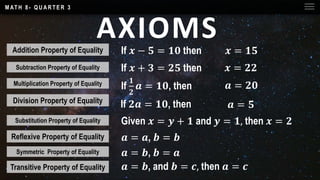
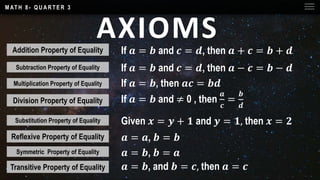
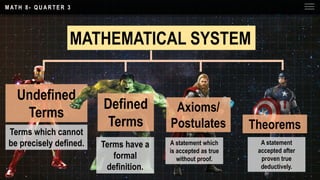
This document outlines key concepts in geometry including postulates, theorems, and properties. It lists seven postulates and three theorems. The theorems proved are: 1) if two lines intersect, their intersection contains one point, 2) if a line intersects a plane, their intersection is a line, and 3) the sum of the interior angles of a triangle is 180 degrees. The document provides definitions and examples of postulates, theorems, and how theorems are logically proven using previously stated facts.