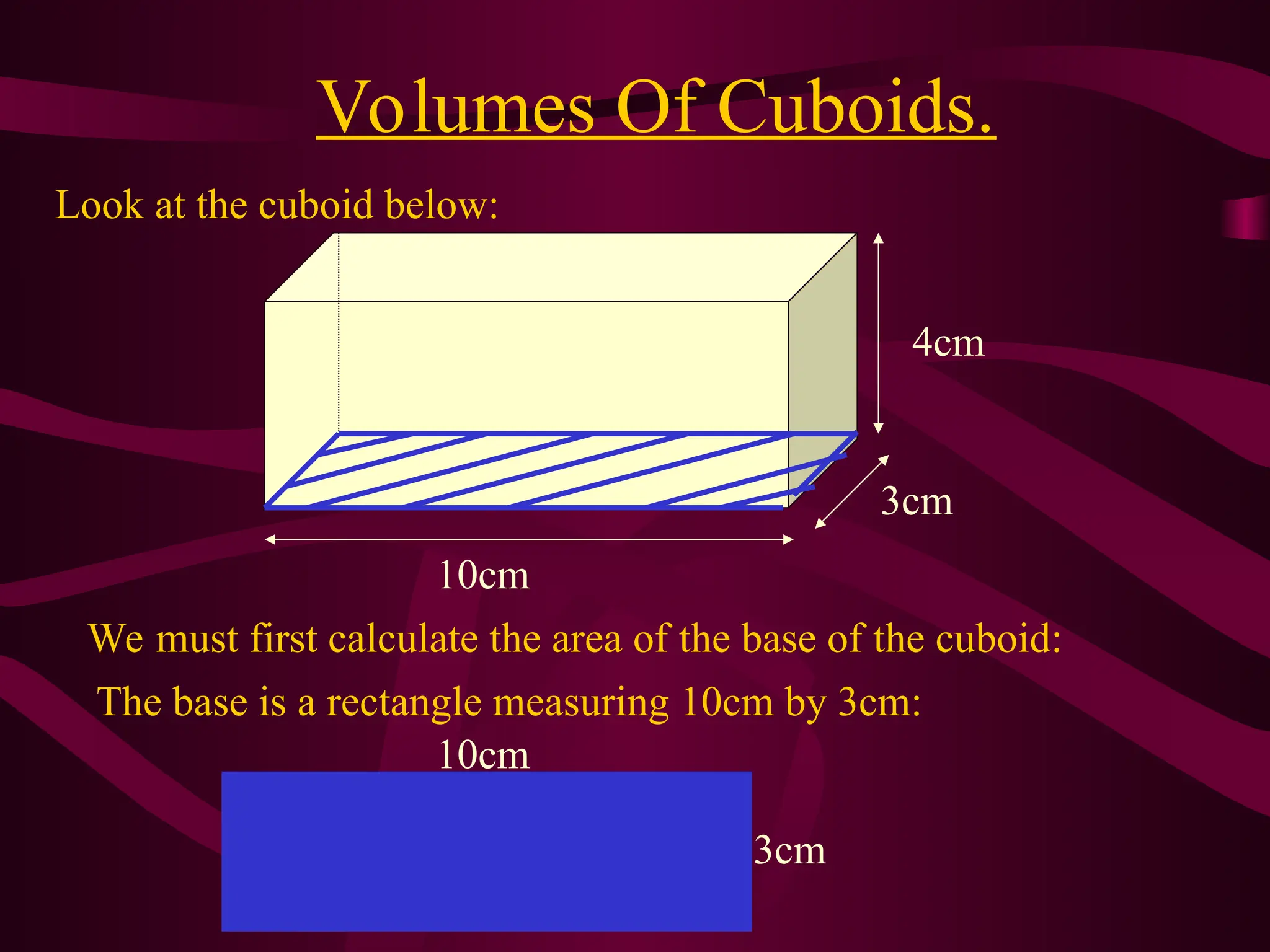
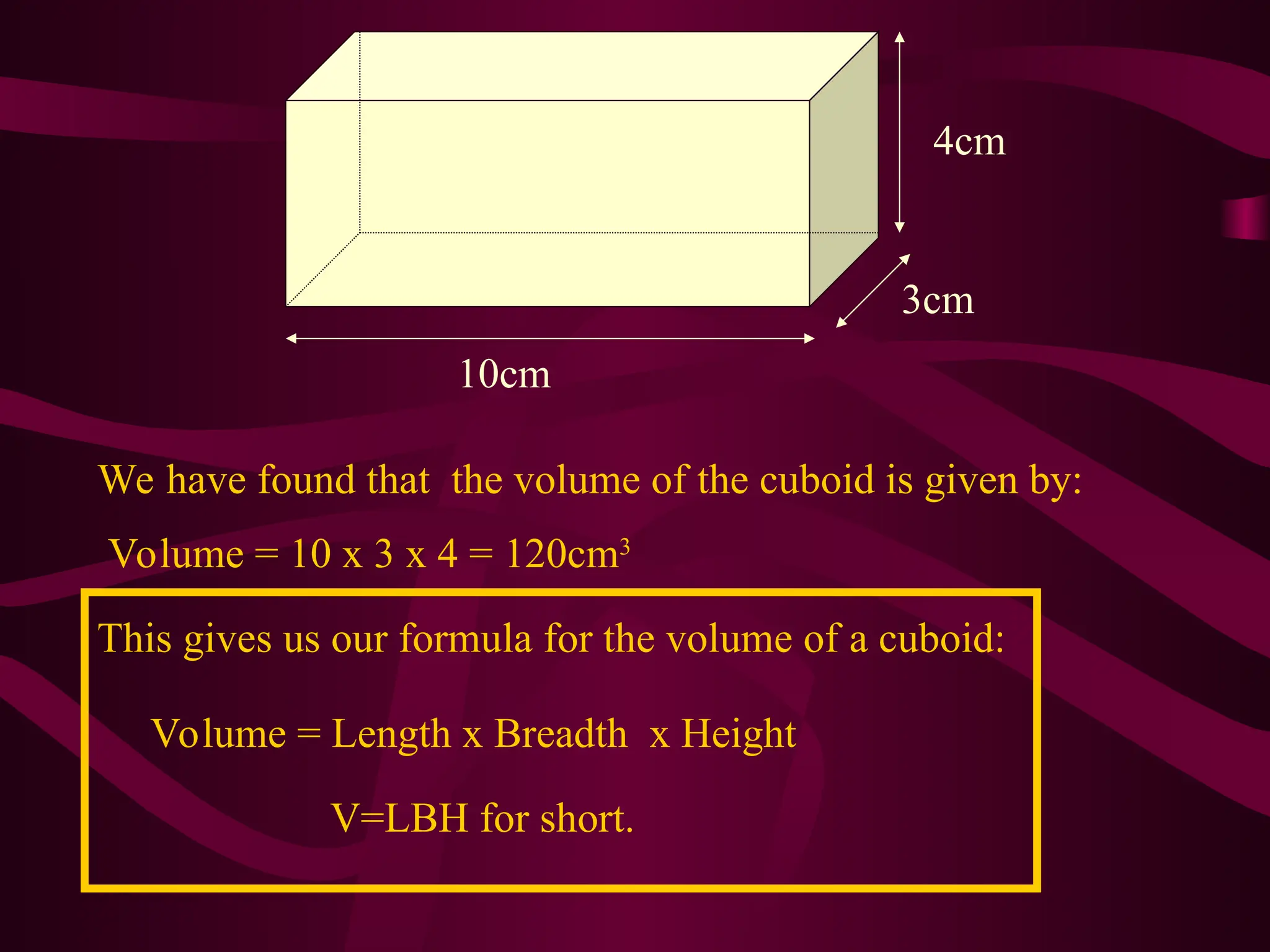
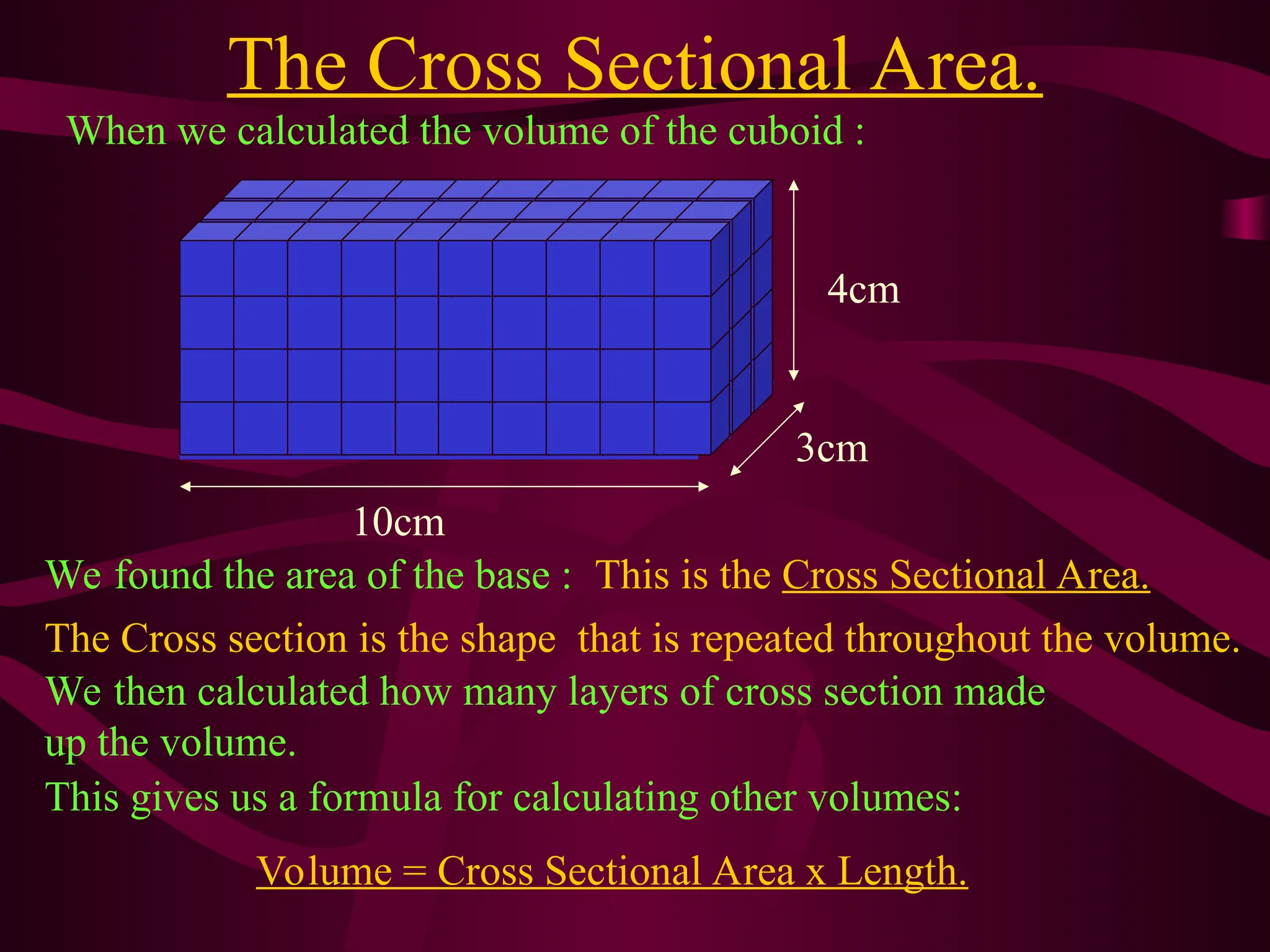
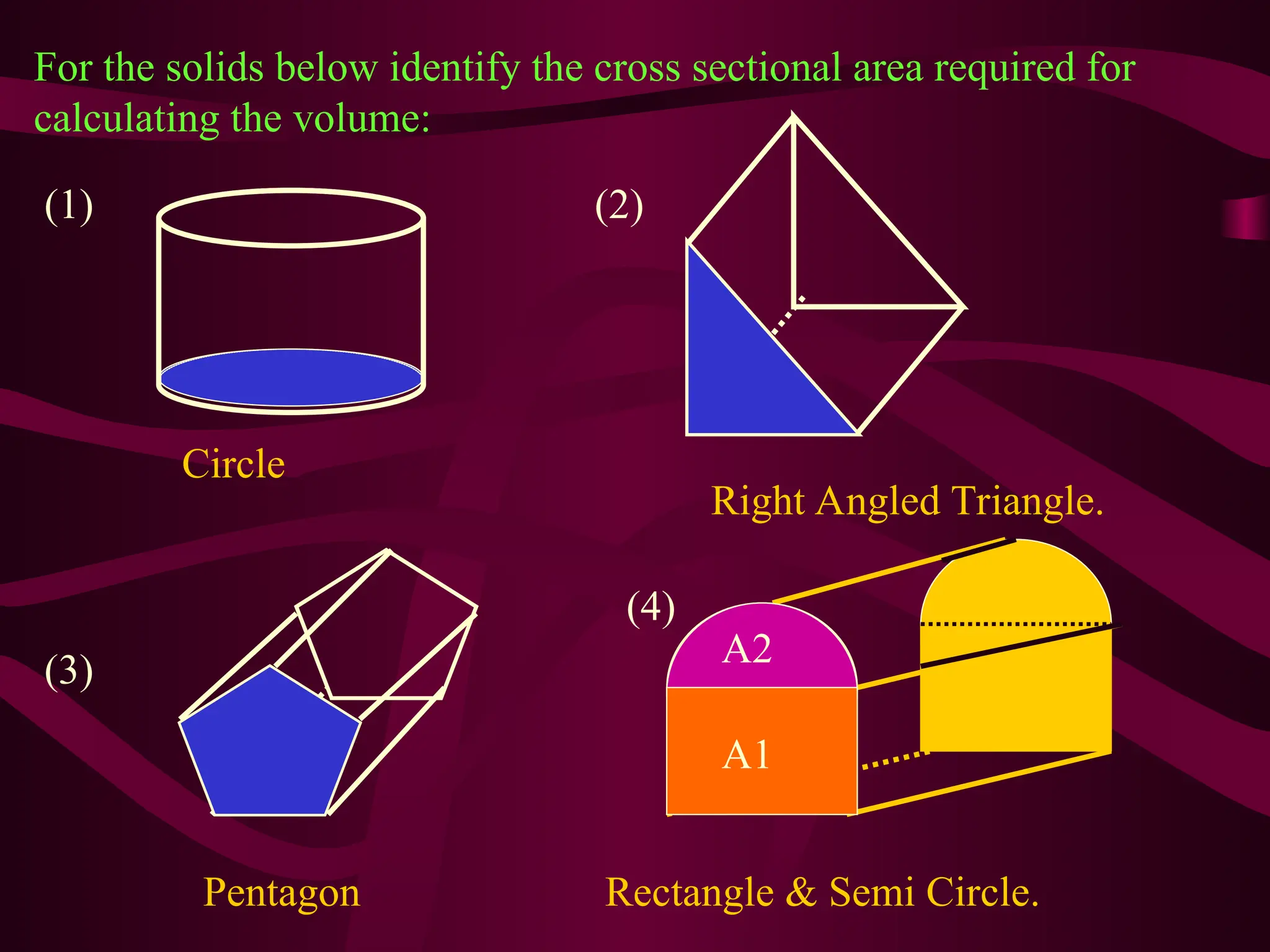
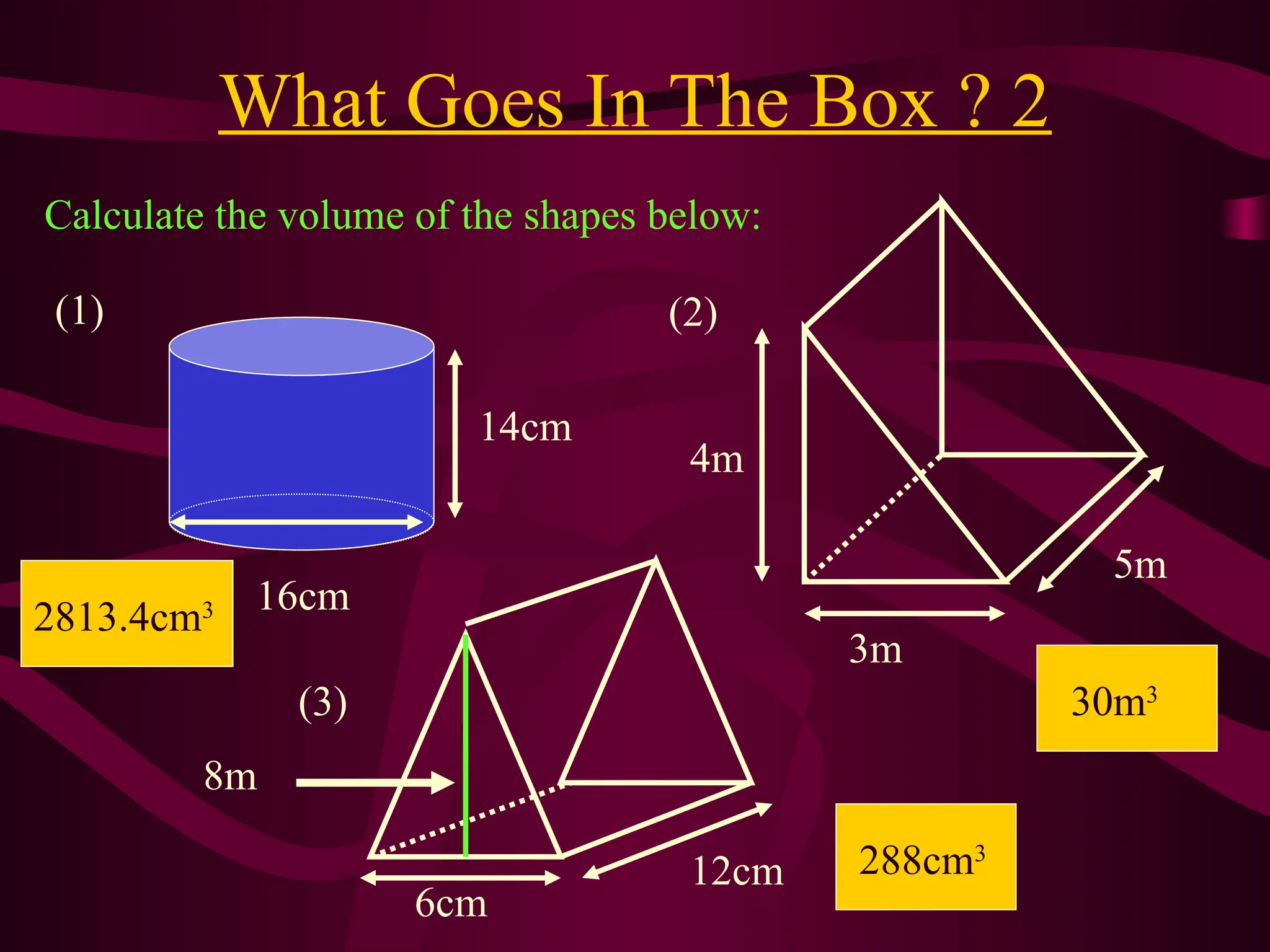
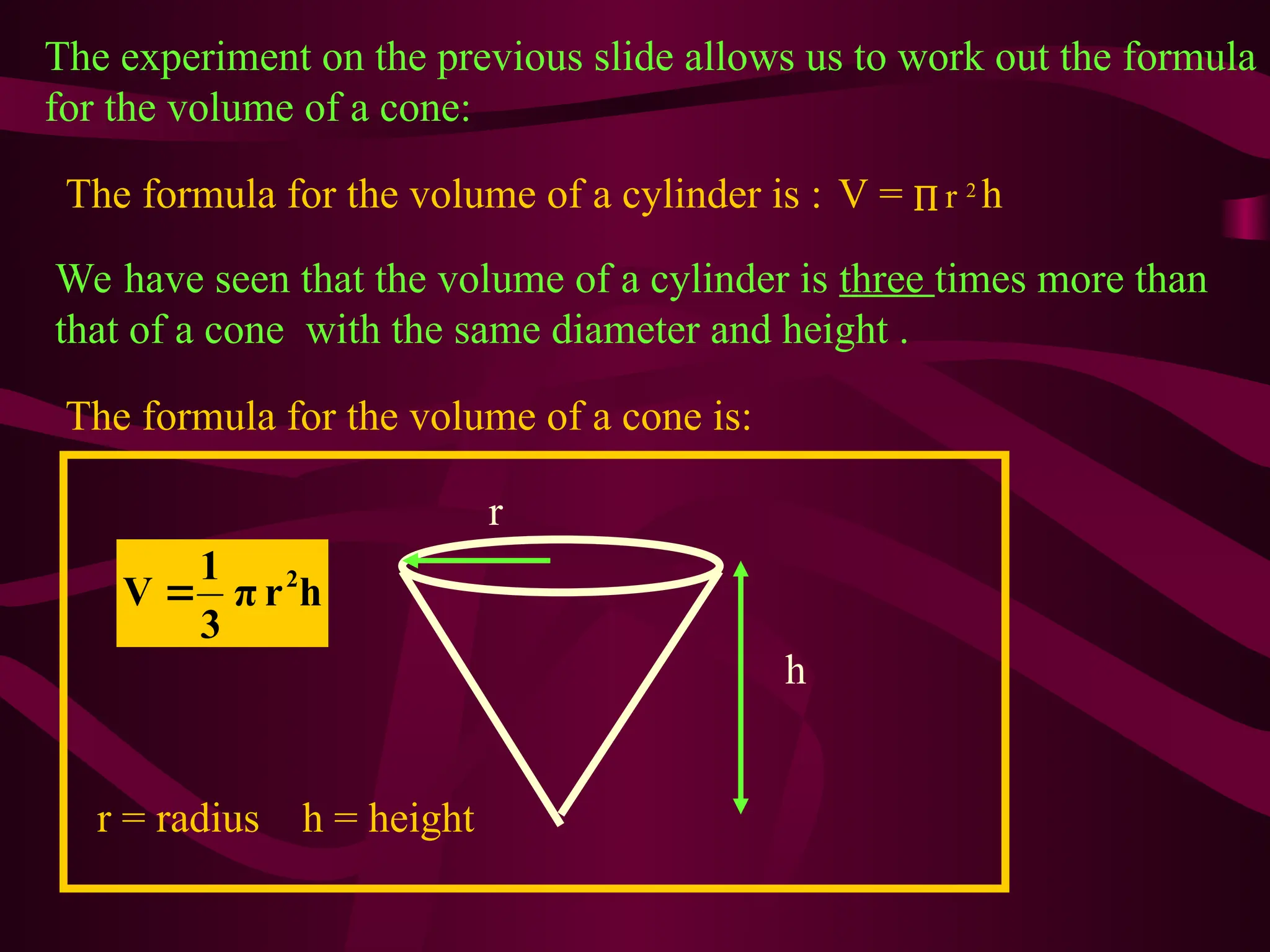
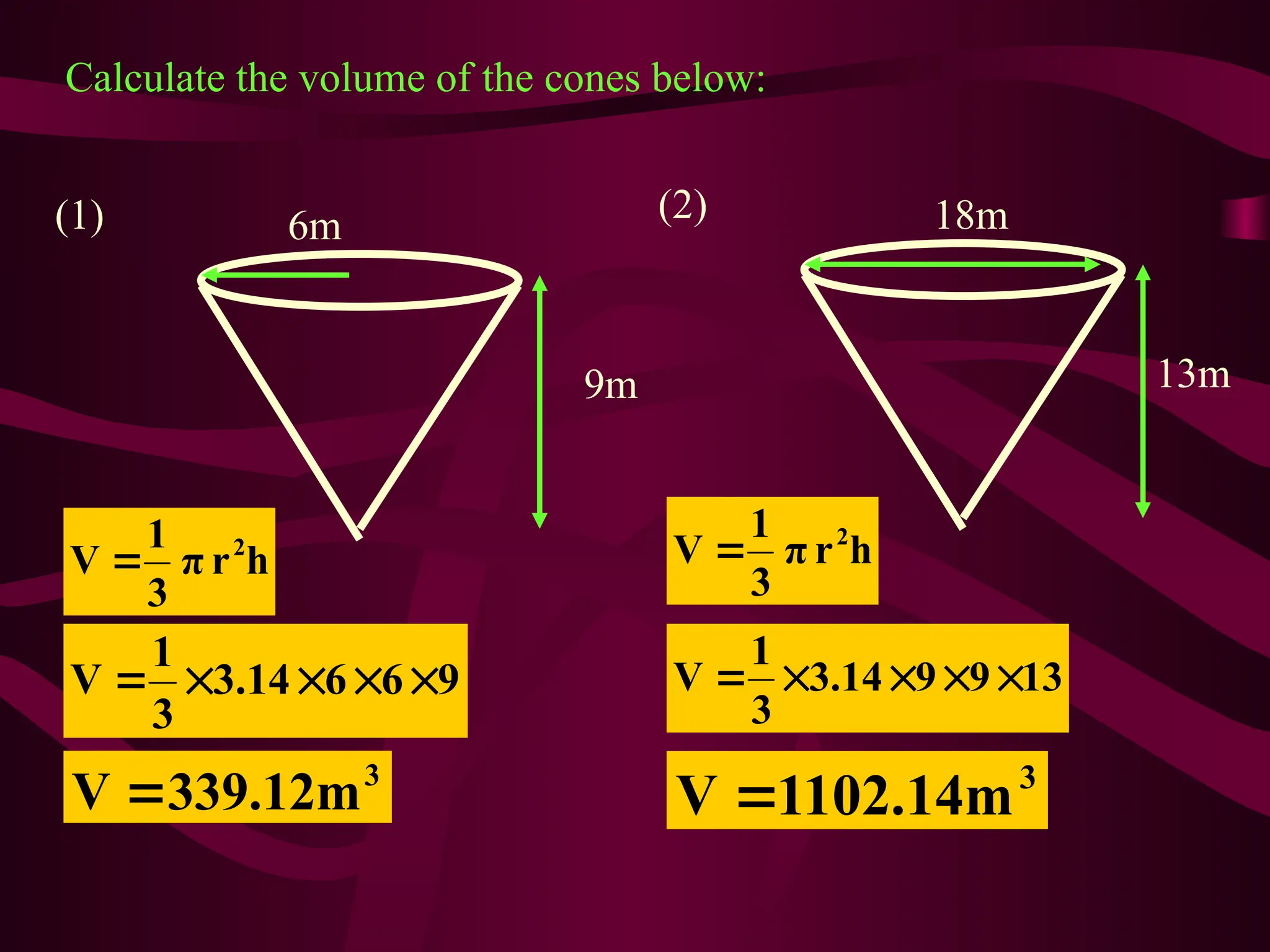
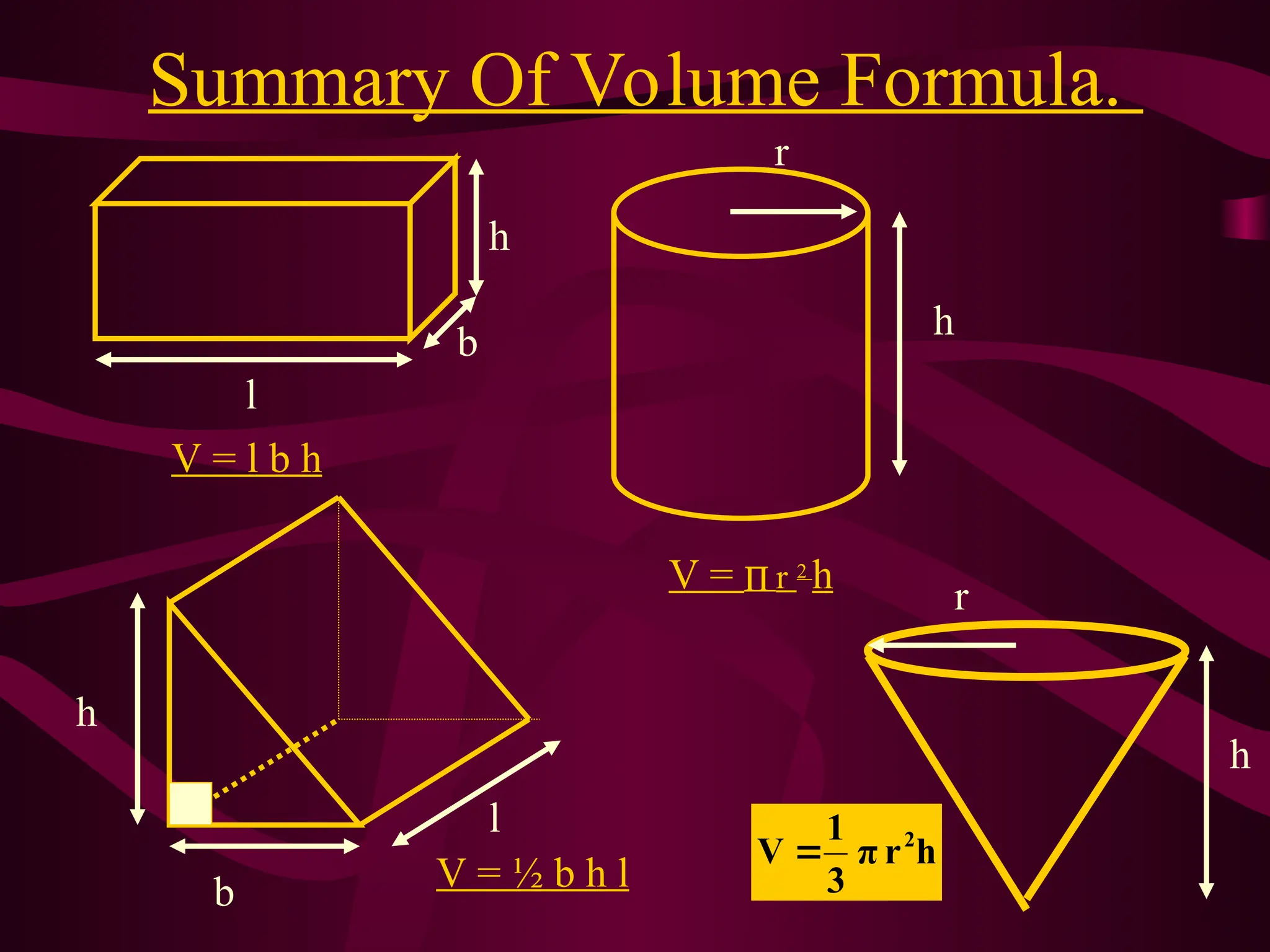
The document explains various methods for calculating the volume of different solids, including cuboids, cylinders, and cones, using specific formulas. It emphasizes the importance of measuring base area and height for accurate volume calculations, providing examples and step-by-step instructions. It also highlights the relationship between volume and cross-sectional area for more complex shapes.