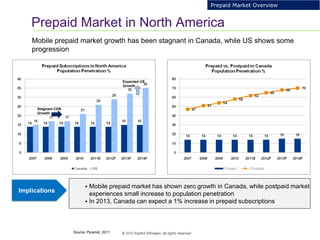
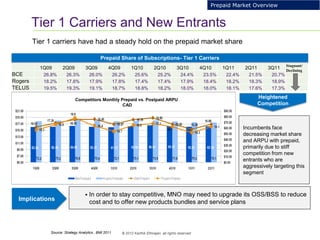
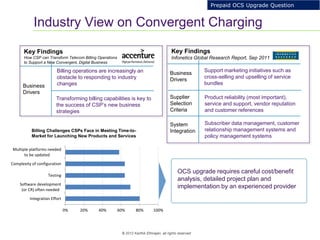
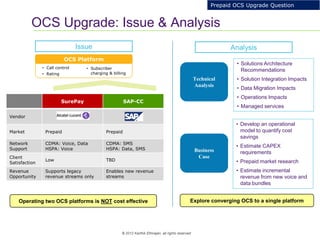
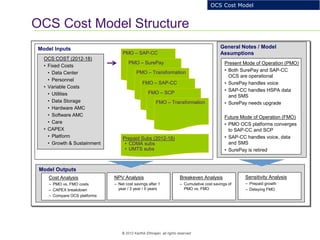
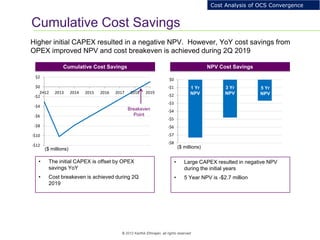
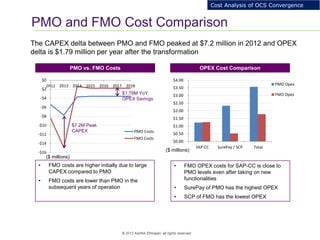
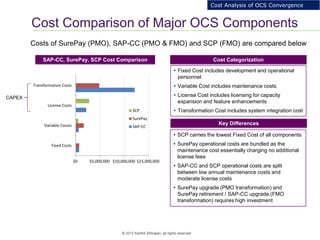
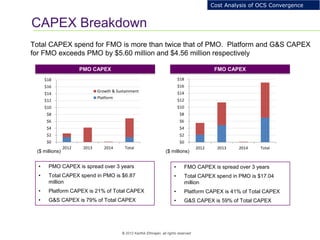
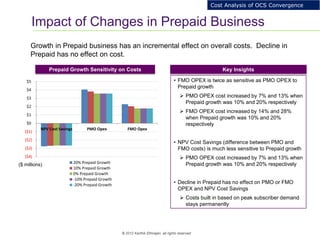
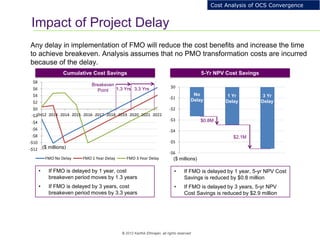
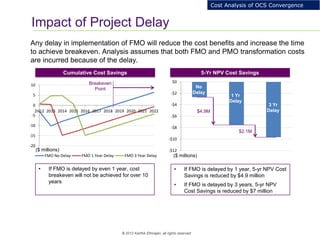
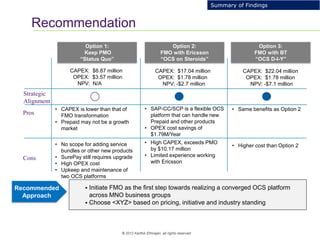
This document provides an analysis of upgrading an operator's OCS platforms to support prepaid services and future business needs. It discusses maintaining two separate platforms (PMO) versus converging to a single platform (FMO). A cost model is developed to analyze the cumulative cost savings of each option over 5 years. The analysis finds that while FMO has higher initial CAPEX, the yearly OPEX savings improve the net present value and cost breakeven is achieved in 2Q 2019. FMO is recommended as the more cost effective approach long-term.