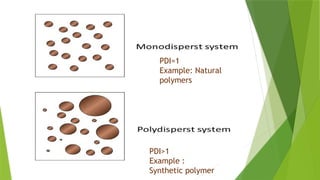
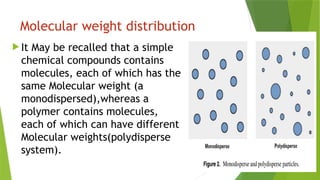
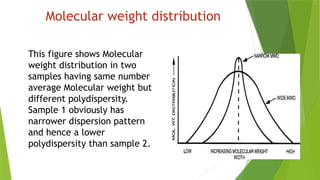
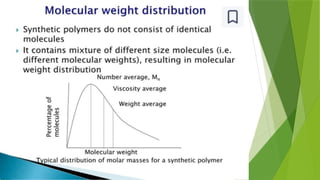
Presentation about polydispersity and Molecular weight distribution in polymers Presentation about polydispersity and Molecular weight distribution in polymers Presentation about polydispersity and Molecular weight distribution in polymers Presentation about polydispersity and Molecular weight distribution in polymers Presentation about polydispersity and Molecular weight distribution in polymers Presentation about polydispersity and Molecular weight distribution in polymers