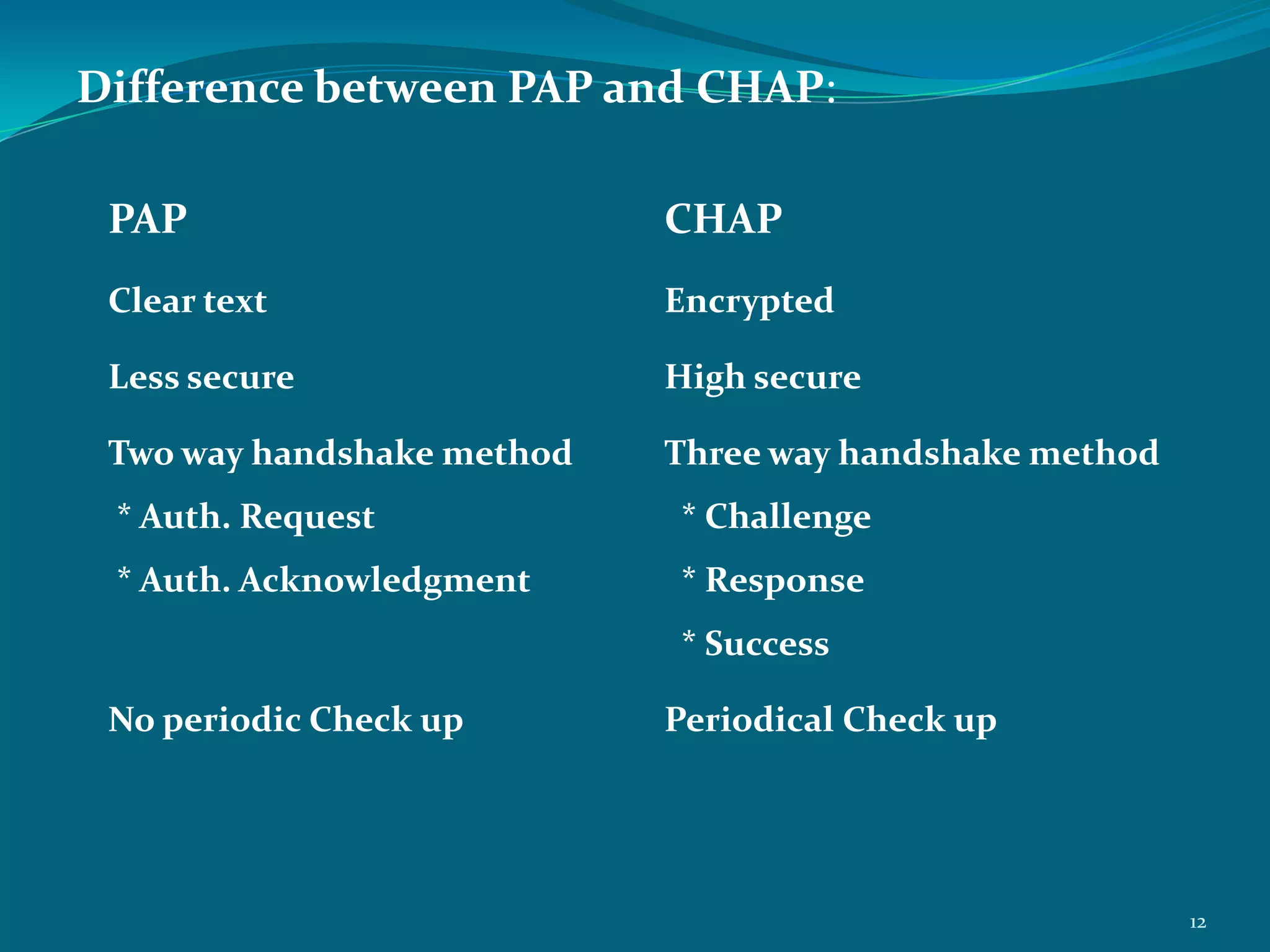
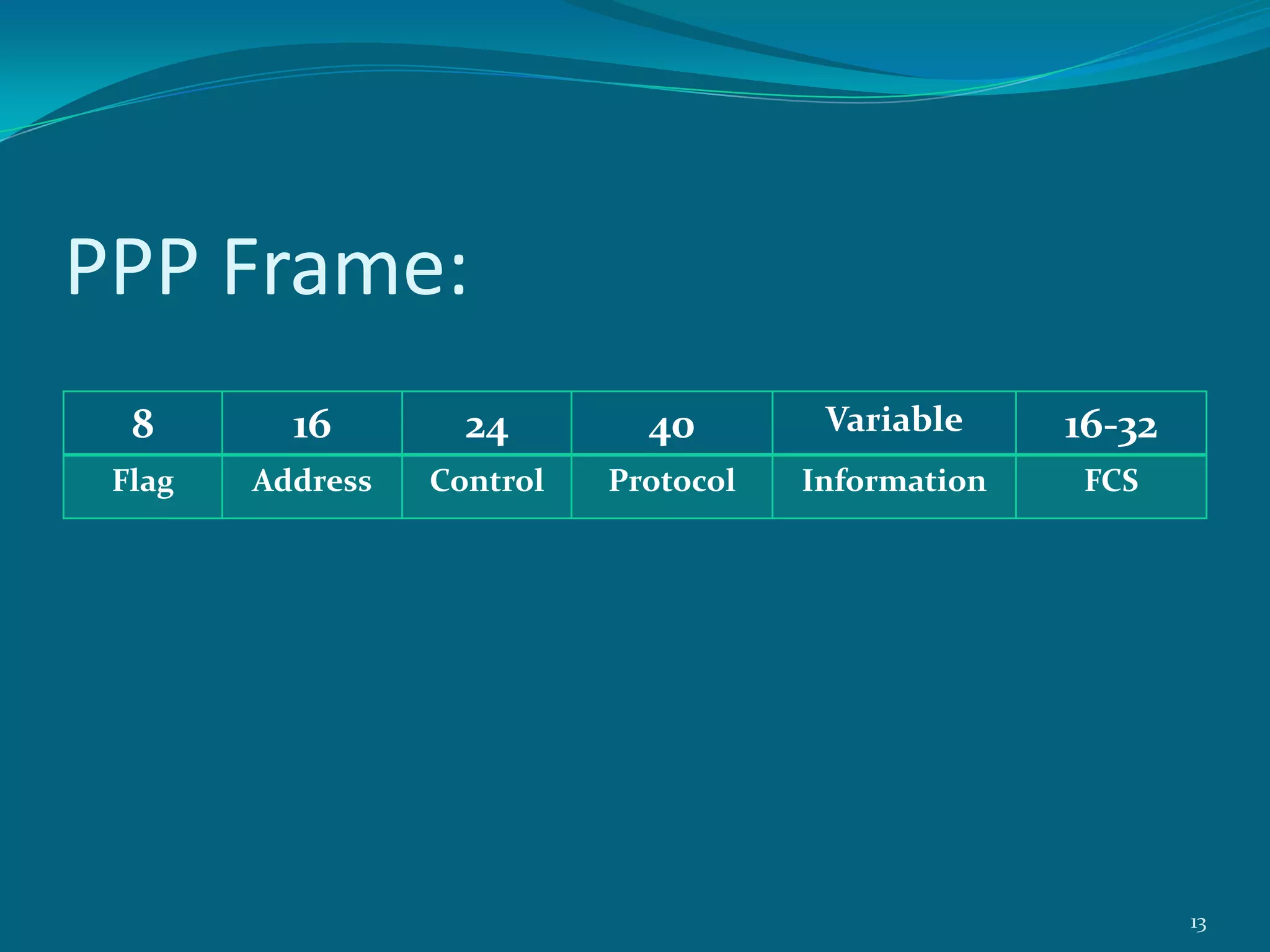
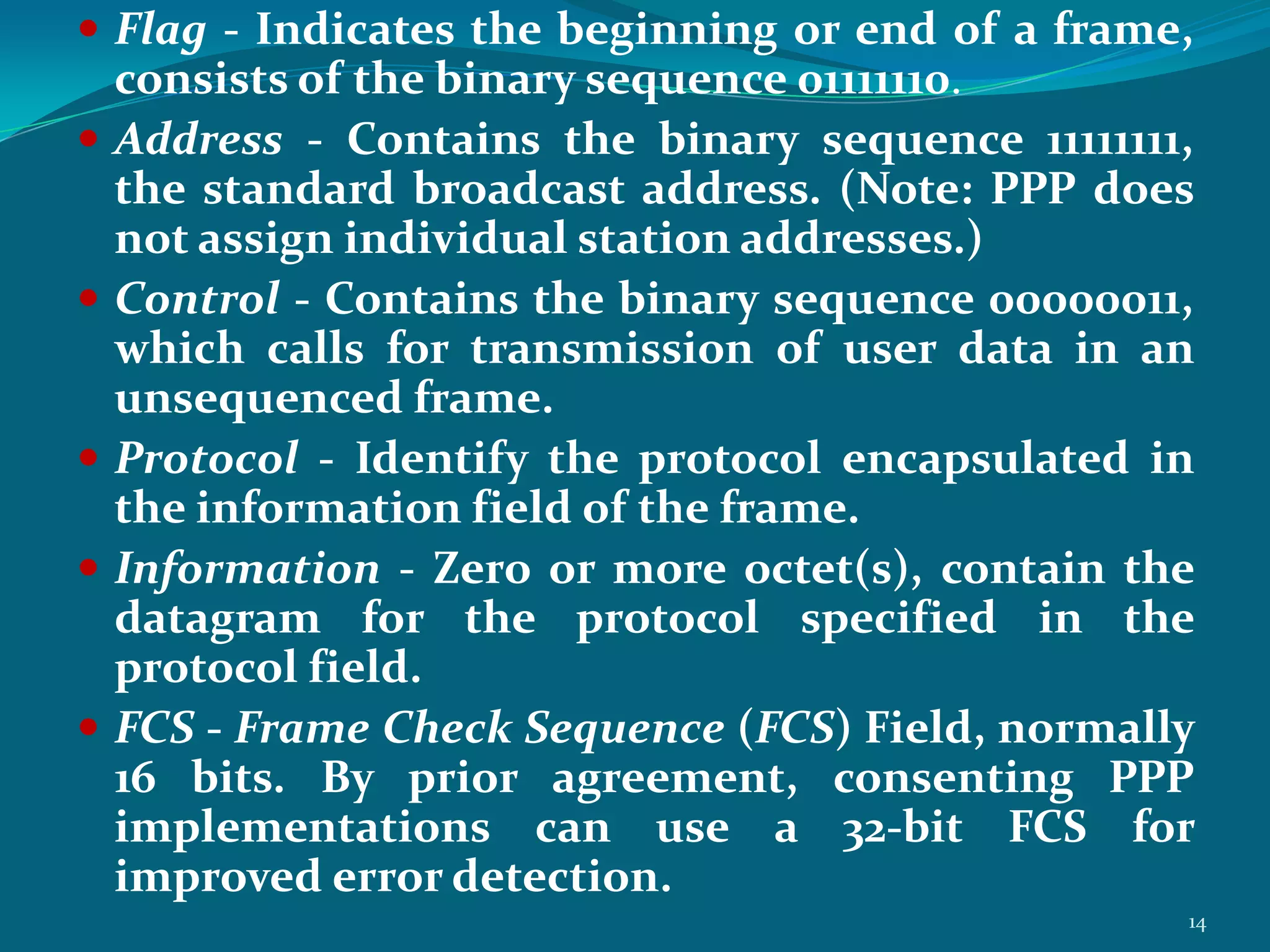
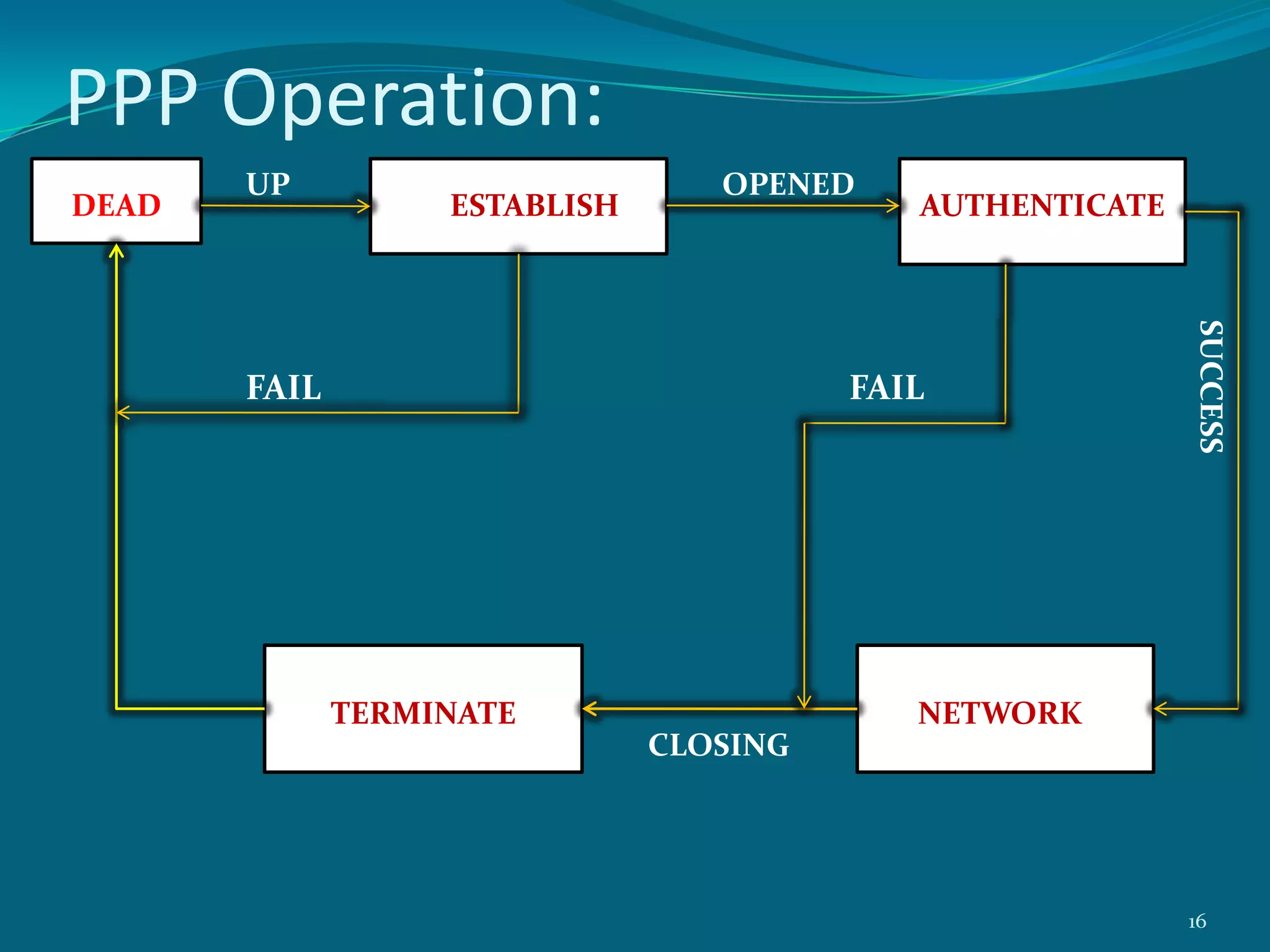
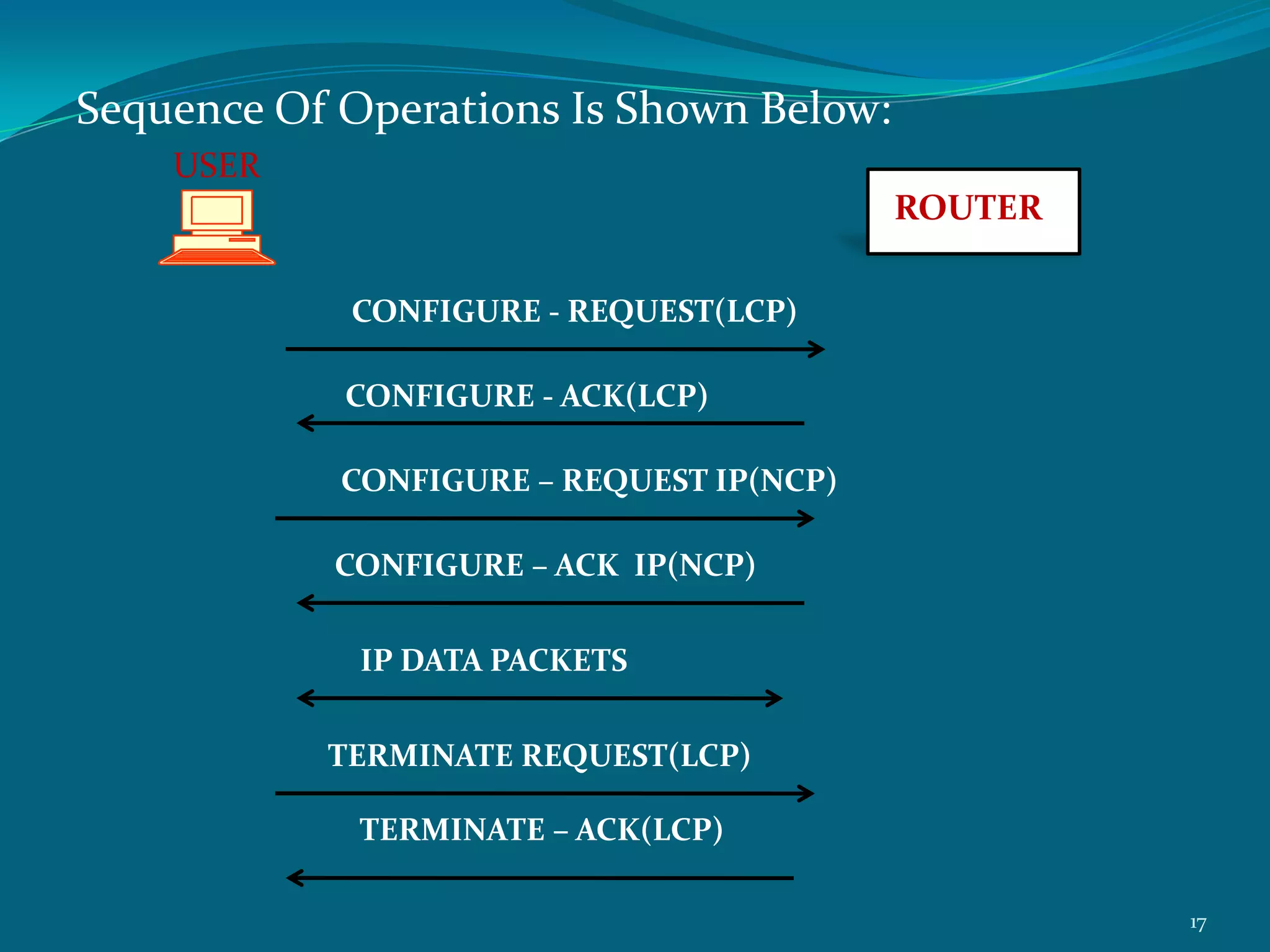
PPP is a data link protocol commonly used to establish a direct connection between two nodes. It provides authentication, encryption, and compression. PPP was developed to overcome deficiencies of the earlier SLIP protocol, such as lack of error detection and support only for IP. PPP uses Link Control Protocol (LCP) to establish and configure the link, Network Control Protocol (NCP) for dynamic IP address assignment, and authentication protocols like PAP and CHAP. It transmits multi-protocol packets between two peers using byte stuffing to flag packet boundaries. The PPP connection process involves link configuration, authentication, IP configuration, data transfer, and termination. PPP is widely used for analog modem connections to ISPs.