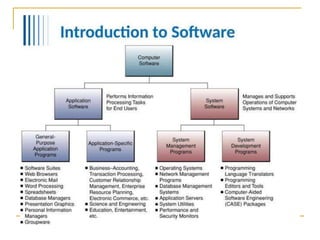
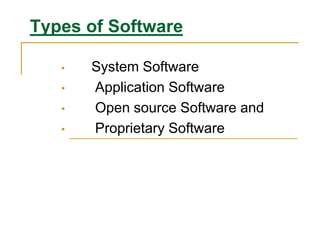
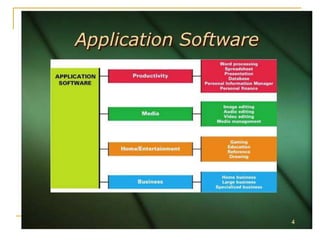
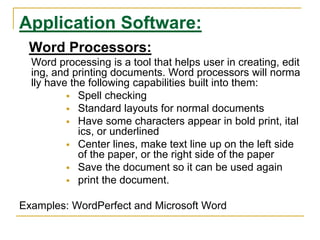
This document discusses an introduction to application software. It defines software and hardware, and describes the main types of software: system software, application software, open source software, and proprietary software. Examples are provided for each type, including operating systems, word processors, spreadsheets, and databases. Key aspects of application software like word processors, presentations, and database management systems are explained.