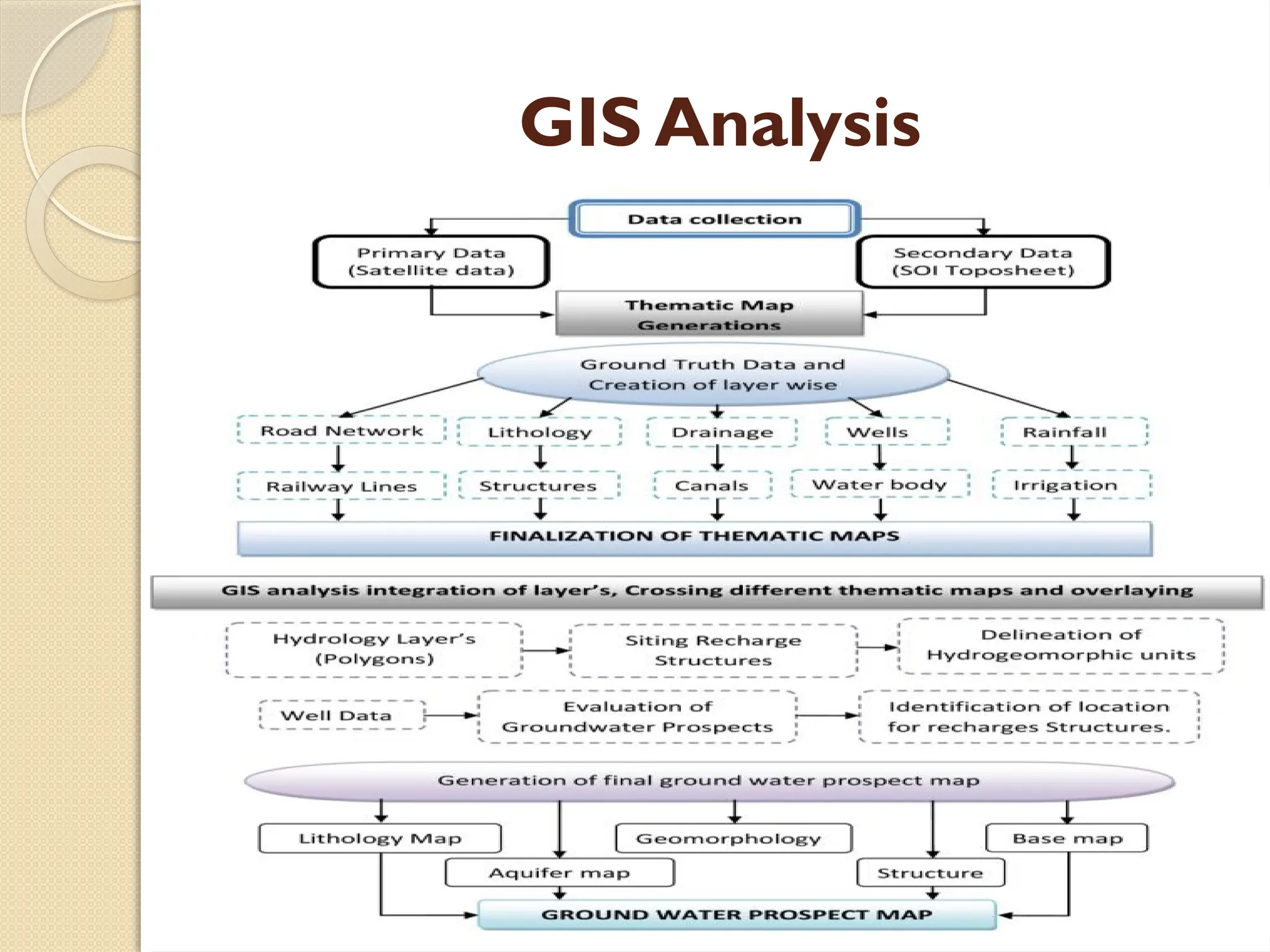
The document discusses the application of remote sensing and GIS in groundwater prospecting, highlighting the benefits and techniques used in this field. It explains how remote sensing works, the key methodologies employed, and the integration with GIS for enhanced analysis. The conclusion emphasizes the promise of future advancements in technology to improve water management practices.