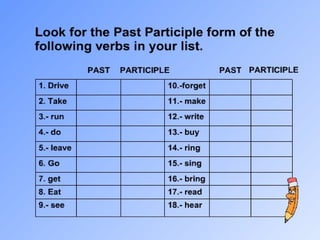
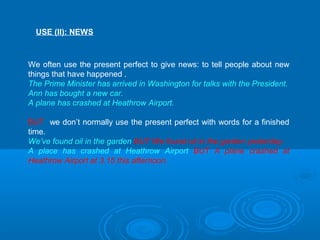
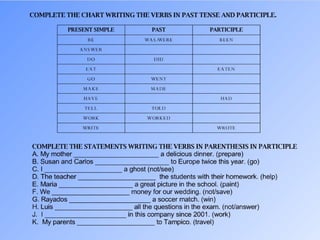
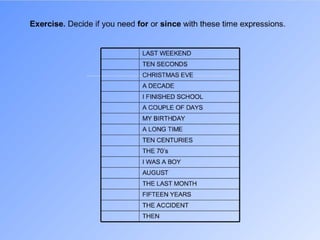
This document provides information about forming and using the present perfect tense in English. It explains that the present perfect is formed using have/has plus the past participle. It discusses regular and irregular past participles. It describes two main uses of the present perfect: for finished actions with present results, and for recent events/news. Examples are given to illustrate using the present perfect for unfinished durations versus finished times. Finally, it covers common words and phrases used with the present perfect like already, yet, just, ever, for and since.