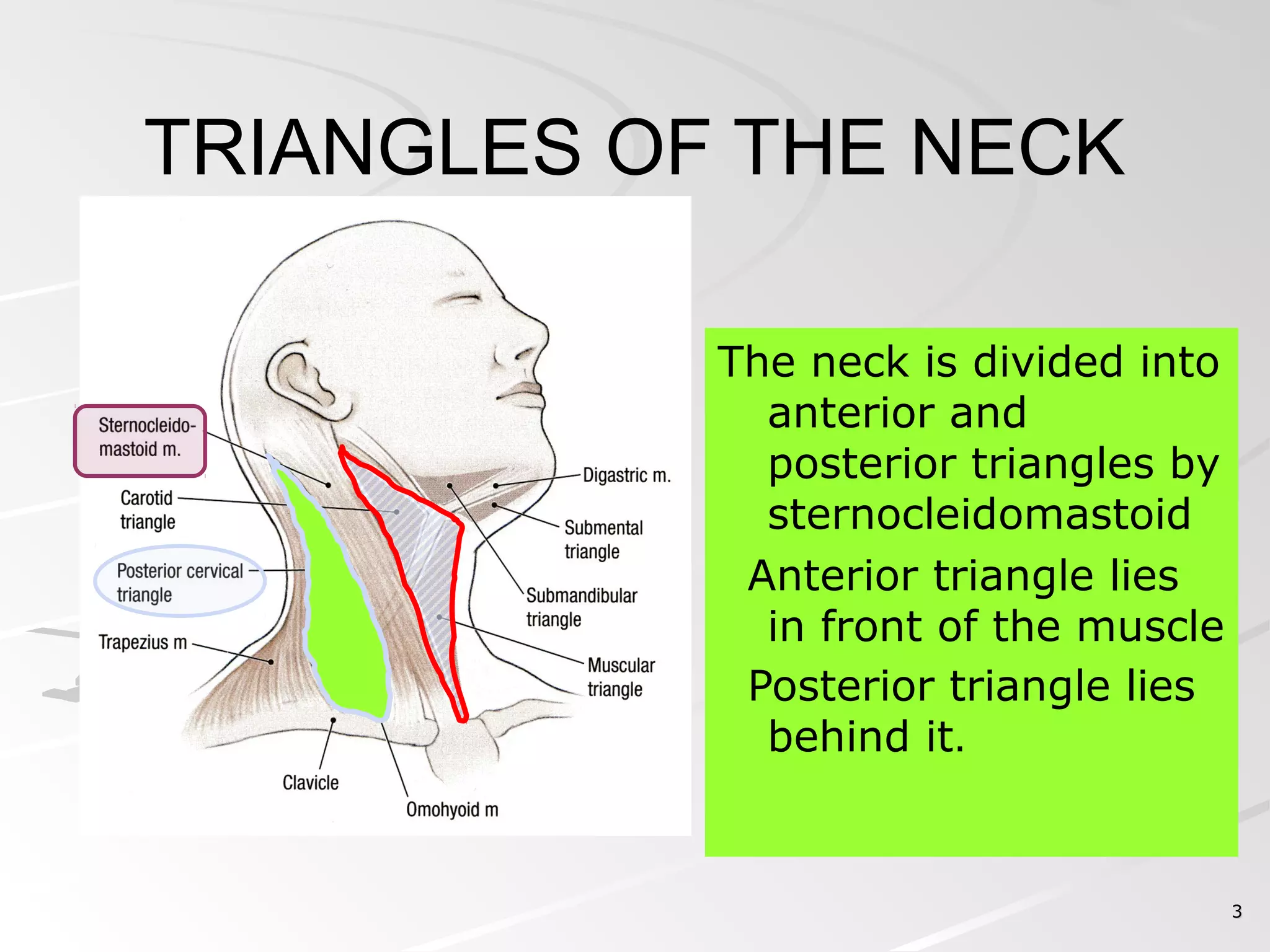
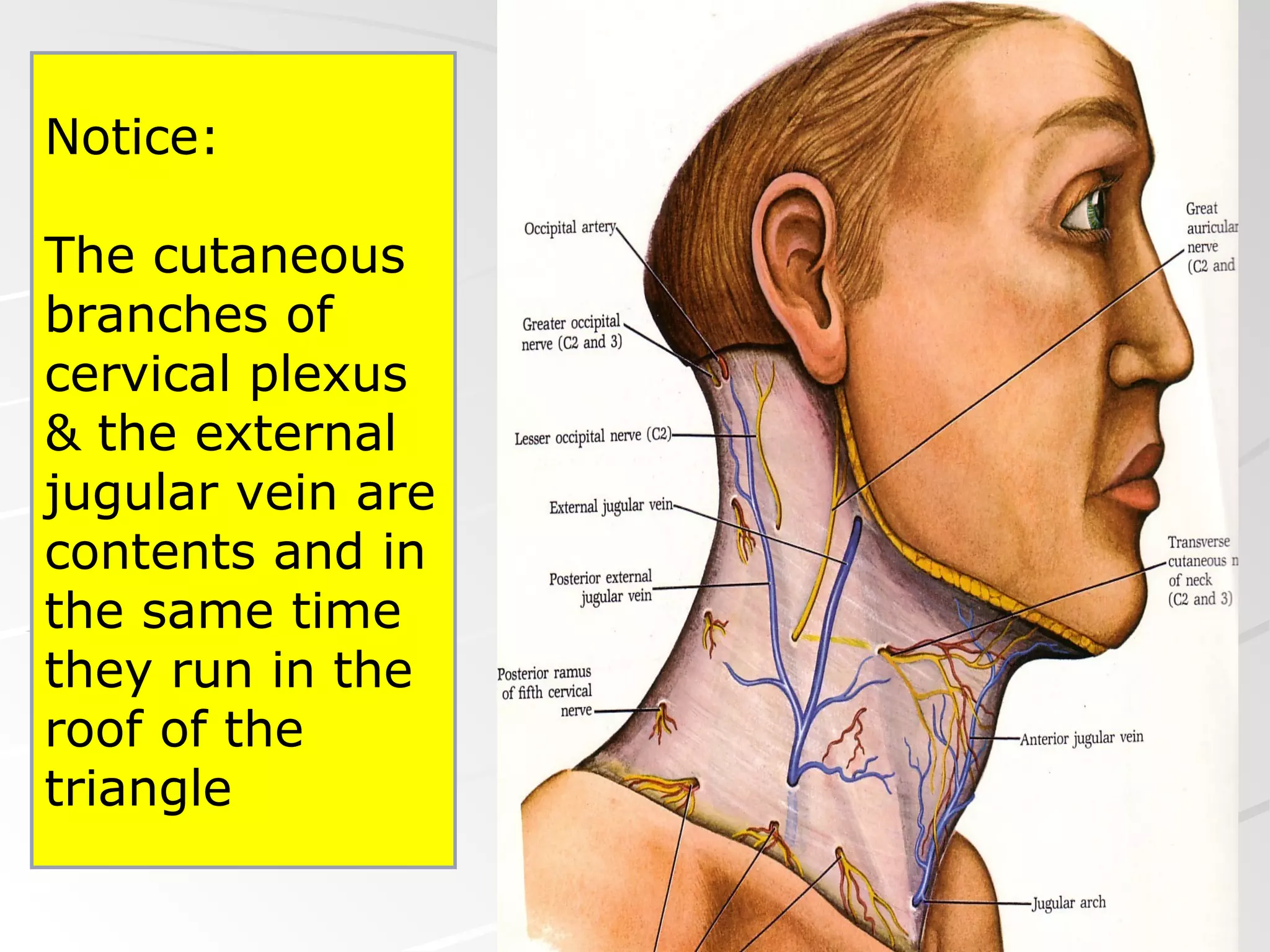
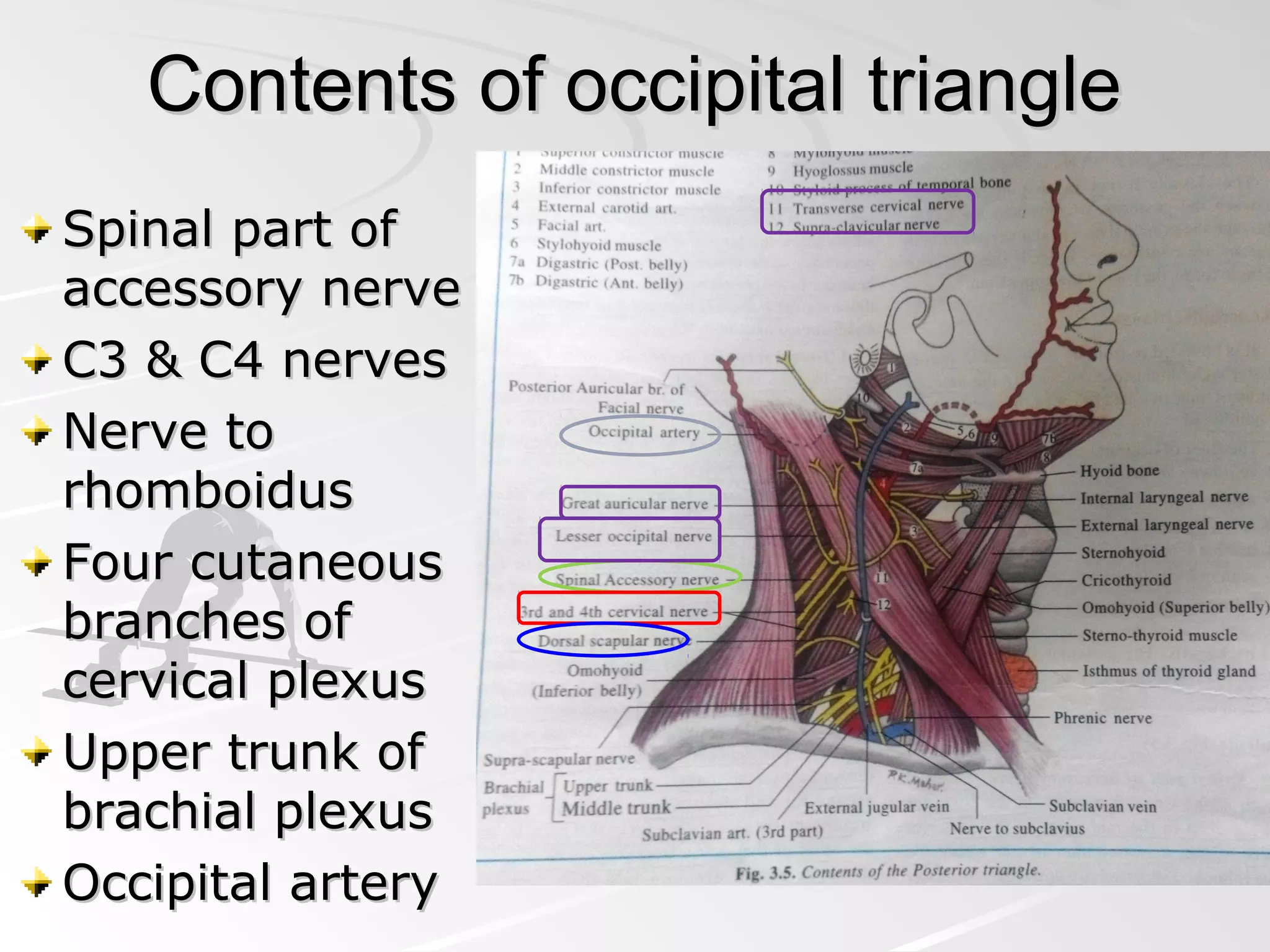
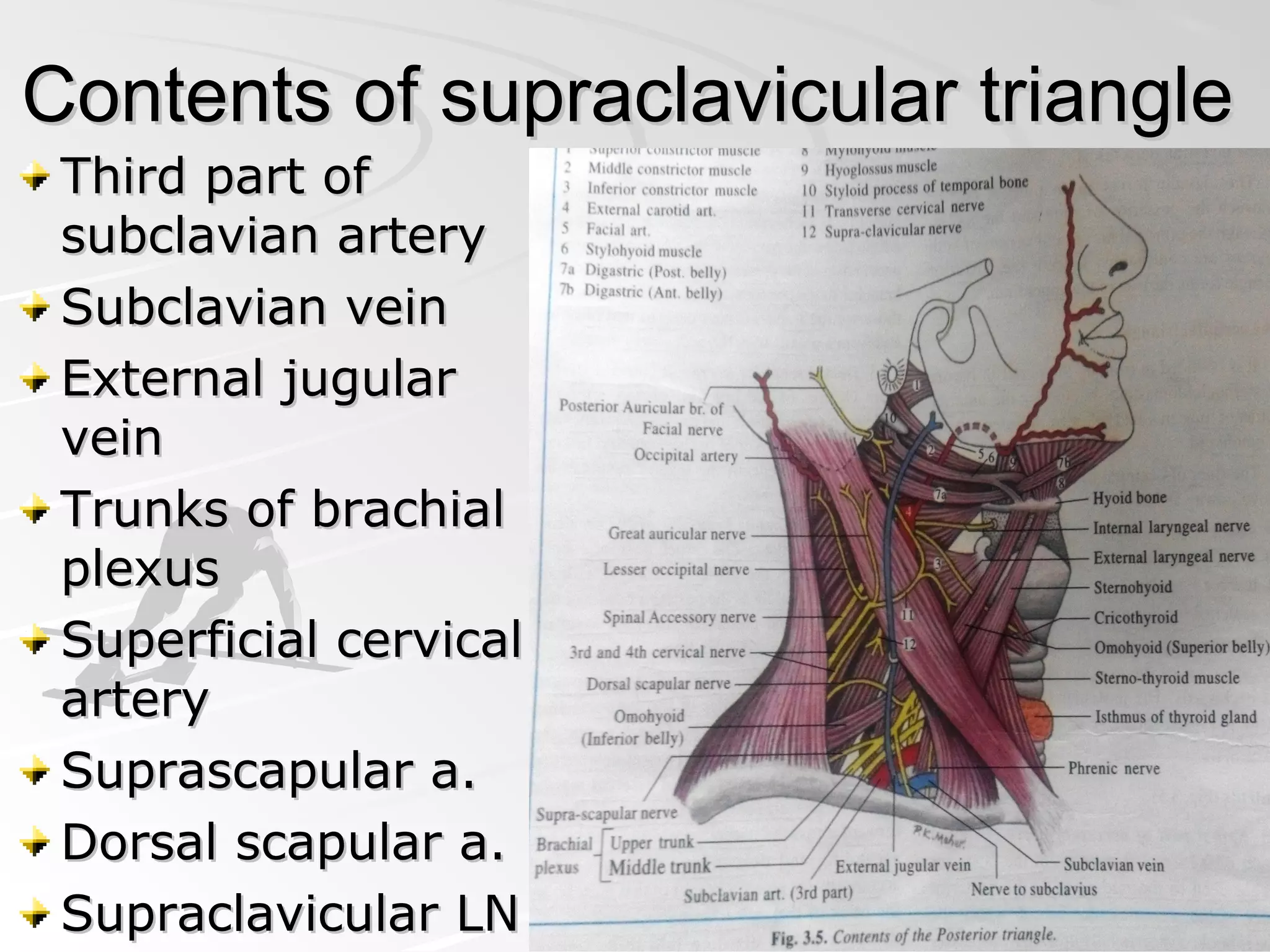
The posterior triangle of the neck is bounded anteriorly by the sternocleidomastoid muscle, posteriorly by the anterior border of the trapezius muscle, and inferiorly by the middle third of the clavicle. It contains the spinal part of the accessory nerve, branches of the cervical plexus, the external jugular vein, and the brachial plexus. The triangle is divided into an occipital triangle superiorly and a supraclavicular triangle inferiorly by the inferior belly of the omohyoid muscle.