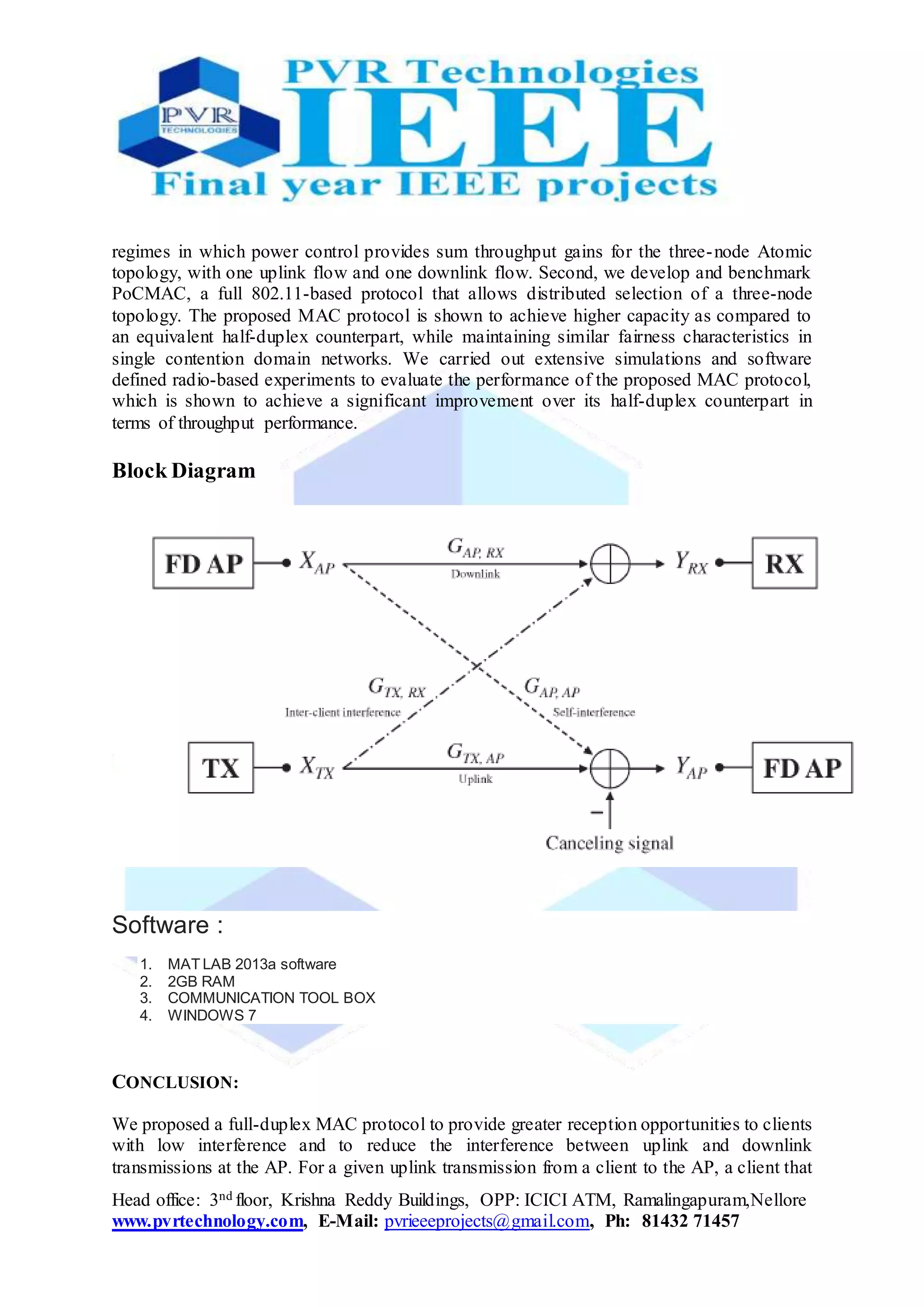
The document proposes a new medium access control (MAC) protocol called PoCMAC that uses distributed power control to manage interference in full-duplex WiFi networks. PoCMAC allows simultaneous uplink and downlink transmissions between an access point and half-duplex clients. It identifies regimes where power control provides throughput gains and develops a full 802.11-based protocol for distributed selection of three-node topologies. Simulations and software-defined radio experiments show PoCMAC achieves higher capacity and throughput compared to half-duplex networks, while maintaining similar fairness.