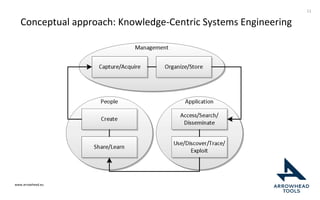
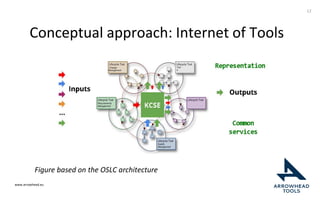
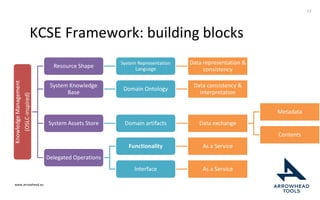
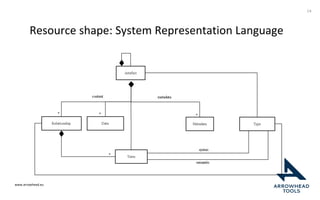
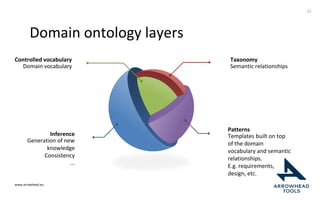
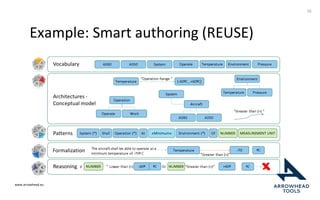
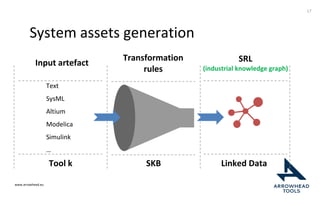
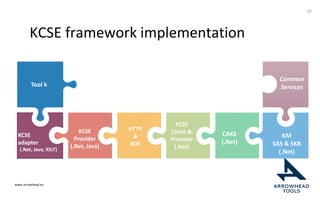
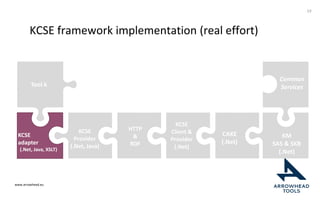
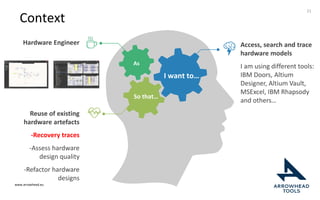
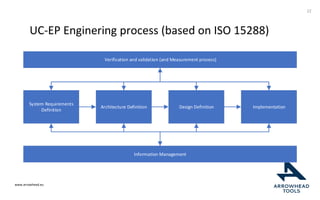
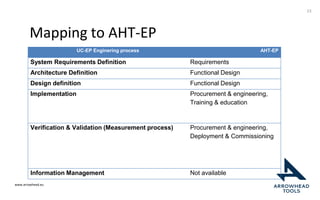
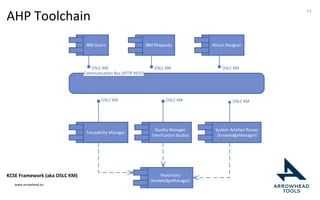
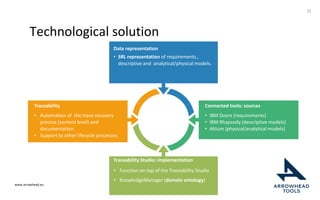
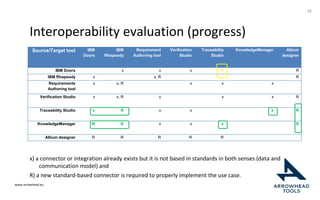
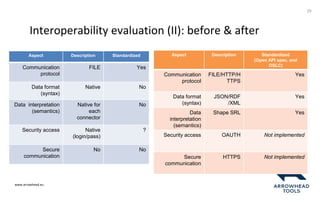
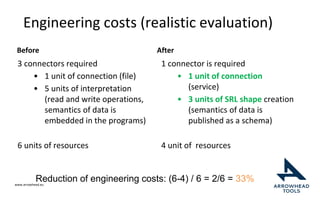
The document discusses a framework for improving the reuse of hardware models through automatic traceability between descriptive and analytical models in systems engineering. It outlines the need for a common representation and interoperable access model that integrates various tools and technologies, while also addressing key challenges like vendor lock-in and data consistency. The proposed approach involves a knowledge-centric systems engineering framework that aims to streamline processes and enhance collaboration across engineering teams.








![www.arrowhead.eu
Some references
[1] Jose María Álvarez Rodríguez, Roy Mendieta, Jose Luis de la Vara, Anabel
Fraga, Juan Lloréns: Enabling System Artefact Exchange and Selection
through a Linked Data Layer. J. UCS 24(11): 1536-1560 (2018)
[2] Jose María Álvarez Rodríguez, Valentin Moreno, Juan Lloréns: Formal
ontologies and data shapes within the Software Engineering development
lifecycle. SEKE 2019: 64-93
32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ahtools-uc3-milan-virtual20200429-200430070557/85/H2020-AHTOOLS-Use-Case-3-Functional-Design-32-320.jpg)
