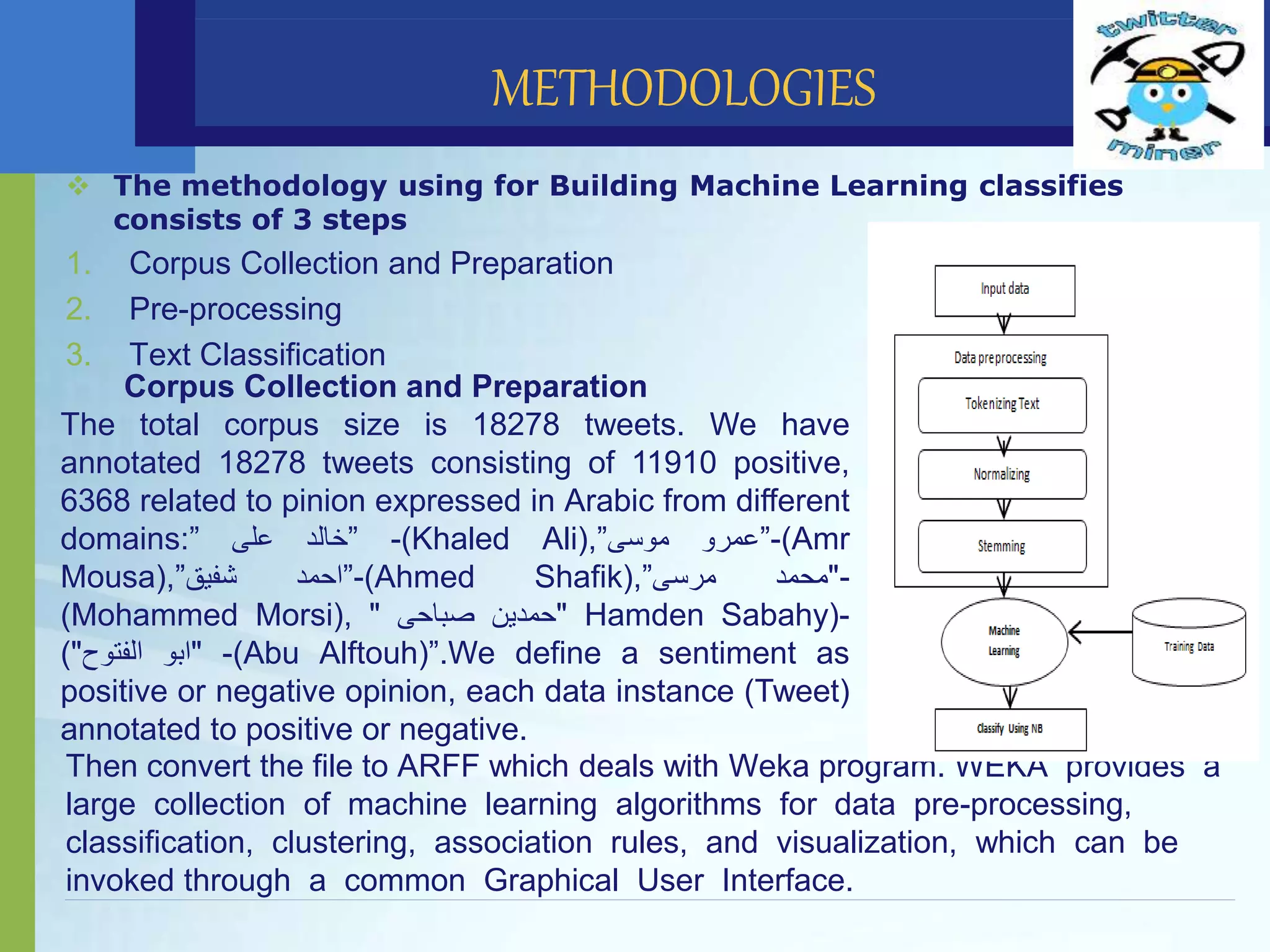
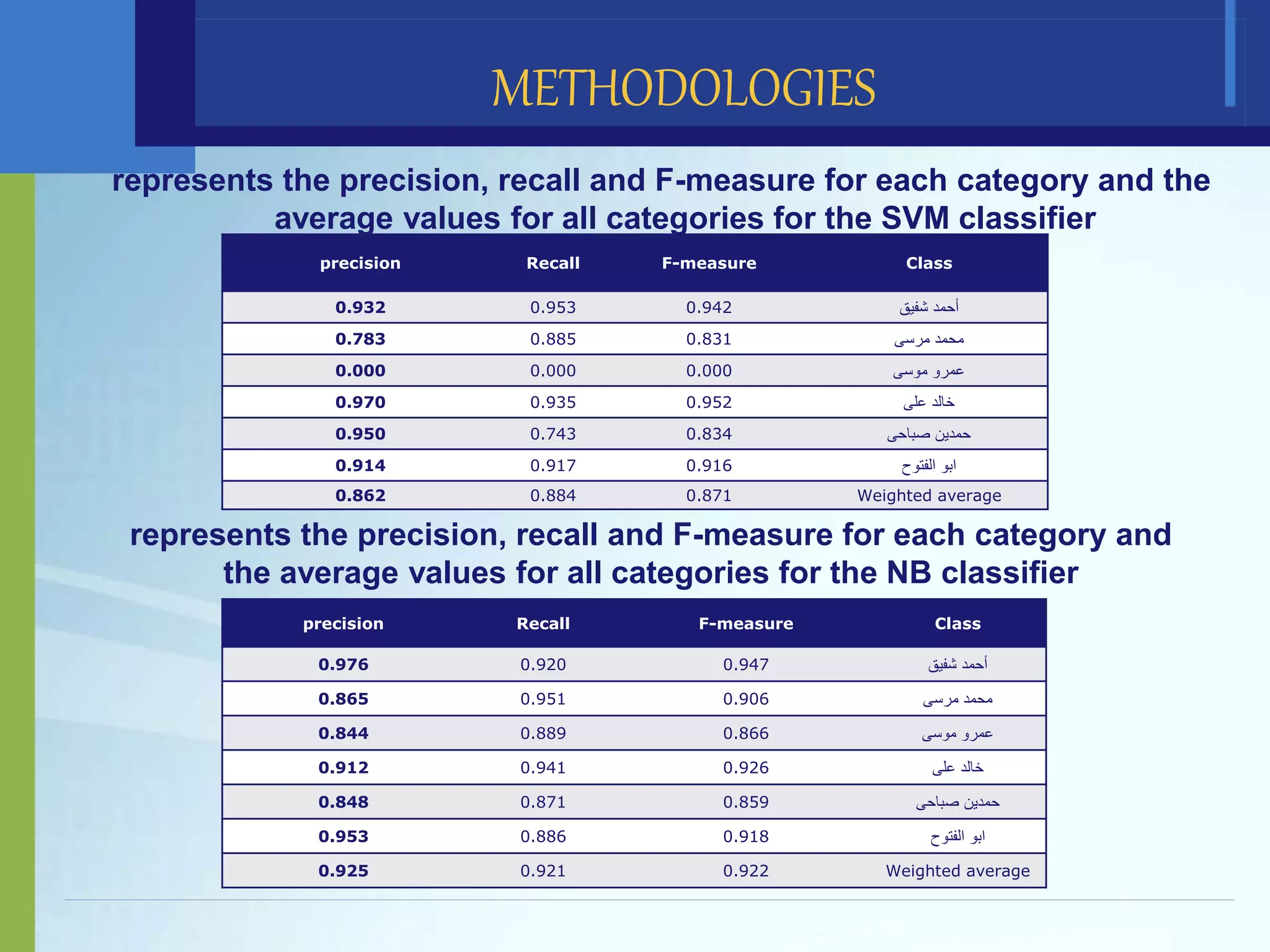
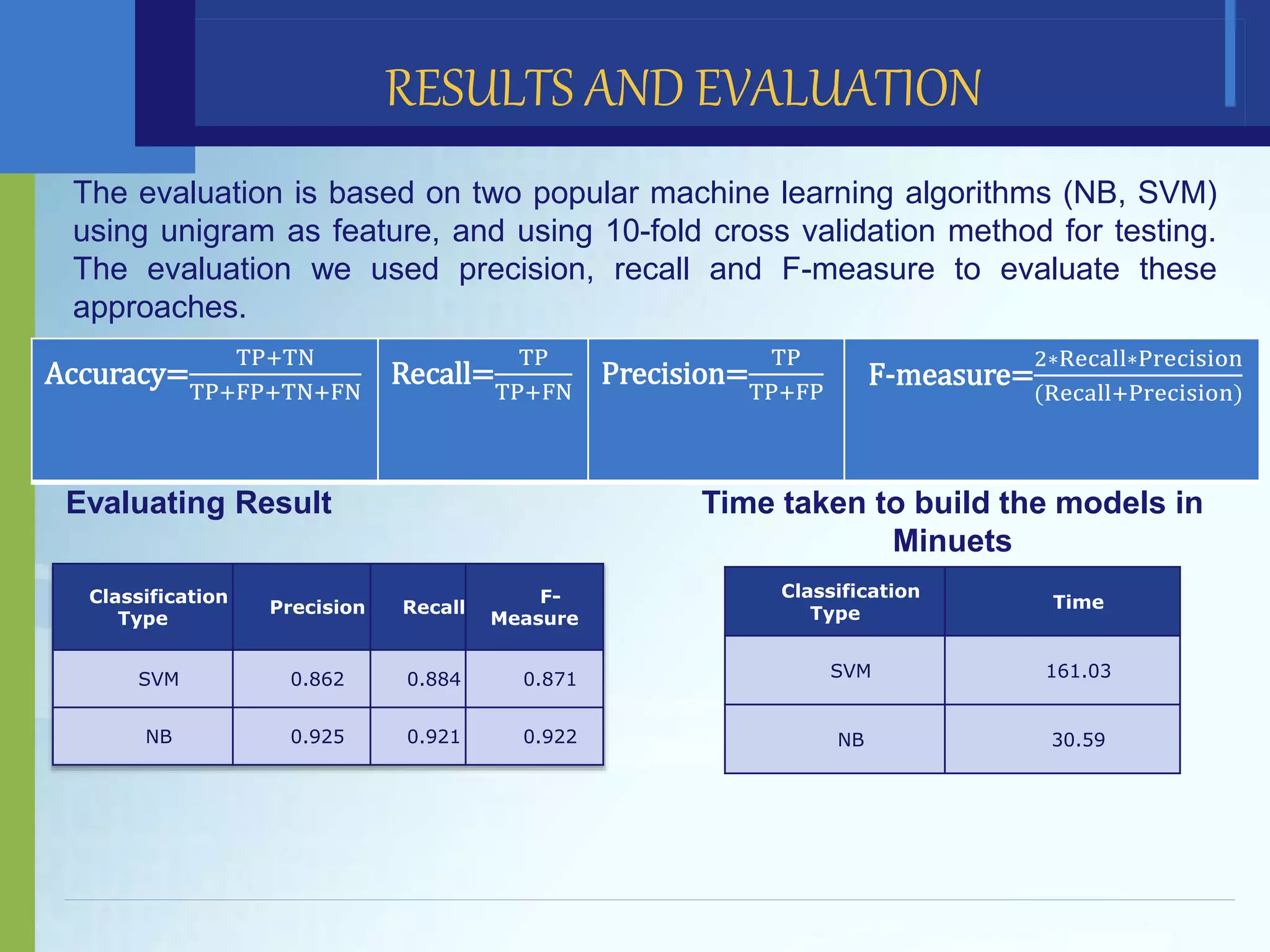
This document discusses political sentiment analysis on Twitter data from Egypt's 2012 presidential election. It presents the methodology used, which involved collecting tweets, preprocessing the text, and classifying the sentiment using support vector machines and Naive Bayes algorithms. The SVM approach achieved a weighted average F-measure of 0.871 while Naive Bayes achieved 0.922. Naive Bayes also was faster, taking 30.59 minutes to build models versus 161.03 minutes for SVM. The study concludes Naive Bayes is an accurate and fast technique for this application, and future work could involve comparing these results to other classifiers and using different preprocessing techniques.