Embed presentation
Downloaded 13 times




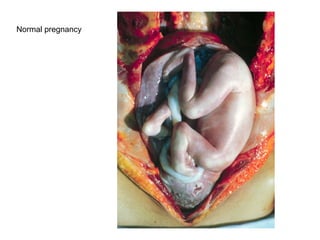
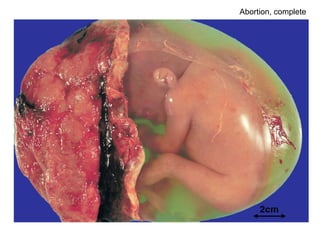
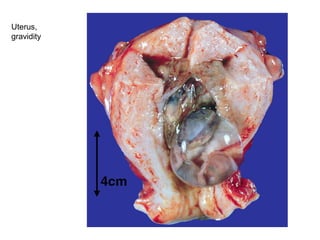
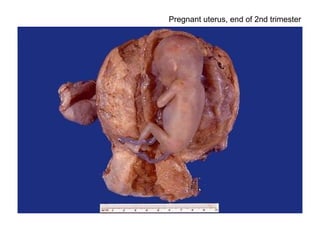
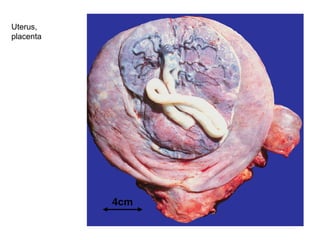
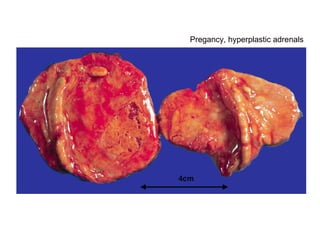
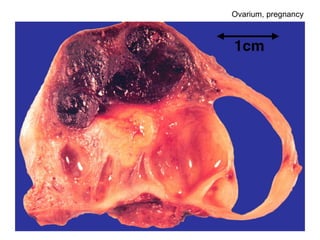

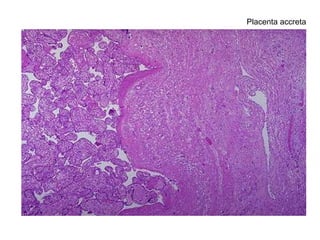
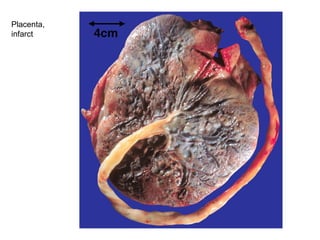
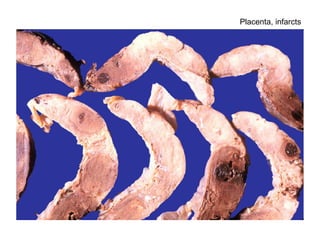
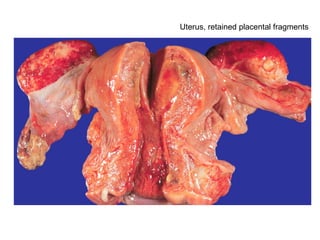
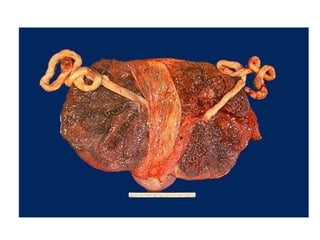

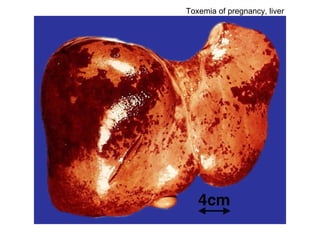
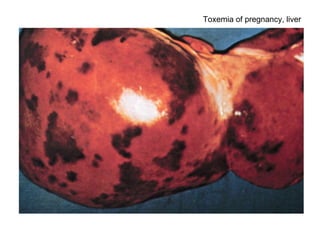
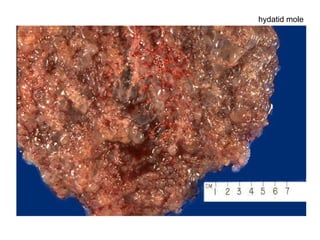
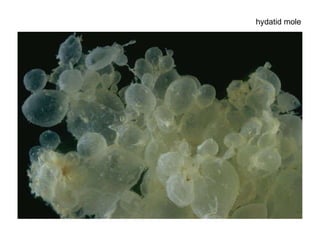
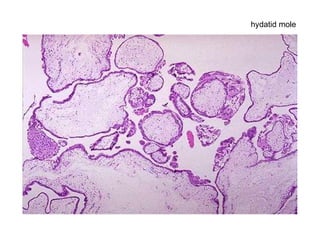
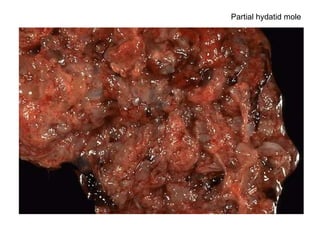

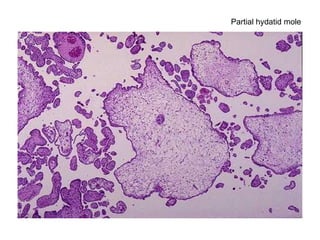
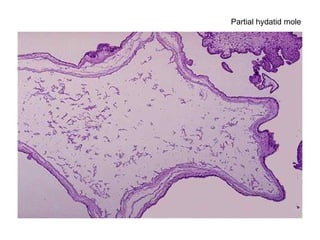
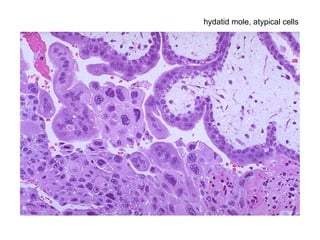
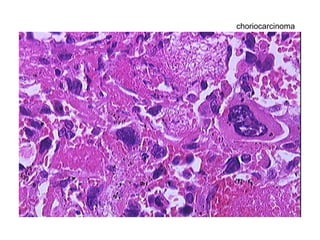
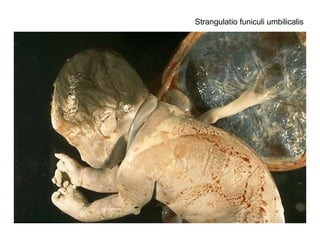
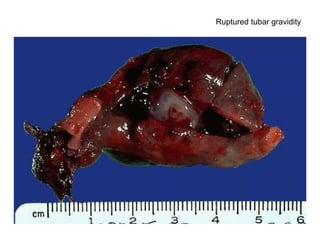
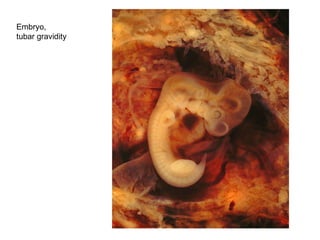
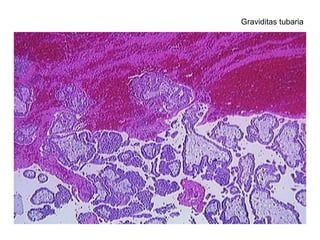
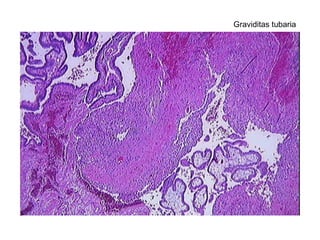
The document summarizes various diseases and conditions that can occur during pregnancy. It discusses changes to the breast during pregnancy including hormonal influences. It also describes changes to the uterus such as endometrial stimulation and uterine wall hypertrophy. Various pathological conditions of the placenta are outlined including insufficiency, infections, hematomas, incorrect positioning, and infarcts. Toxemia of pregnancy is discussed in relation to reduced placental blood flow and its manifestations including preeclampsia and eclampsia. Gestational trophoblastic diseases such as complete and partial hydatid moles and choriocarcinoma are also summarized.

































