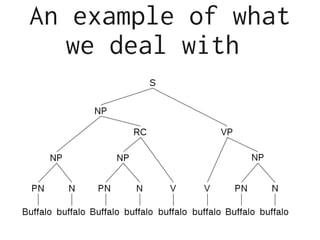
This document discusses using Lisp for practical natural language processing (NLP). It begins with an overview of NLP practice, including research work like setting goals, devising algorithms, training models, and testing accuracy. It then discusses some pros and cons of using Lisp for NLP, including its support for interactivity, mathematical foundations, and tree structures. Examples are given of interactive Lisp programs and APIs. The document emphasizes that data is key for NLP and discusses sources for collecting data. It concludes that Lisp is well-suited for NLP research and development due to its interactive and flexible nature.