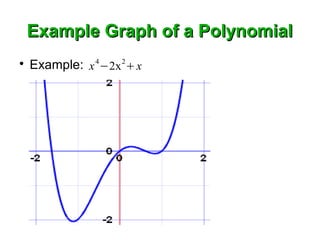
Polynomials are algebraic expressions made up of terms that are added, subtracted, or multiplied, where each term involves variables raised to non-negative integer powers. Polynomials can be composed of constants, single variables, or multiple variables with positive exponents, and adding or multiplying polynomials results in another polynomial. Standard form for polynomials lists terms in descending order of variable exponents from highest to lowest.





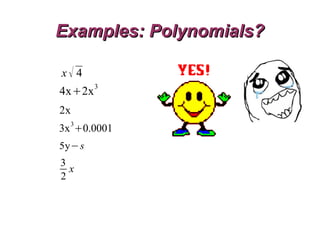
![POLYNOMIALS?
2
1. √ x 2. 23x
[ x−1]
2 −1
3. 23x 4. y
√x 2
5. −1
( )
2
z](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/poly-120922190751-phpapp01/85/Polynomials-8-320.jpg)




