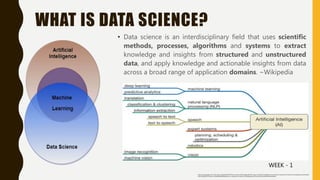
This document provides an introduction to data science and the Python programming language. It outlines key topics including what data science is, its main branches, Python data types and structures, built-in methods, control statements and loops, functions and classes. These concepts are explained over the course of a weekly course on data science fundamentals using Python for data analysis, visualization and modeling.






![AN INTRODUCTION TO PYTHON
Python Functions/Methods and Classes
A function is a block of code meant for a specific
purpose and its reusable.
• Class = data + method
• An Object is the instance of a class.
• More on Python Classes:
• https://github.com/JosephItopa/Drop_of_my_Pyt
hon_Projects/blob/master/Intro_to_python_serie
s/Introduction_To_Python_Webinar_Series_4.ipyn
b
WEEK - 1
def function_name( parameters ):
"function_docstring"
function_suite
return [expression]
class ClassName:
'Optional class documentation string'
class_suite](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontodatascience-210508093311/85/Introduction-to-data-science-9-320.jpg)


