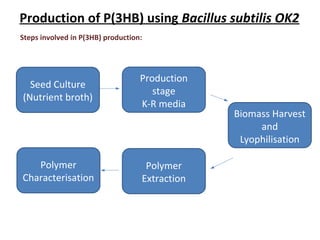
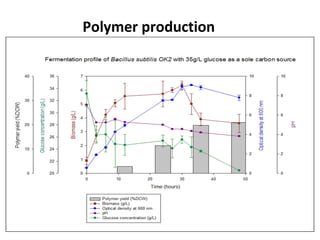
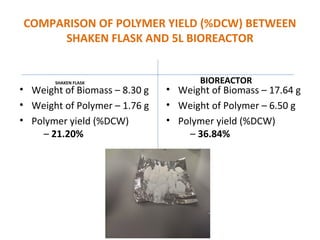
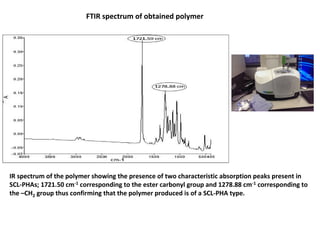
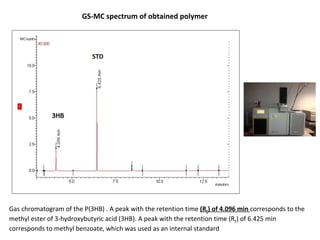
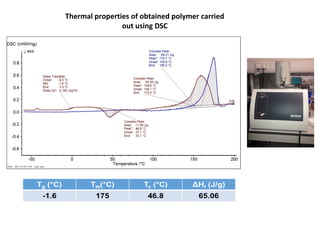
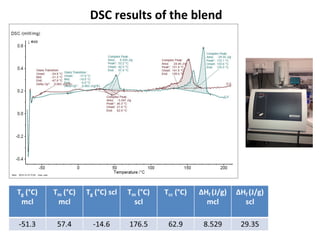
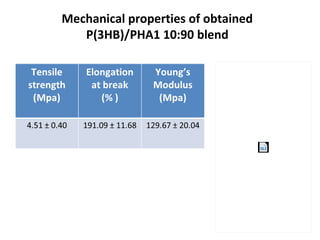
The document discusses the development of short chain length polyhydroxyalkanoates (scl-PHA) for cardiovascular tissue engineering, highlighting the production of p(3hb) using Bacillus subtilis and the creation of 2D mcl-scl PHA blend films. Key properties of the produced polymers were evaluated through various characterizations including FTIR, GC-MS, and DSC, confirming their suitability for cell attachment and tissue regeneration. Future work includes biocompatibility studies and further optimization of the blend films for enhanced performance in cardiovascular applications.