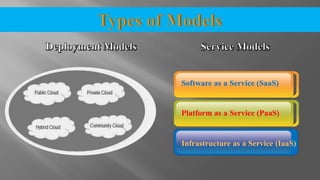
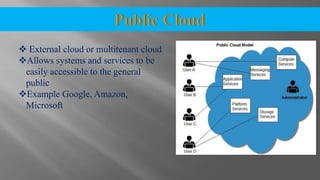
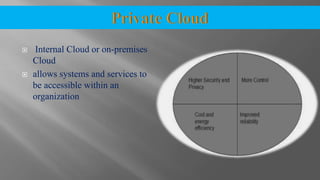
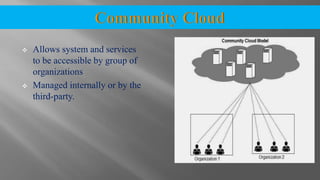
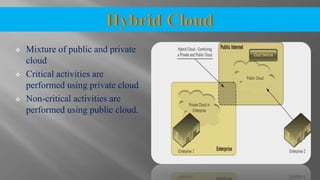
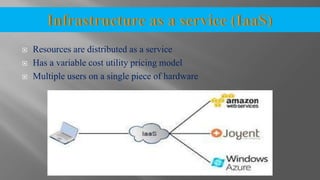
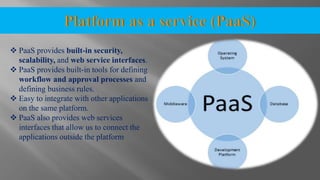
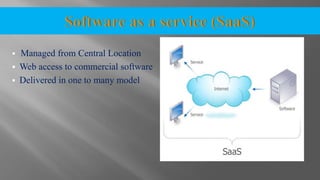
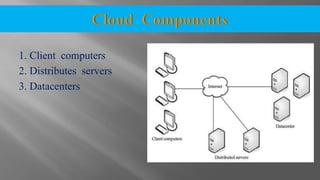
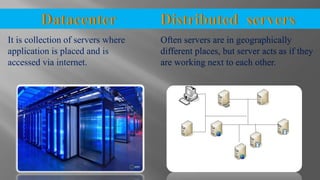
The document discusses cloud computing and its various models including Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). It describes public clouds which allow general public access and internal/private clouds for access within an organization. Hybrid clouds that use a mix of public and private clouds are also mentioned. The document outlines some advantages of cloud computing like cost effectiveness, scalability, and reliability while also noting security and data loss concerns.