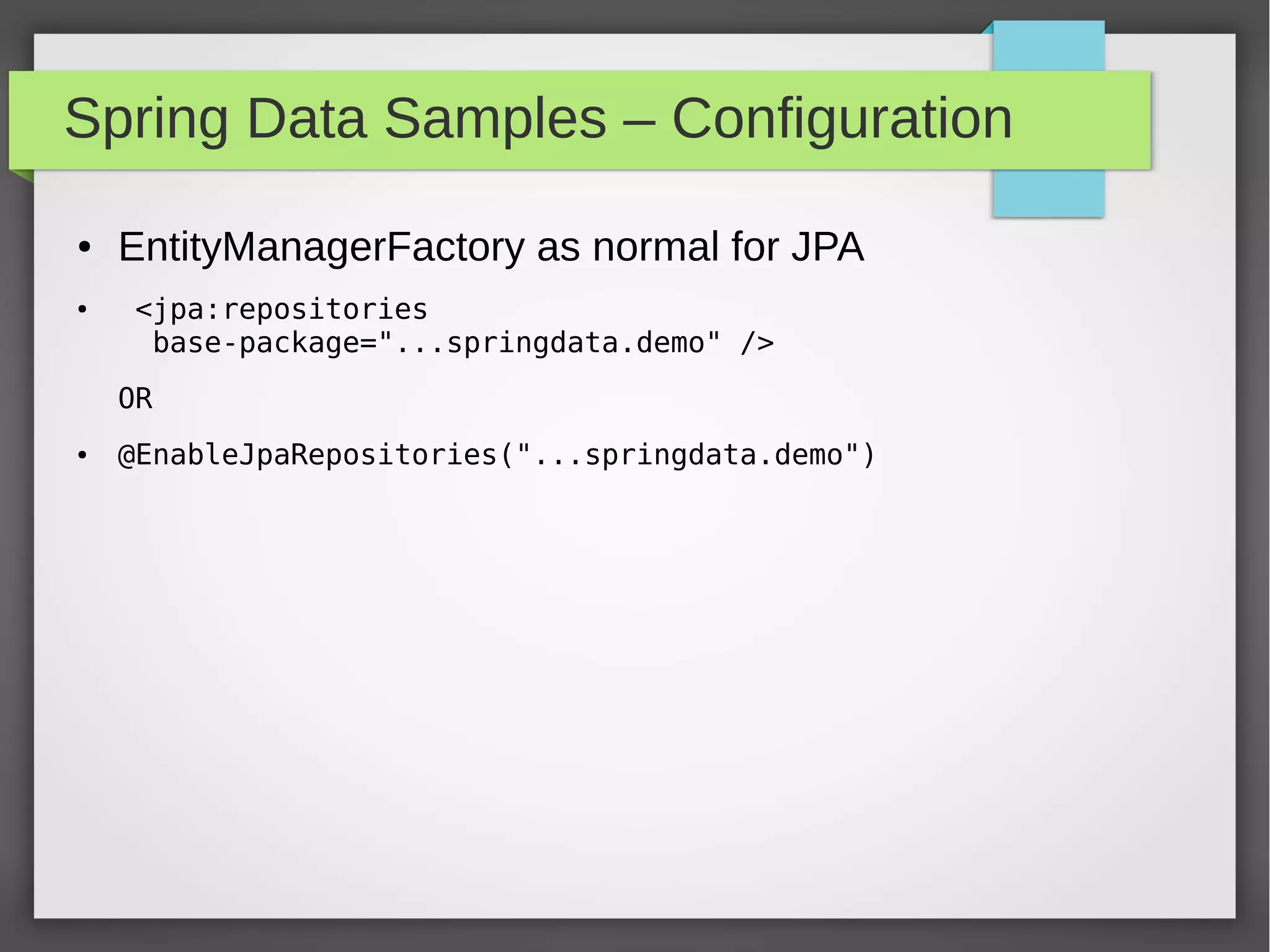
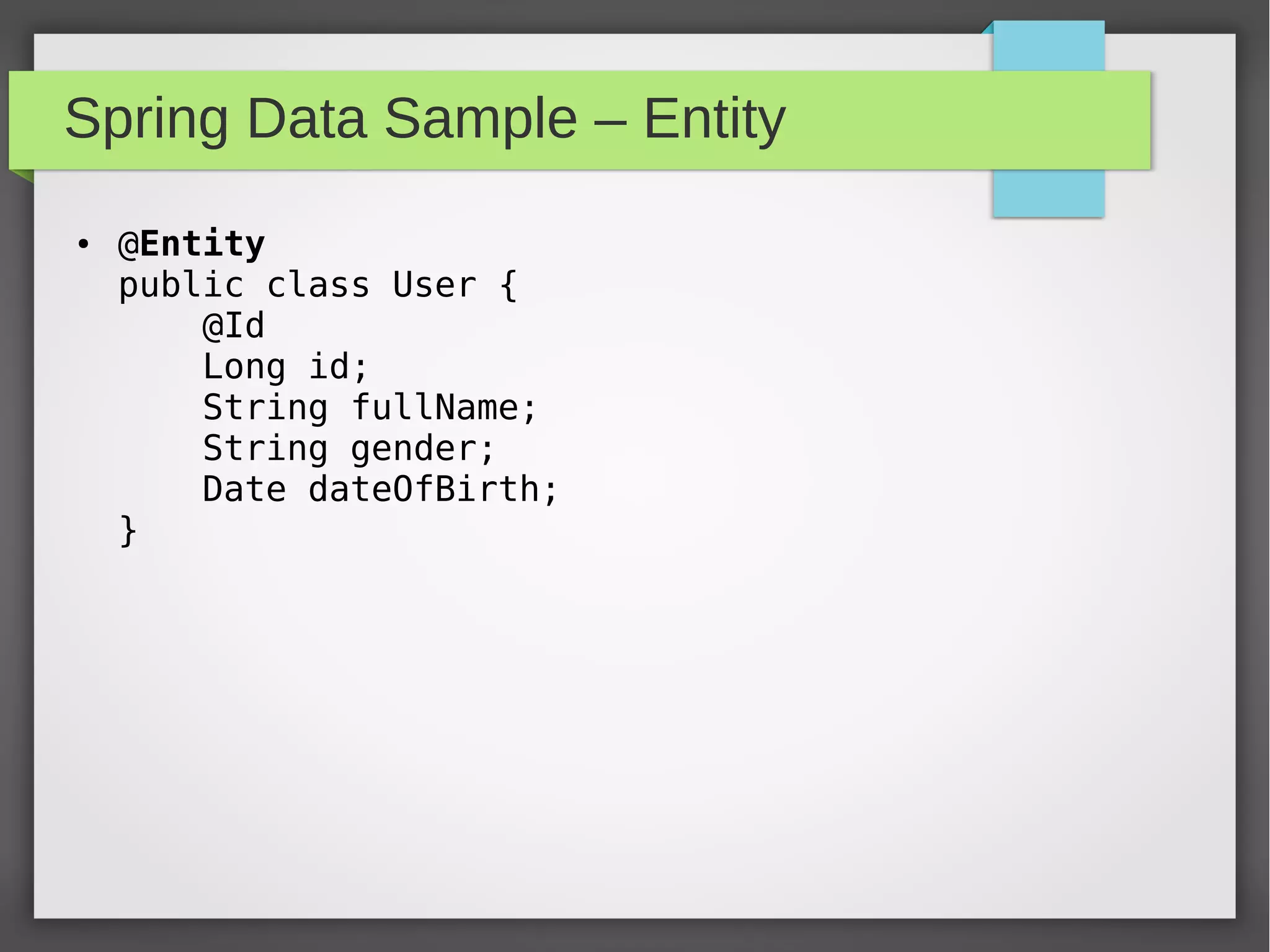
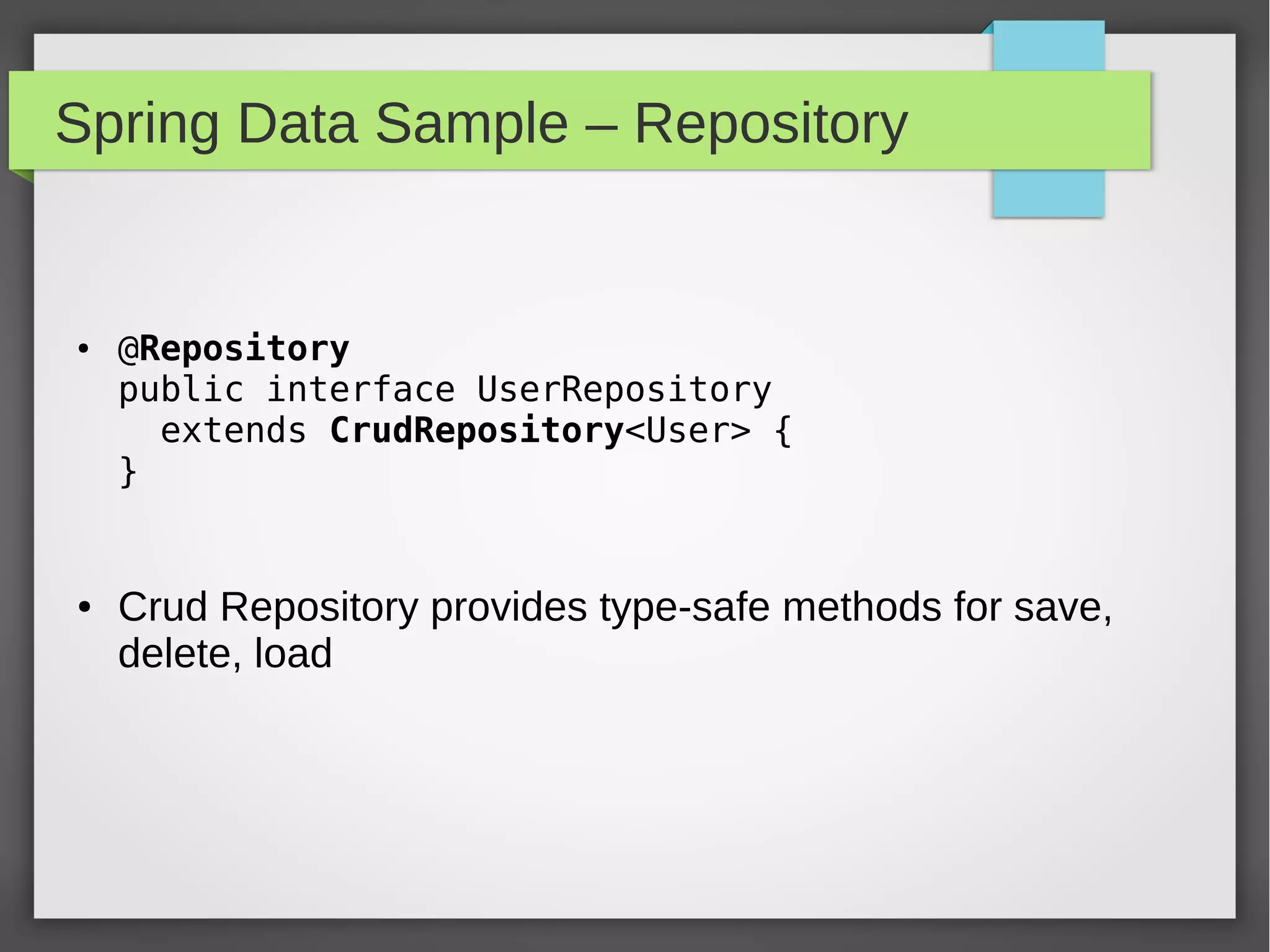
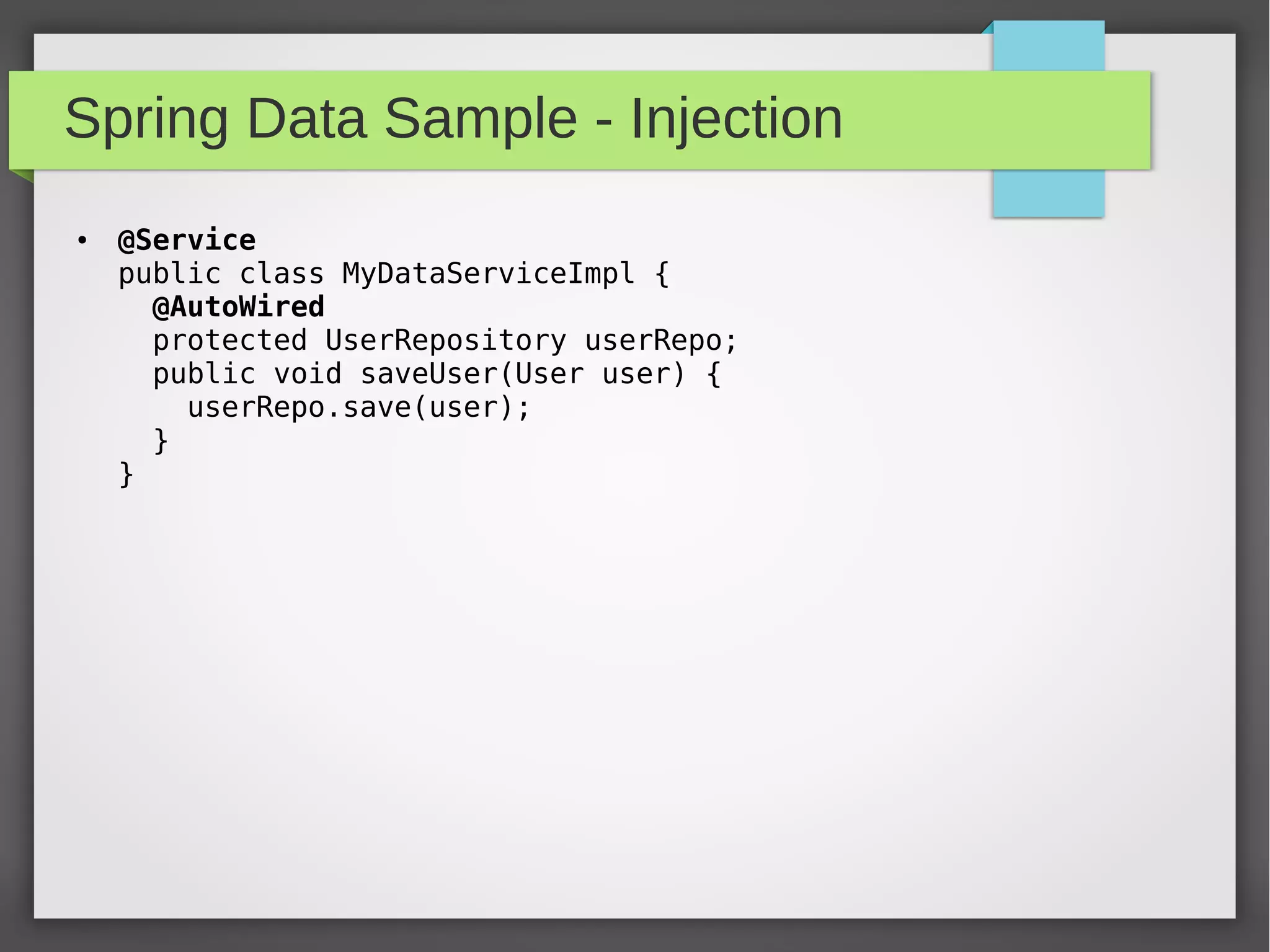
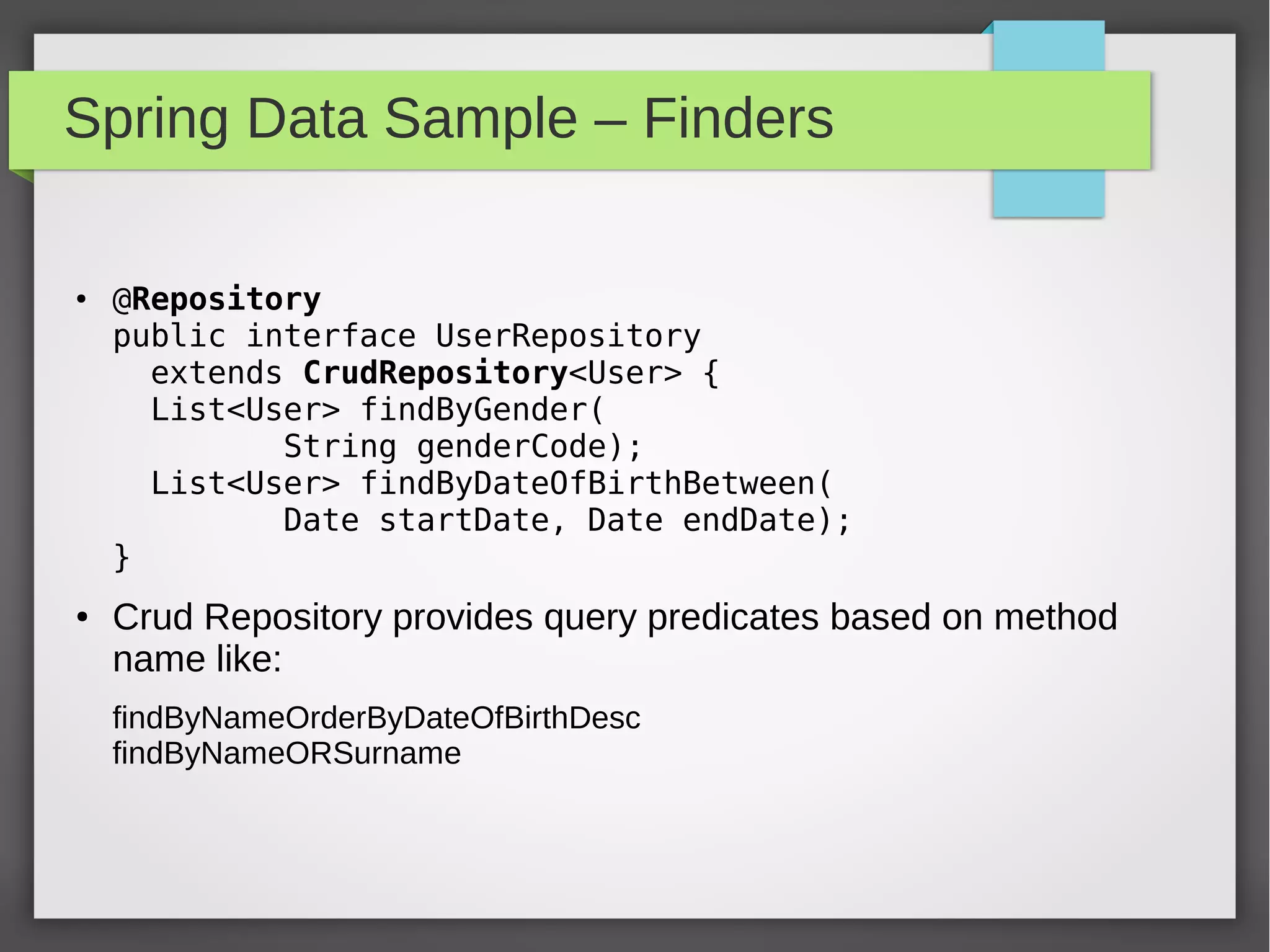
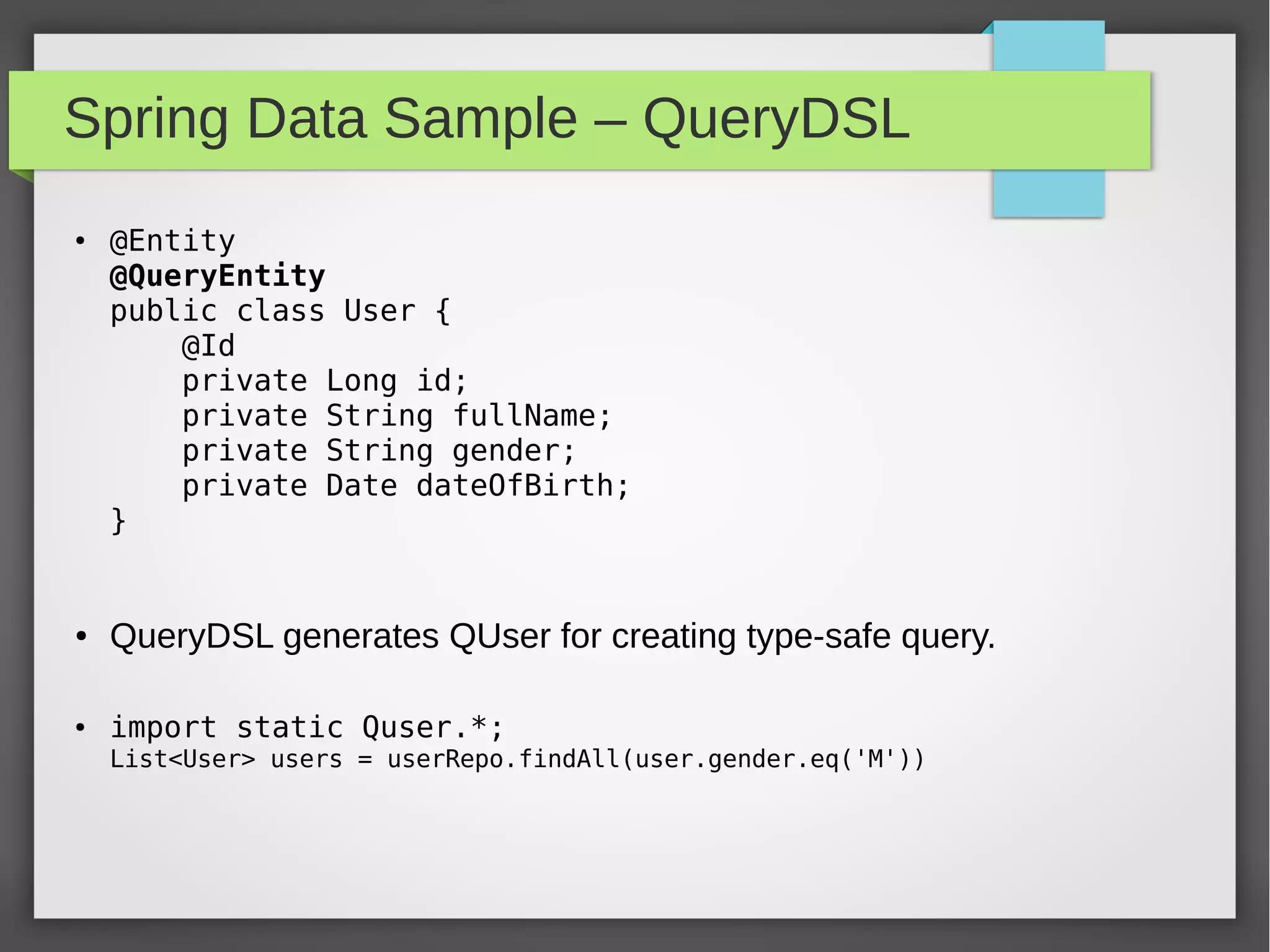
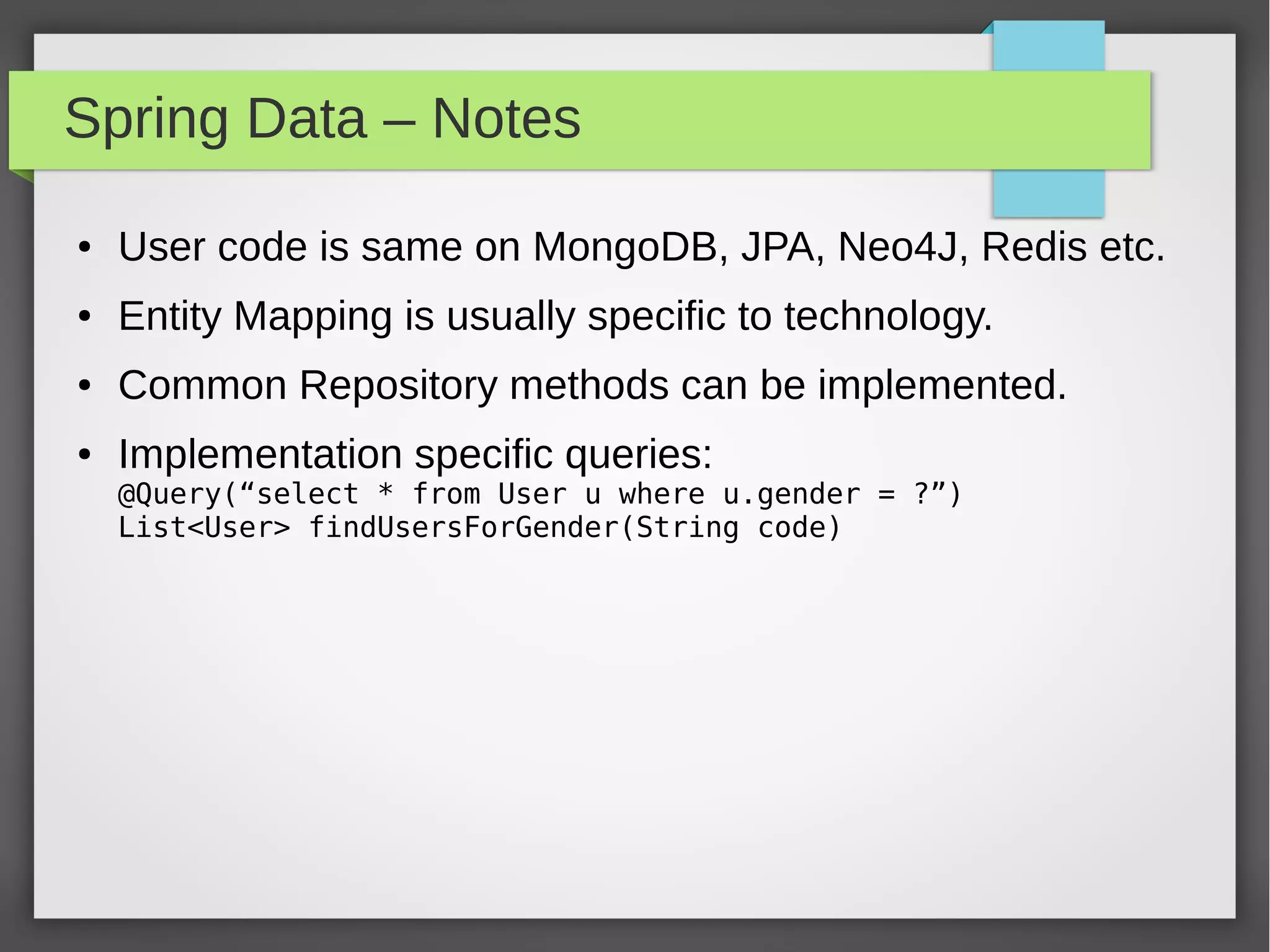
Spring Data provides a common data access layer for various data stores like MongoDB, JPA, Neo4J, and Redis. It simplifies polyglot persistence through repositories that provide common CRUD methods. Developers define entities specific to the data store and a repository interface with finder methods. Spring Data generates an implementation that interacts with the underlying data store transparently. This allows writing data access code that is portable across data sources.