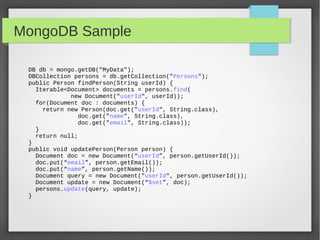
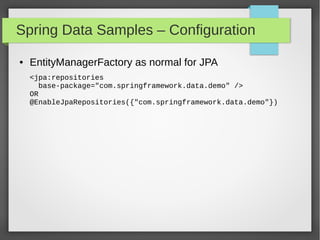
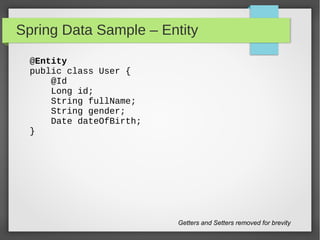
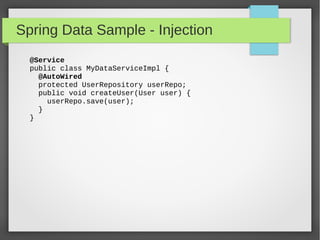
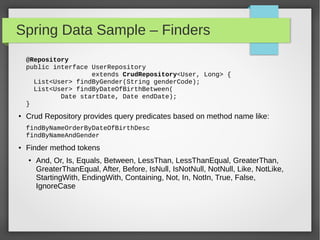
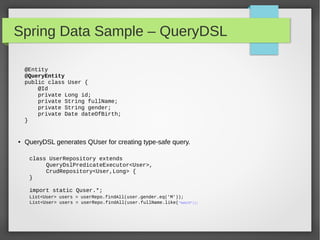
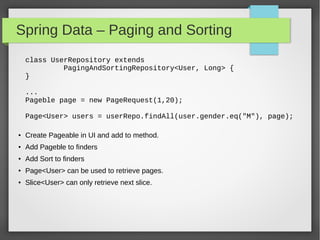
This document discusses polyglot persistence using Spring Data. It describes how Spring Data provides a common programming model for data access across different data stores like SQL databases, NoSQL databases and more. It provides examples of defining entities, repository interfaces and queries using Spring Data's JPA, MongoDB and QueryDSL modules. Spring Data aims to improve developer productivity by simplifying data access code and enabling applications to use multiple data sources.