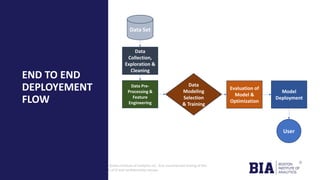
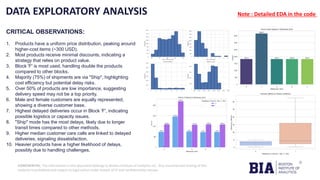
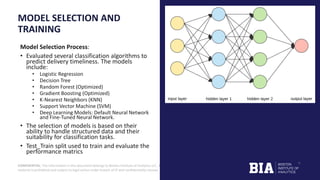
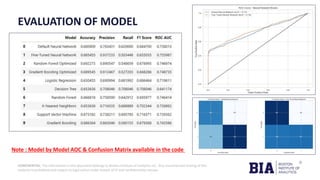
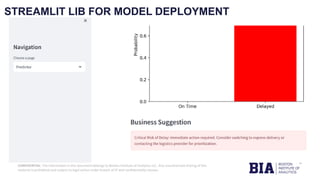
The document outlines a project by the Boston Institute of Analytics to develop machine learning models for predicting product delivery timeliness in an international e-commerce context. Key objectives include improving customer satisfaction and optimizing logistics through various analytical techniques and end-to-end deployment using Streamlit and Power BI. A fine-tuned neural network model has been selected for deployment due to its high performance and adaptability after optimization.