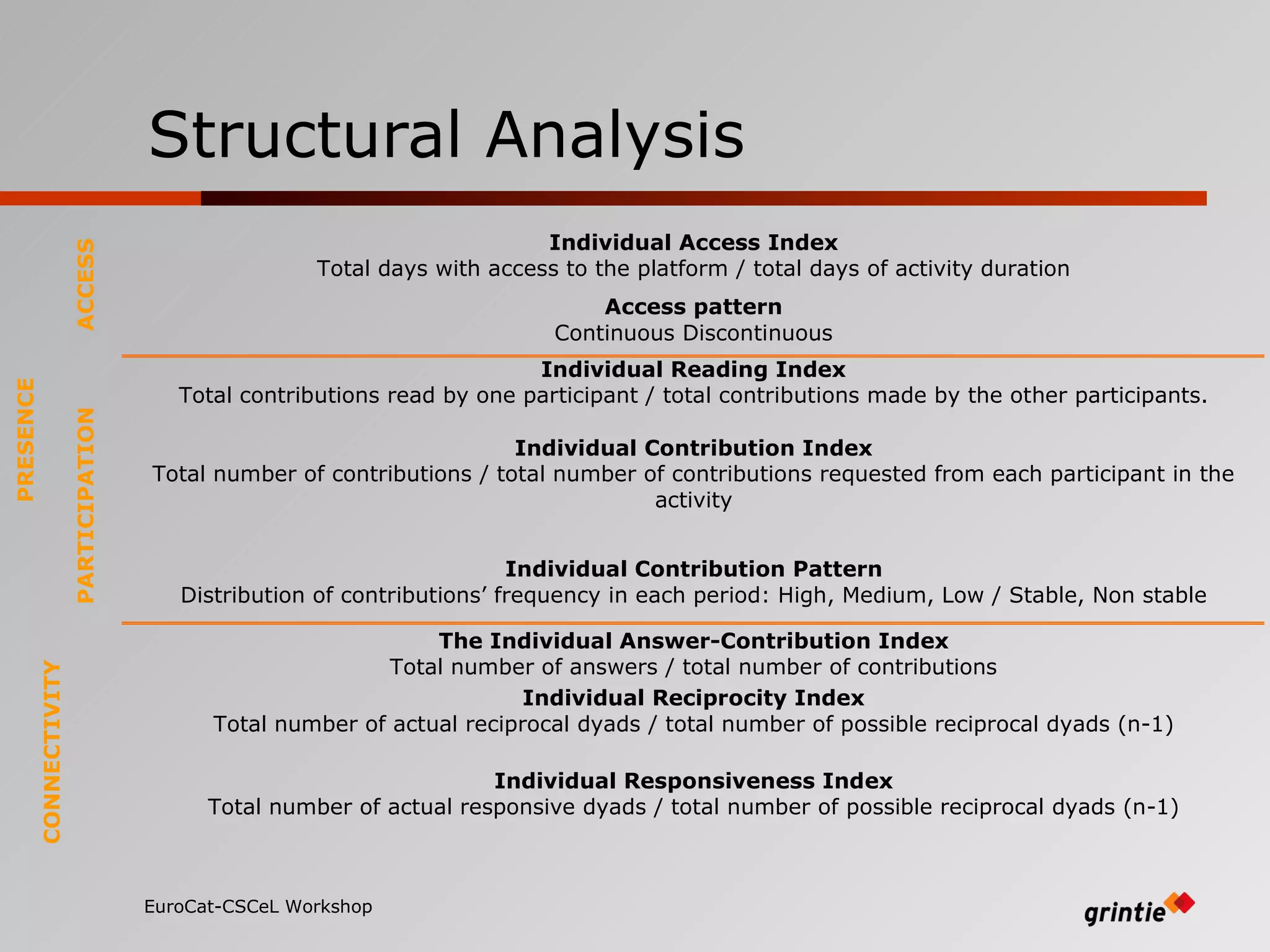
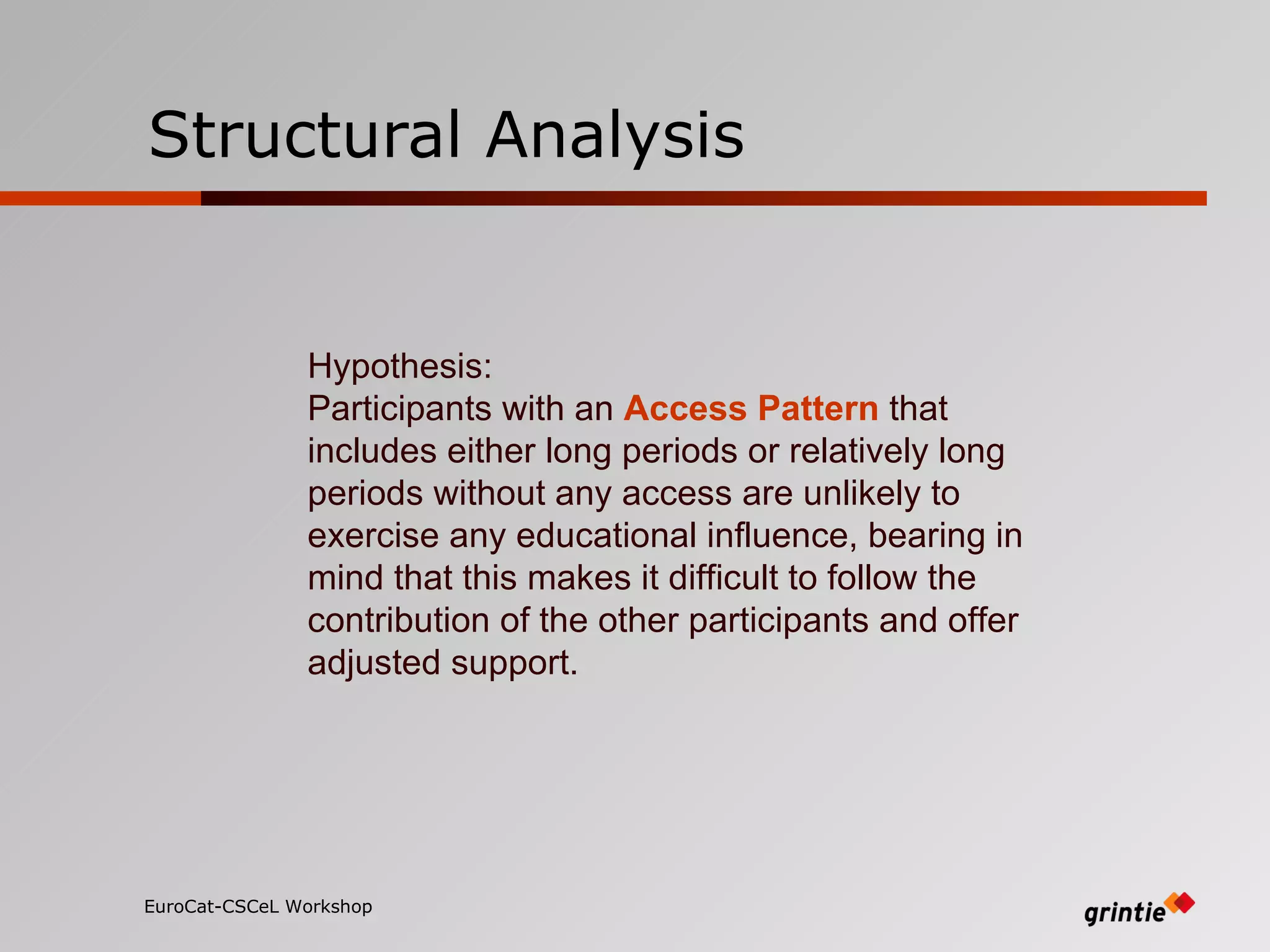
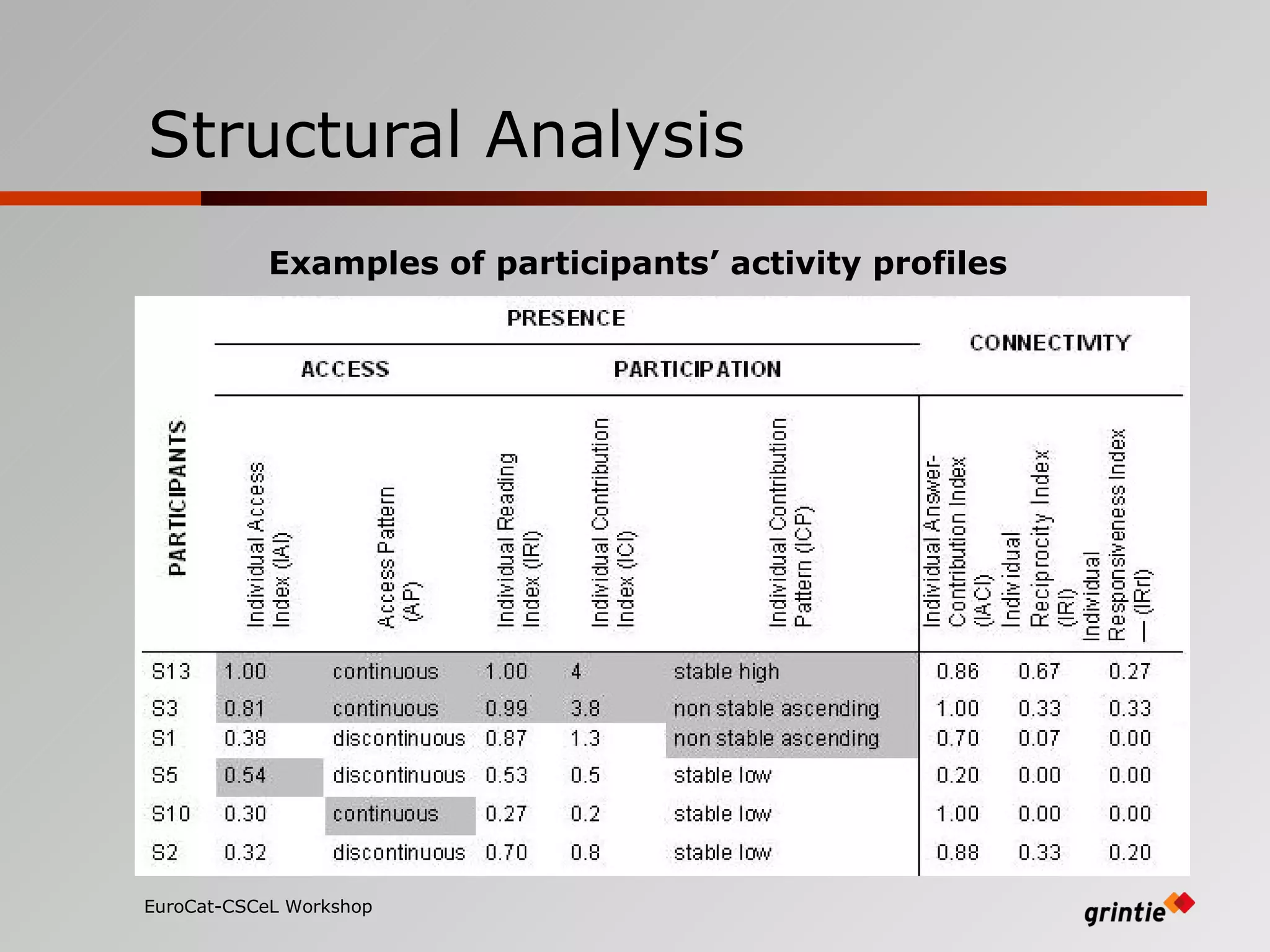
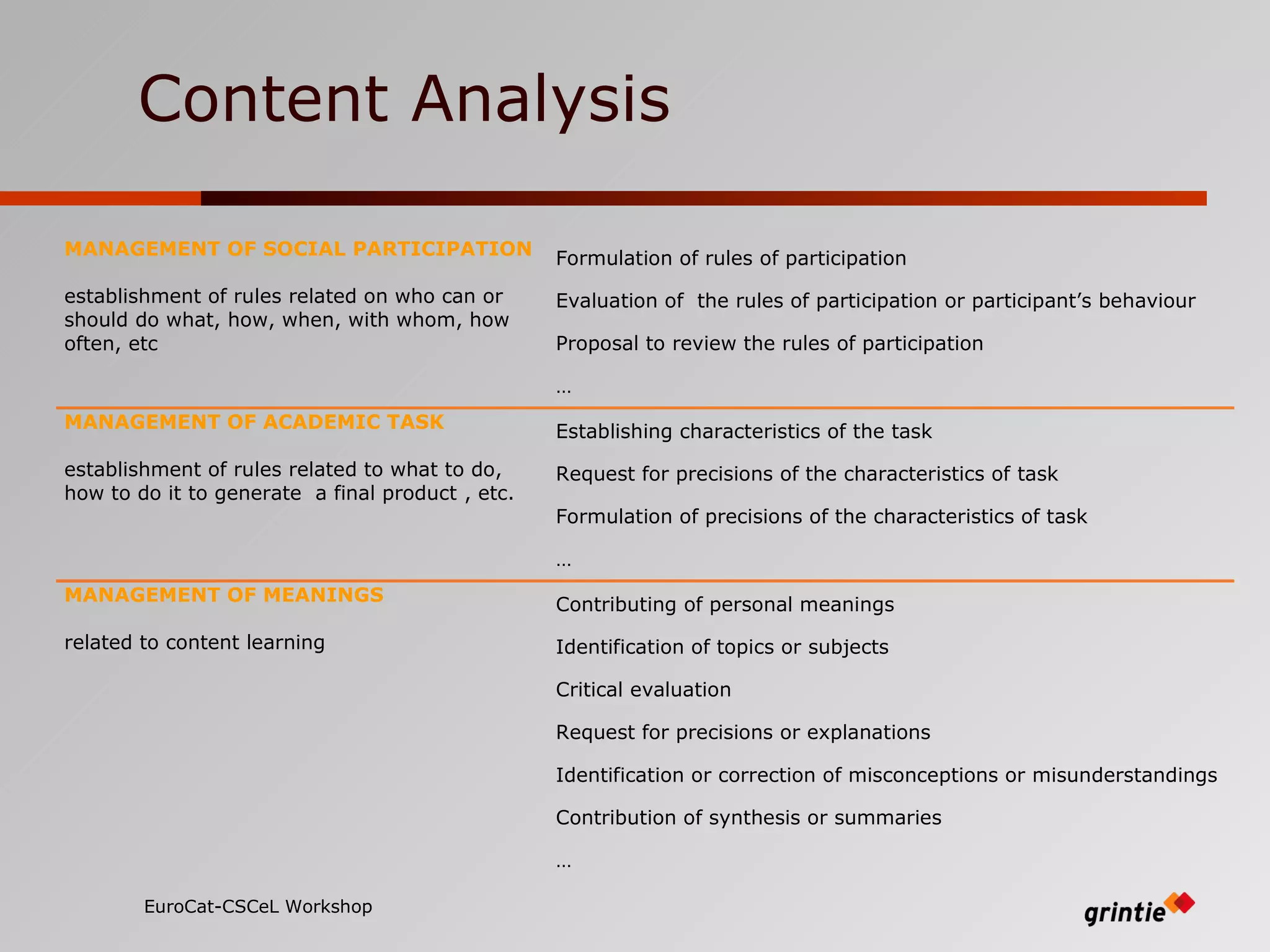
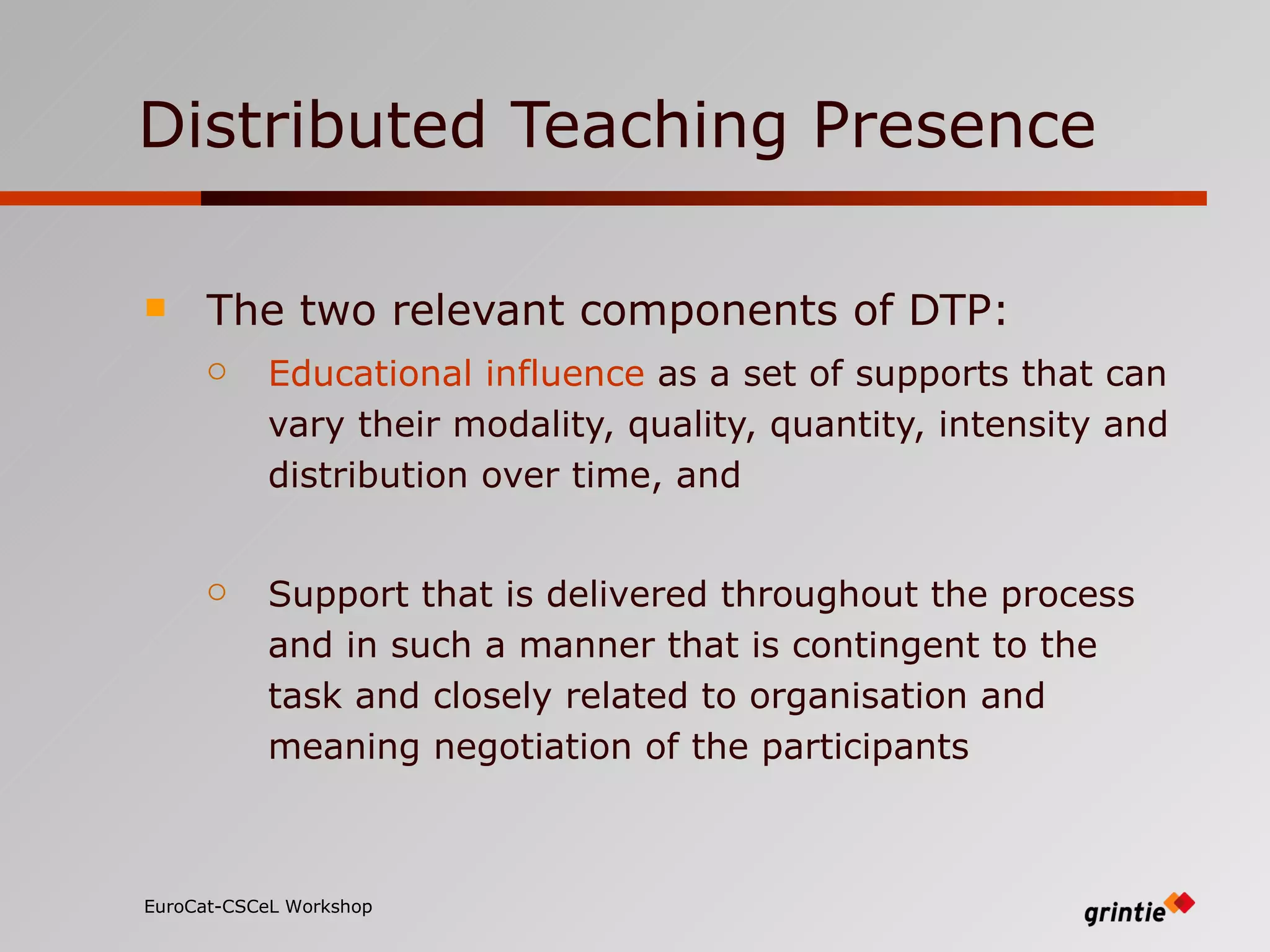
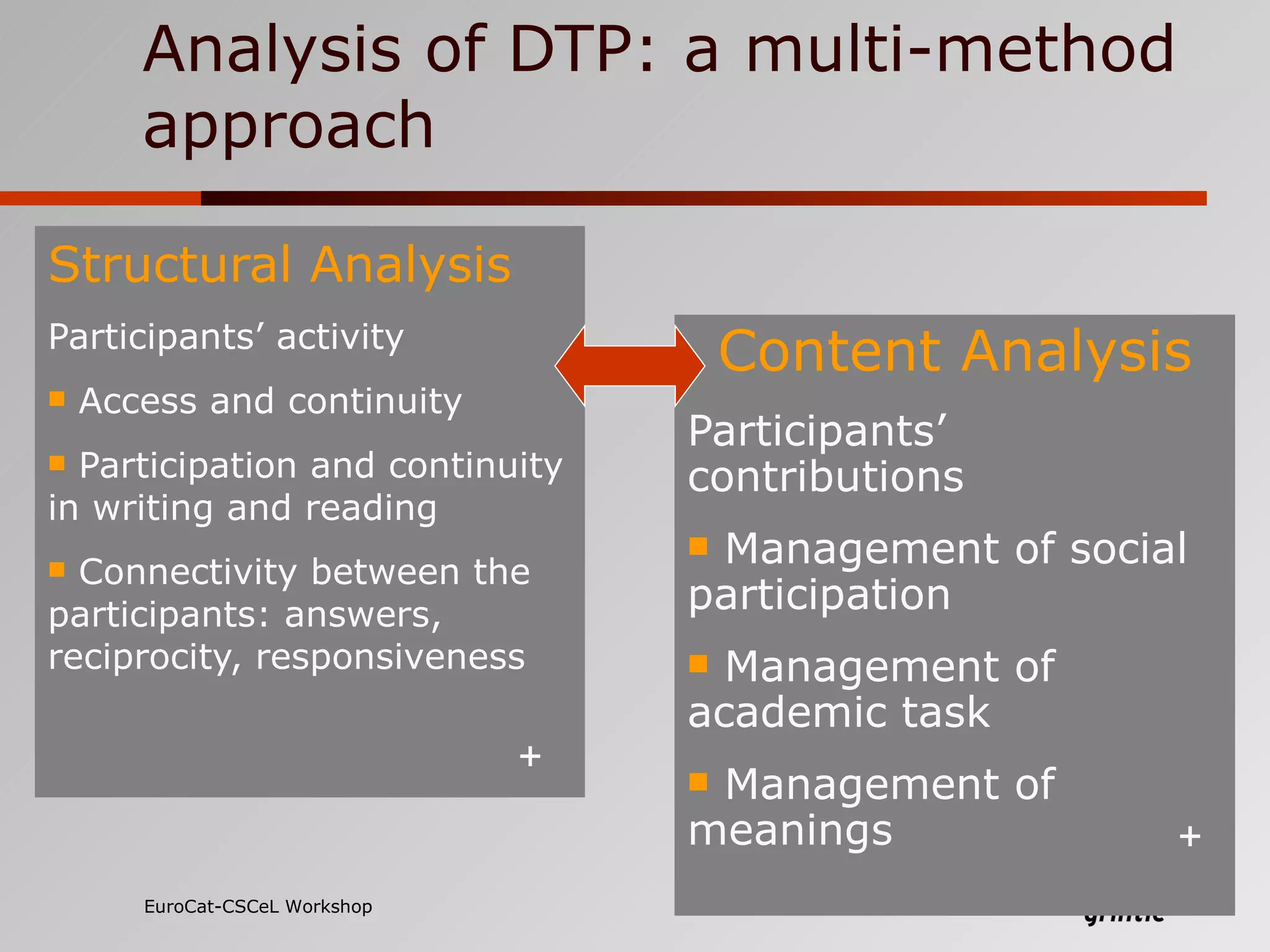
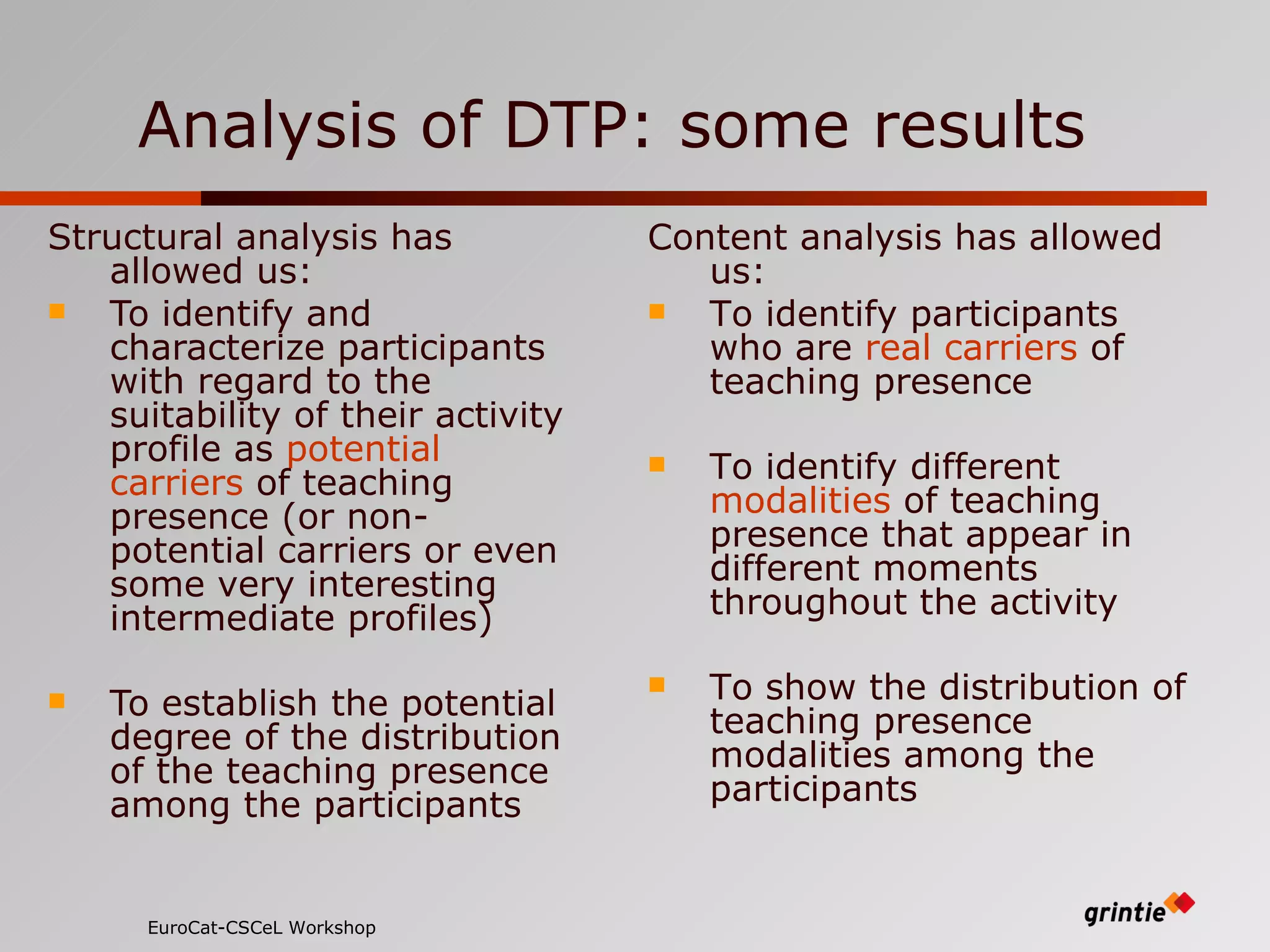
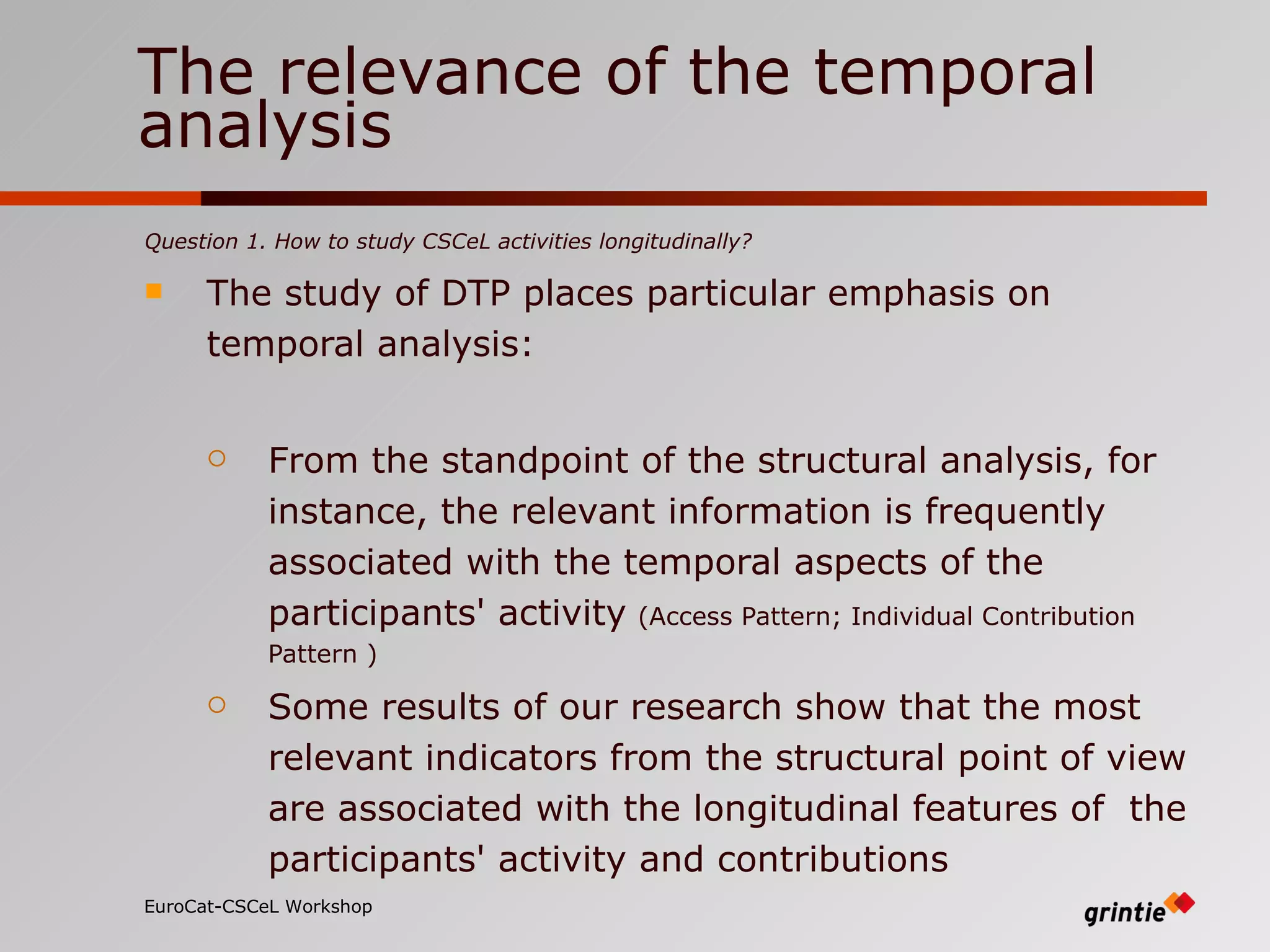
The document discusses a model for analyzing distributed teaching presence (DTP) in online learning environments. It addresses the importance of temporal and organizational analysis. Regarding temporal analysis, DTP is best understood through longitudinal study of student participation patterns and content over time. Organization is also crucial, as meaningful learning depends on managing social interactions and tasks. Awareness tools could help by providing longitudinal representations of individual and group activity to promote DTP.






![Gracias por su atención THE STUDY OF DISTRIBUTED TEACHING PRESENCE IN CSCL SETTINGS: temporal and organisational considerations C. Coll, A. Bustos & A. Engel [email_address] www.psyed.edu.es/grintie](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prescsceleurocatccabae201005final-12654773716468-phpapp01/75/Presentation-at-EuroCAT-Workshop-13-2048.jpg)