Exponents and powers are perhaps the most fundamental concepts found in mathematics, which has made it easy to get the same number multiplied times over again. An exponent is how many times that number, known as a base, is multiplied to itself. For instance, in (2^3), the number 2 is the base, and the exponent (power) being 3 shows that this number, 2 is multiplied by itself three times (same base) i.e. (2 times 2 times 2 =8). The result obtained from such multiplication is power. The result obtained from such multiplication is referred to as the power. These concepts are vital in understanding the difference between exponential and power functions and their applications in mathematics, from basic arithmetic to advanced algebra and scientific calculations. Mastering the rules of exponents and powers is crucial for solving equations, simplifying expressions, and efficiently addressing real-world problems. This ensures that calculations are devised and executed streamlined and simplified.
Exponents and powers are mathematical tools that make writing and calculating repeated multiplication of the same number easy.
Let's break it down step by step to better understand powers and exponents with important rules
An exponent is the number written above and to the right of another number. It tells us how many times the base number is multiplied by itself. The exponent tells how many times a number is multiplied by its power.
For example, (2^3) (read as two raised to the power of 3) means (2 times 2 times 2 = 8).
Here, 3 is the exponent of a number.
2 is the base (the number being multiplied).
3 is the exponent (the number of times 2 is multiplied by itself).





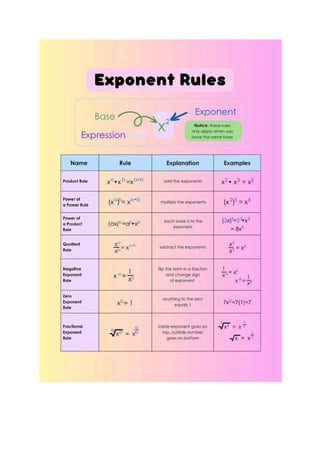
![Understanding the rules of exponents enables us to work with them easily.
Here are some of the most important ones:
1. Multiplying Powers with the Same Base: When multiplying numbers
with the same base, add the exponents. a^m times a^n = a^{m+n}
Example: (2^3 times 2^2 = 2^{3+2} = 2^5 = 32).
2. Dividing Powers with the Same Base: When dividing numbers with
the same base, subtract the exponents. a^m div a^n = a^{m-n}
Example: (5^4 div 5^2 = 5^{4-2} = 5^2 = 25).
3. Power of a Power Rule:
When raising a power to another power, multiply the exponents.
[
(a^m)^n = a^{m times n}
]
Example: ((3^2)^3 = 3^{2 times 3} = 3^6 = 729).
4. Zero Exponent Rule:
Any number raised to the power of 0 is always 1 (except 0 itself).
[a^0 = 1]
Example: (4^0 = 1).
5. Negative Exponent Rule: The negative exponent means the
reciprocal (or the "flipped" version) of the base raised to the positive
exponent.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatareexponentsandpowers-250519101419-e4bd3d4d/85/What-are-Exponents-and-Powers-Definitions-Rules-and-Examples-7-320.jpg)
![[ a^{-n} = frac{1}{a^n}]
Example: (2^{-3} =frac{1}{2^3} = frac{1}{8}).
Why Are Exponents and Powers Useful?
Exponents and powers help us compactly express large or small numbers.
For example:
- The large number 1,000,000 can be written as (10^6).
- The tiny number 0.00001 can be written as (10^{-5}).
Exponents and powers are also used in sciences to calculate growth, in
computing to measure speed or storage, and in geometry to calculate area
and volume.
What Is an Exponent and Power?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatareexponentsandpowers-250519101419-e4bd3d4d/85/What-are-Exponents-and-Powers-Definitions-Rules-and-Examples-8-320.jpg)

![Real-Life Examples
Following are the real-life situations which involve exponents and power
exponents exponent.
Doubling Bacteria Growth
Imagine one bacterium doubles every hour. By the end of 3 hours, the
cumulative total number of bacteria is:
Expression: [2^3 = 2 times 2 times 2 = 8]
Such exponents make the multiple growths easily computable.
It can also be used to ascertain the pH scale.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatareexponentsandpowers-250519101419-e4bd3d4d/85/What-are-Exponents-and-Powers-Definitions-Rules-and-Examples-10-320.jpg)
![Square Area
In finding the area of a square with a side length of 4, we multiply the side
by itself:
[4^2 = 4 times 4 = 16]
Large Numbers in Science
In astronomy, the distance from Earth to the Sun is roughly (1.5 times 10^8)
kilometres. That's a lot more concise than 150,000,000 kilometres.
Why Does It Matter To Know Exponents and Powers?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatareexponentsandpowers-250519101419-e4bd3d4d/85/What-are-Exponents-and-Powers-Definitions-Rules-and-Examples-11-320.jpg)










