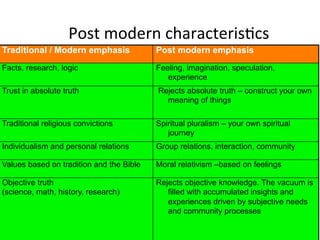
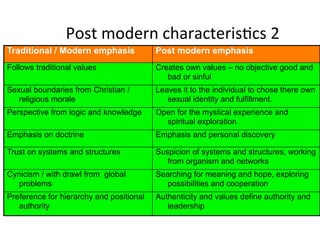
Postmodernism is characterized by skepticism of objective truth and focus on subjective experiences. It questions traditional systems and values. The document discusses how postmodernism shapes identity and self-reflection, with identity seen as a narrative project and reflection tied to the physical body. Postmodern thinking emphasizes feelings over facts and rejects absolute truths.