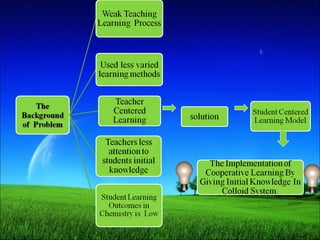
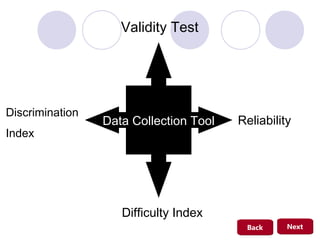
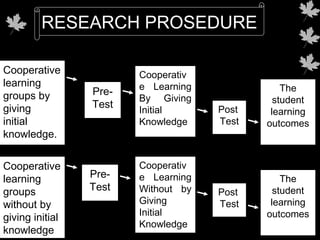
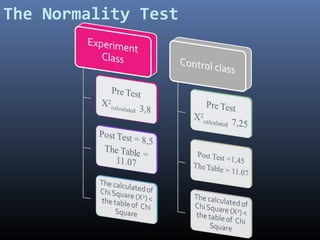
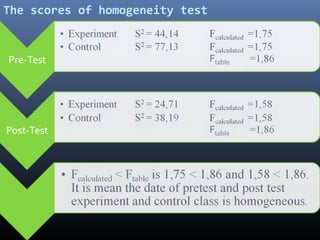
The study evaluates the impact of cooperative learning with initial knowledge on student outcomes in chemistry, specifically the colloid system, at SMA Negeri 3 Binjai. Results indicate that students receiving initial knowledge perform better than those who do not, with significant differences in learning outcomes. The findings suggest cooperative learning combined with preliminary knowledge enhances both academic performance and social collaboration among students.