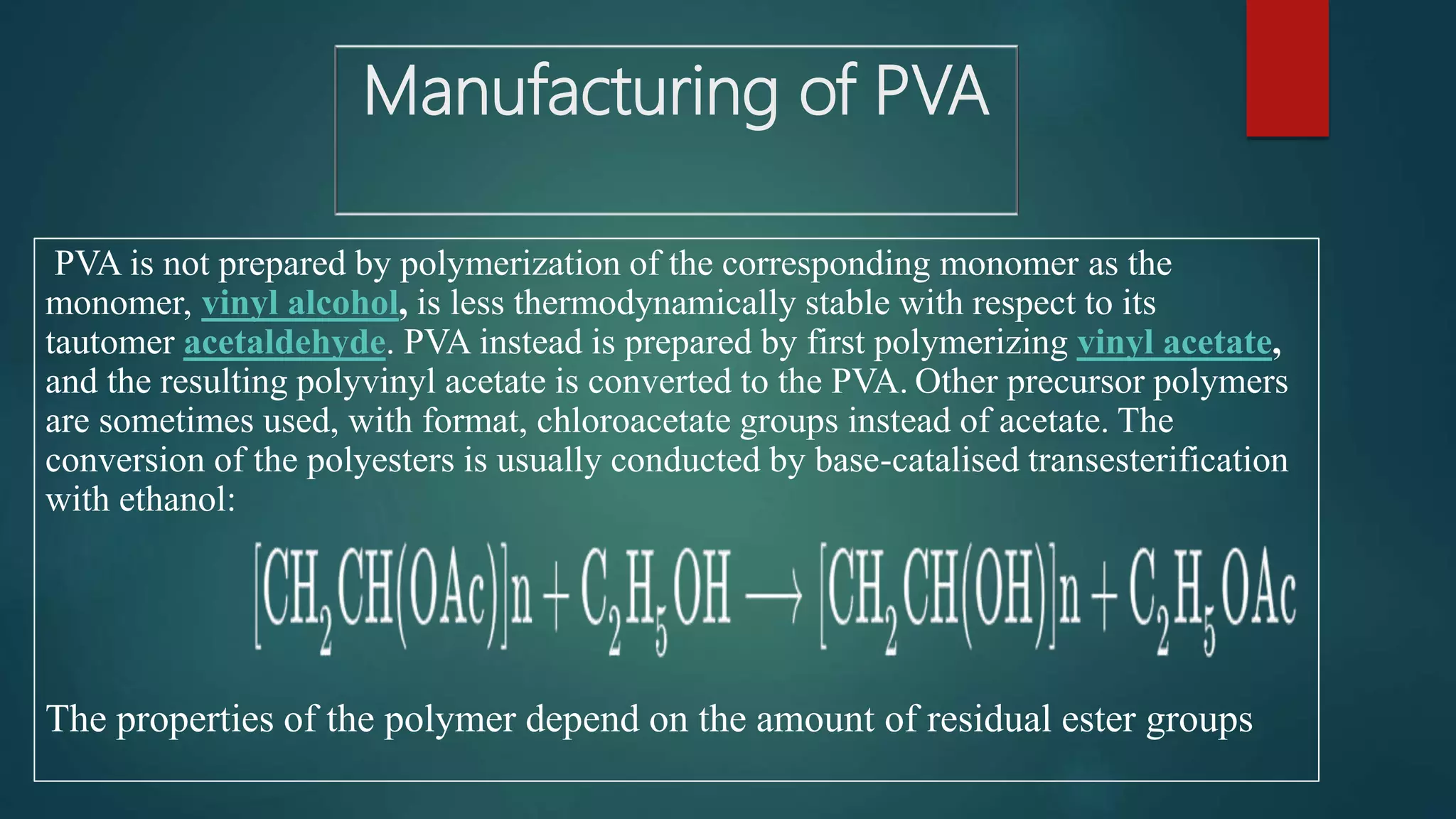
The document presents a presentation about Captain Mohiuddin Jahangir, a significant figure in the 1971 Bangladesh Liberation War, highlighting his bravery and the honor he received posthumously. Additionally, it discusses Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA), detailing its properties, manufacturing process, and various applications across medical and industrial fields. PVA is recognized for its versatility and effectiveness as a polymer in different contexts, including adhesives and textile reinforcement.