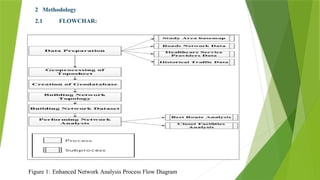
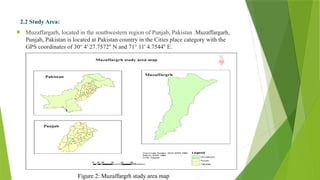
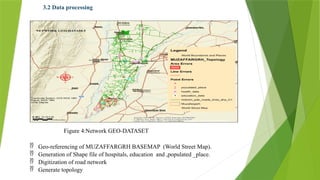
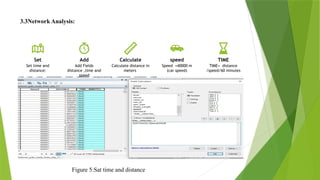
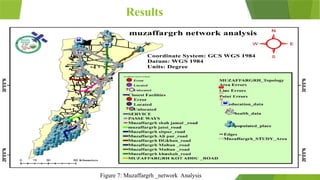
The document details a network analysis conducted in Muzaffargarh city using GIS techniques to improve urban planning and service delivery. The study aims to identify efficient travel routes and define optimal service areas for essential facilities. Methods include data collection, geo-database creation, and network analysis to enhance transportation infrastructure and accessibility in the region.