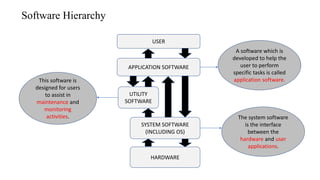
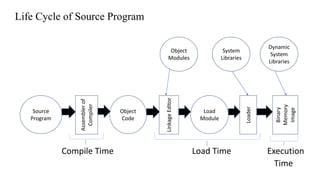
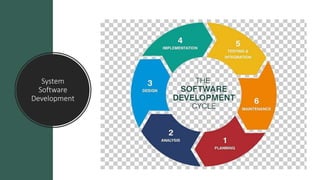
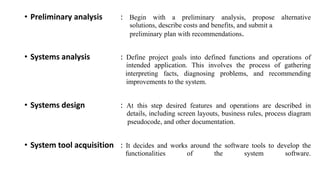
The document outlines the system software life cycle, detailing stages from preliminary analysis to maintenance, emphasizing the role of system software in bridging hardware and user applications. It describes the software hierarchy, including application software and system software, alongside recent trends in software development such as frameworks and mobile applications. Key aspects of system programming and execution phases are also highlighted, outlining the technical processes involved in effective software development and implementation.