Embed presentation
Downloaded 63 times


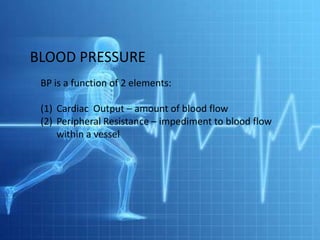
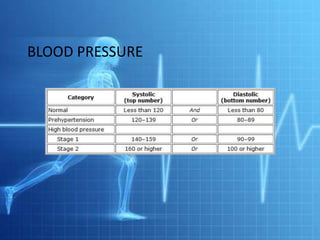



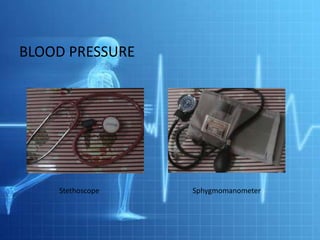






Blood pressure refers to the force that blood exerts against vessel walls, represented by systolic and diastolic pressures. Blood pressure is determined by cardiac output and peripheral resistance. Postural hypotension is a sudden drop in blood pressure when moving from lying to standing. Hypovolemia and hypervolemia refer to abnormally low or high blood volume. Measuring blood pressure involves using a sphygmomanometer and stethoscope to listen for sounds over the brachial artery at different cuff pressures.












