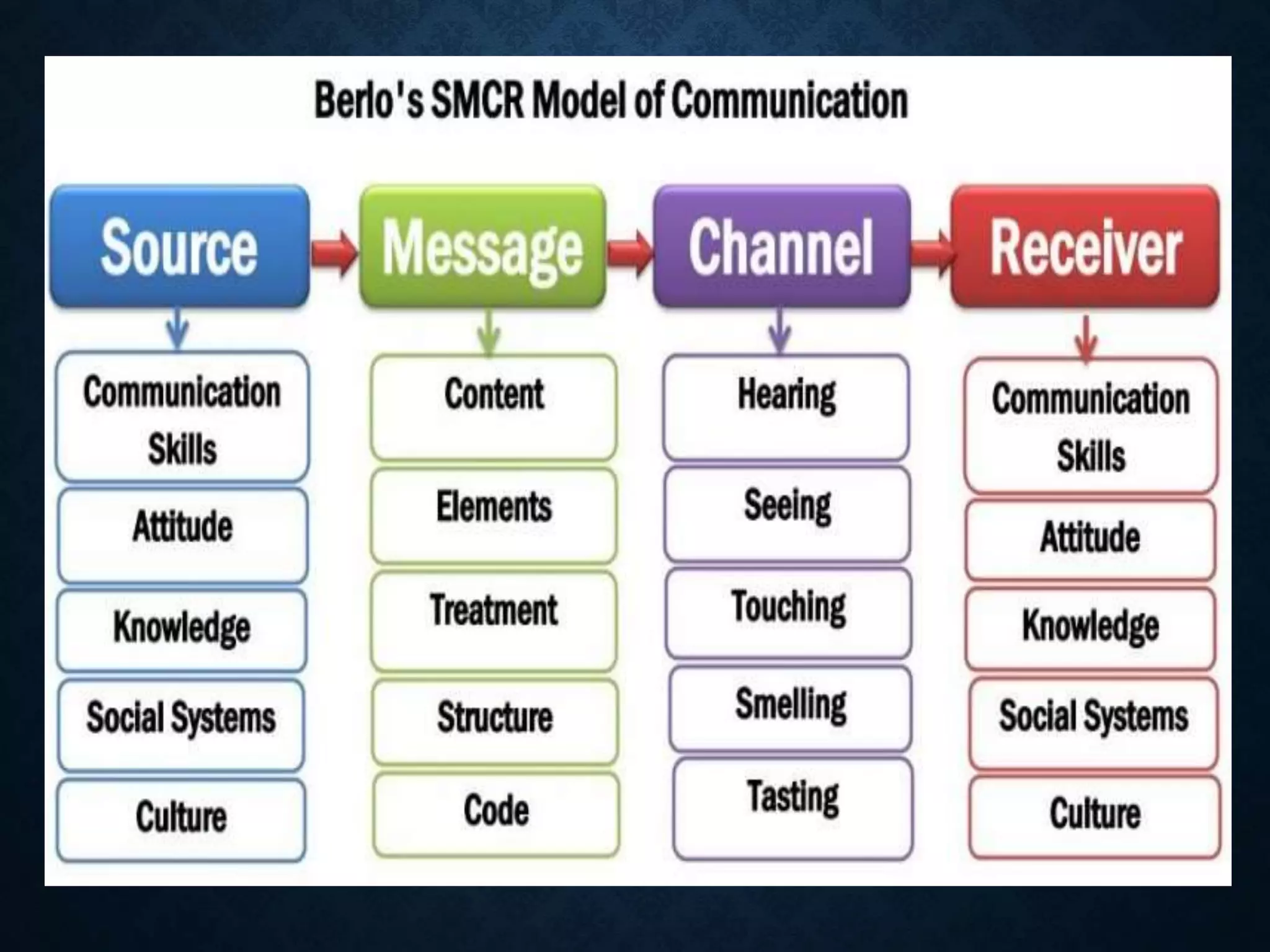
This document discusses the key elements of communication:
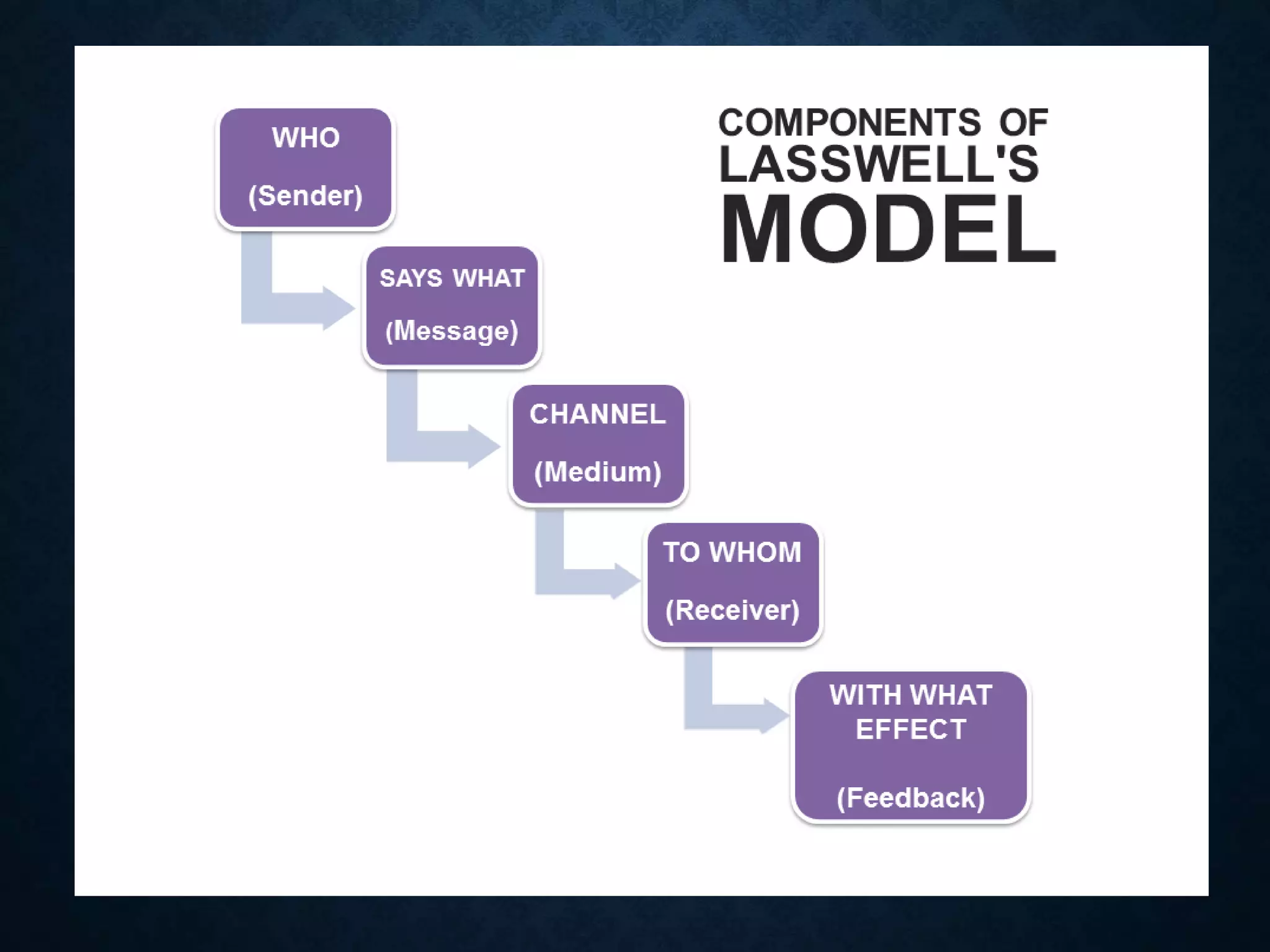
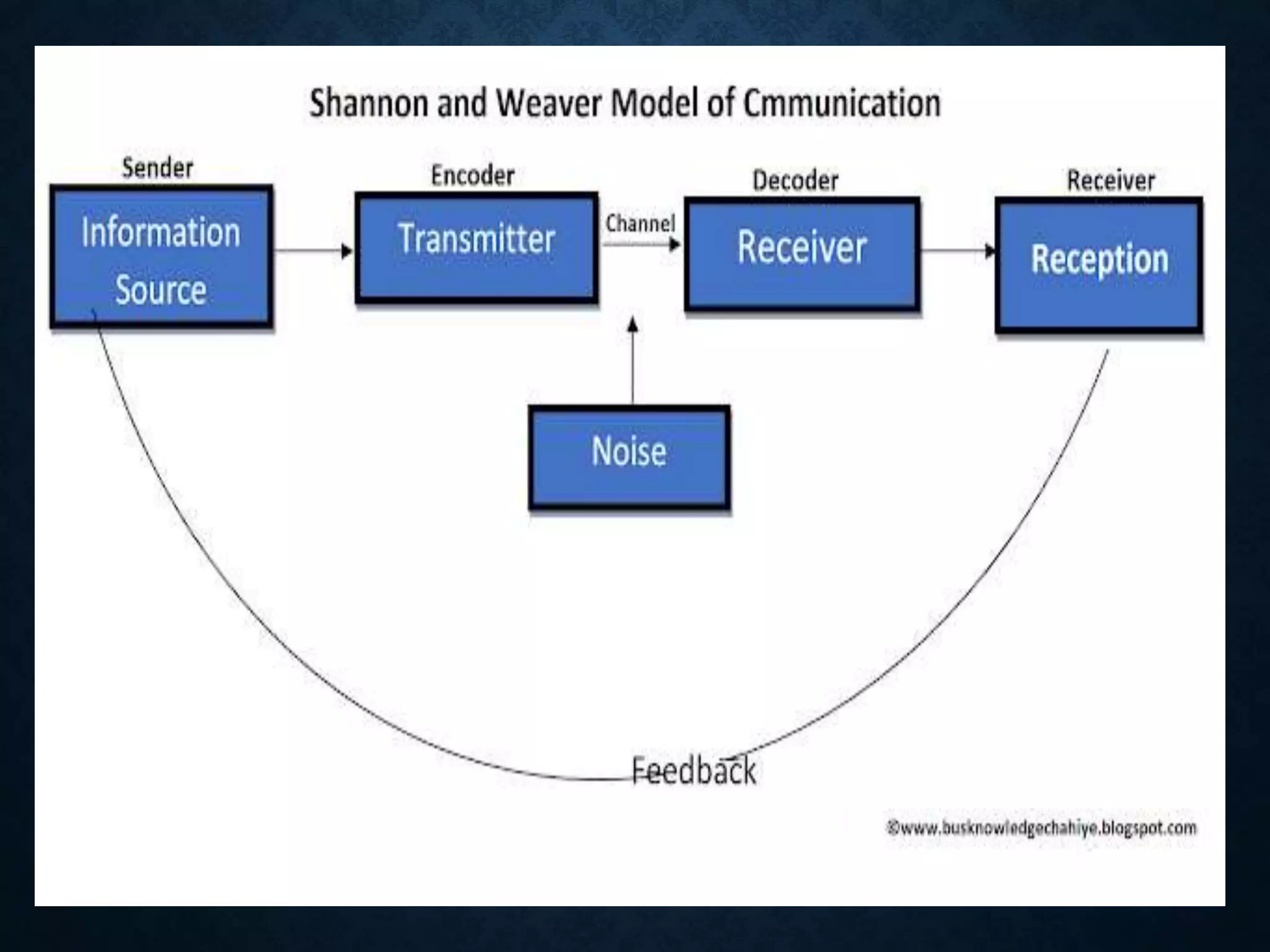
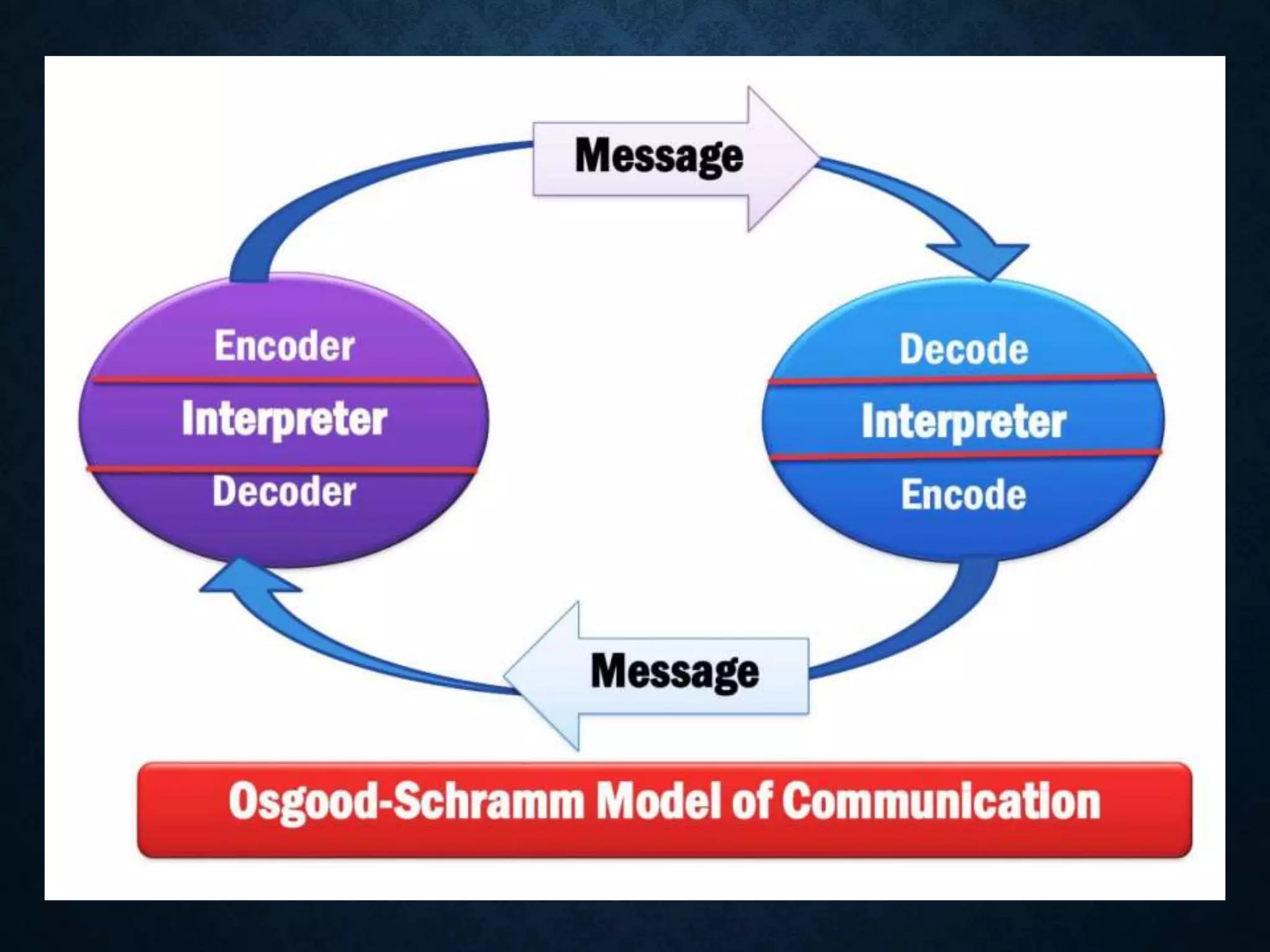
1. A speaker encodes a message and transmits it through a channel to a receiver.
2. The encoding process involves converting the message into words, actions or other forms.
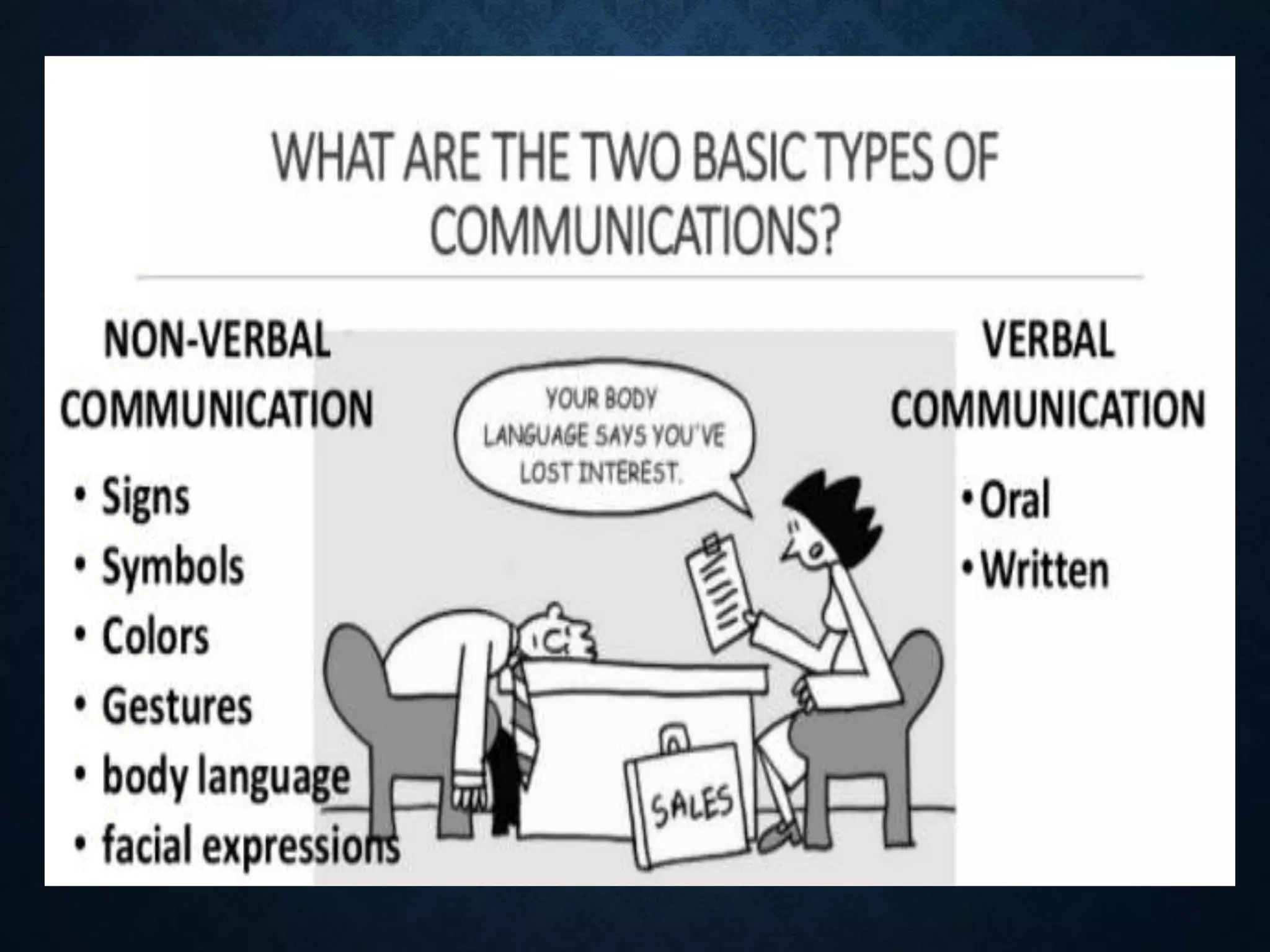
3. Channels of communication include personal and non-personal, verbal and nonverbal means of conveying the encoded message.
4. The receiver decodes and interprets the message through the process of feedback.
5. Context and barriers can influence the communication process.