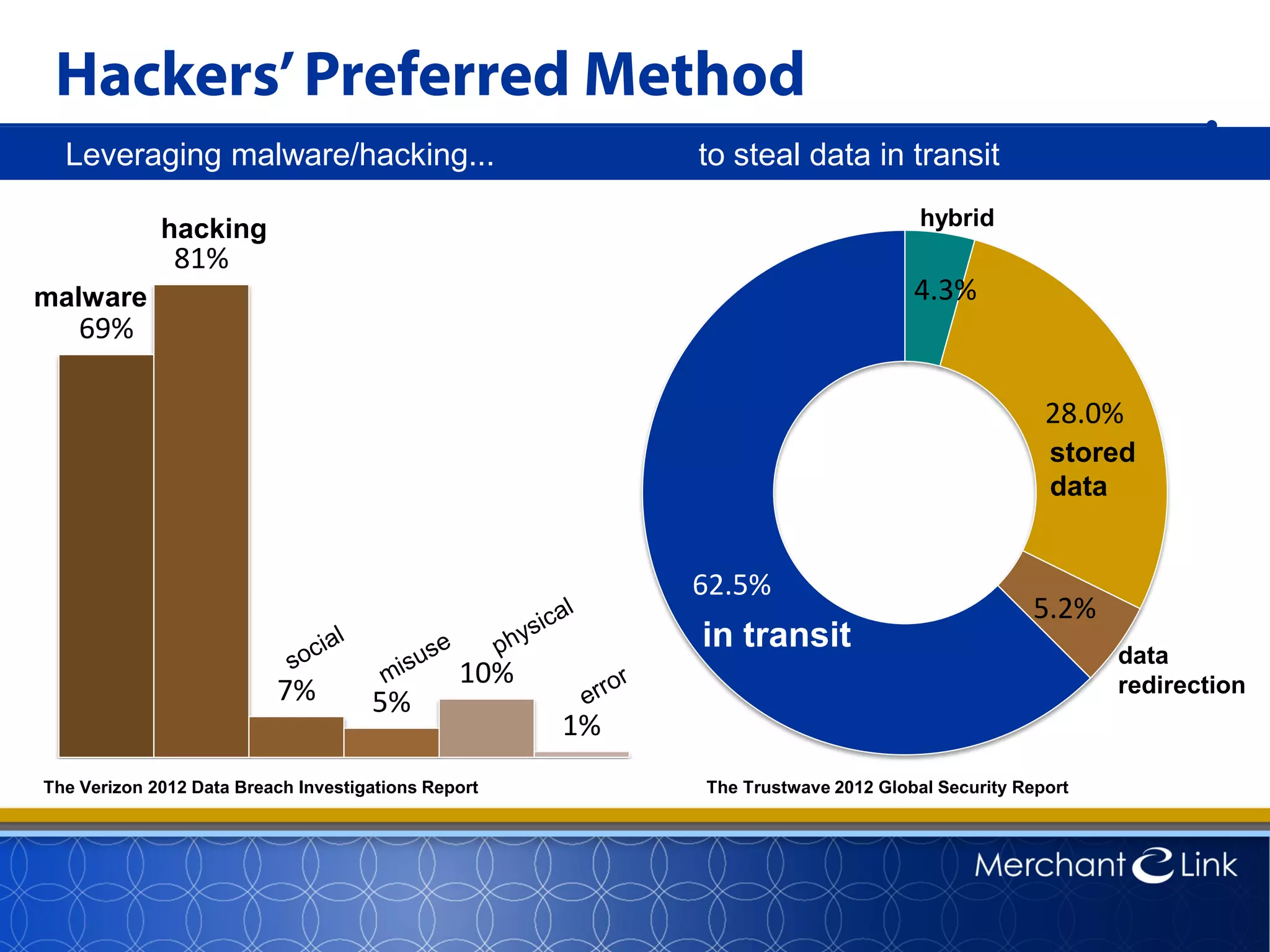
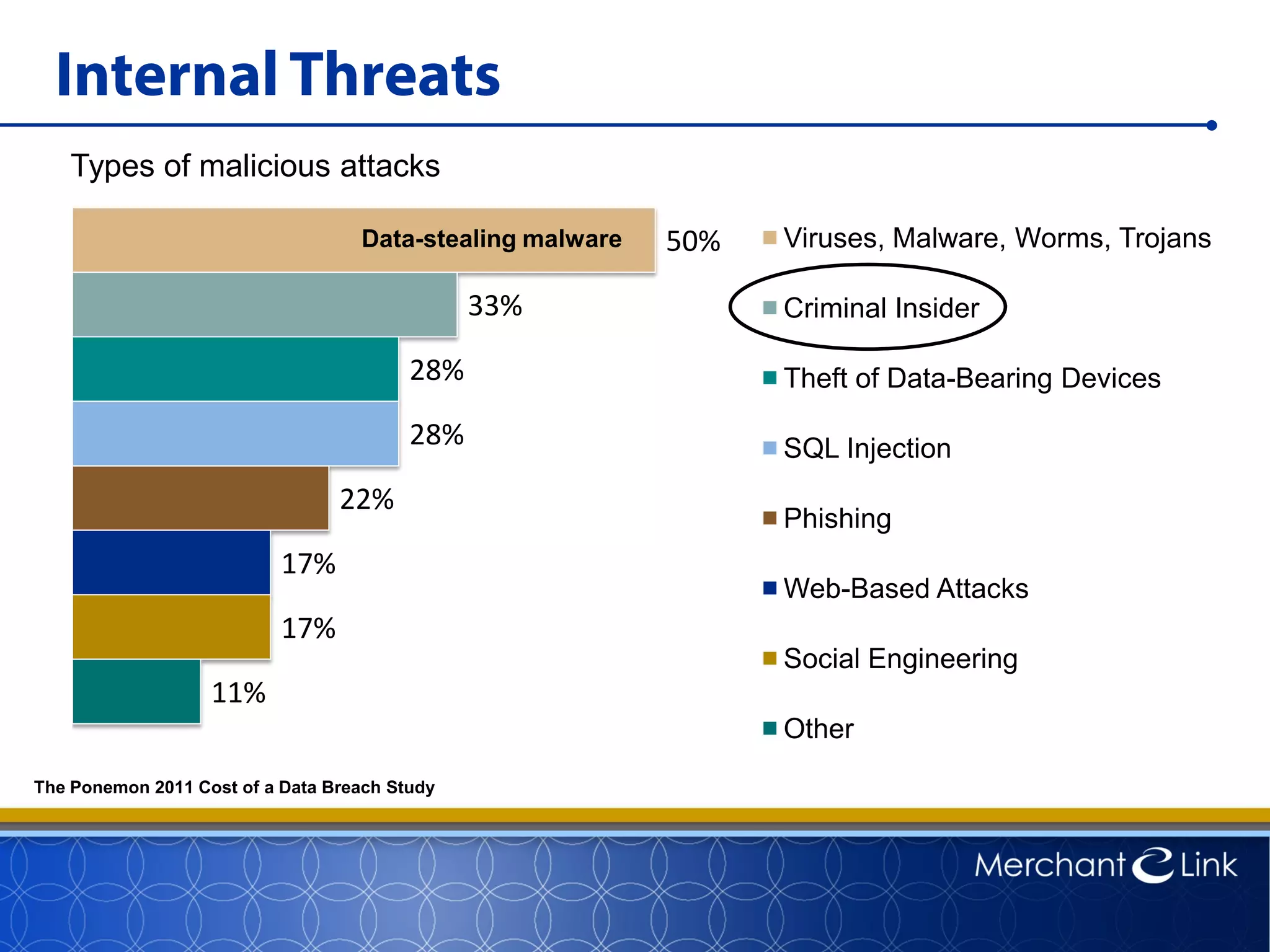
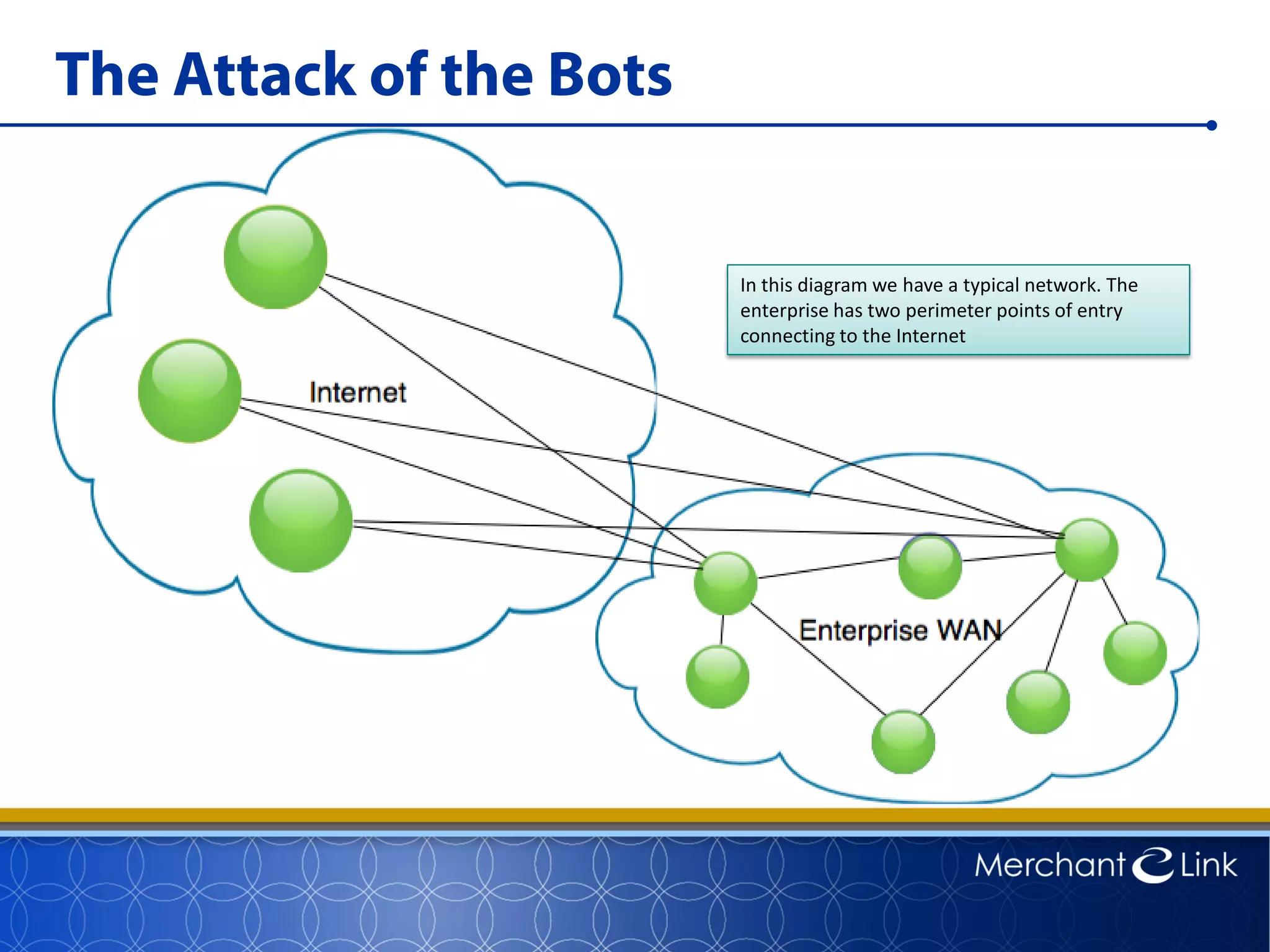
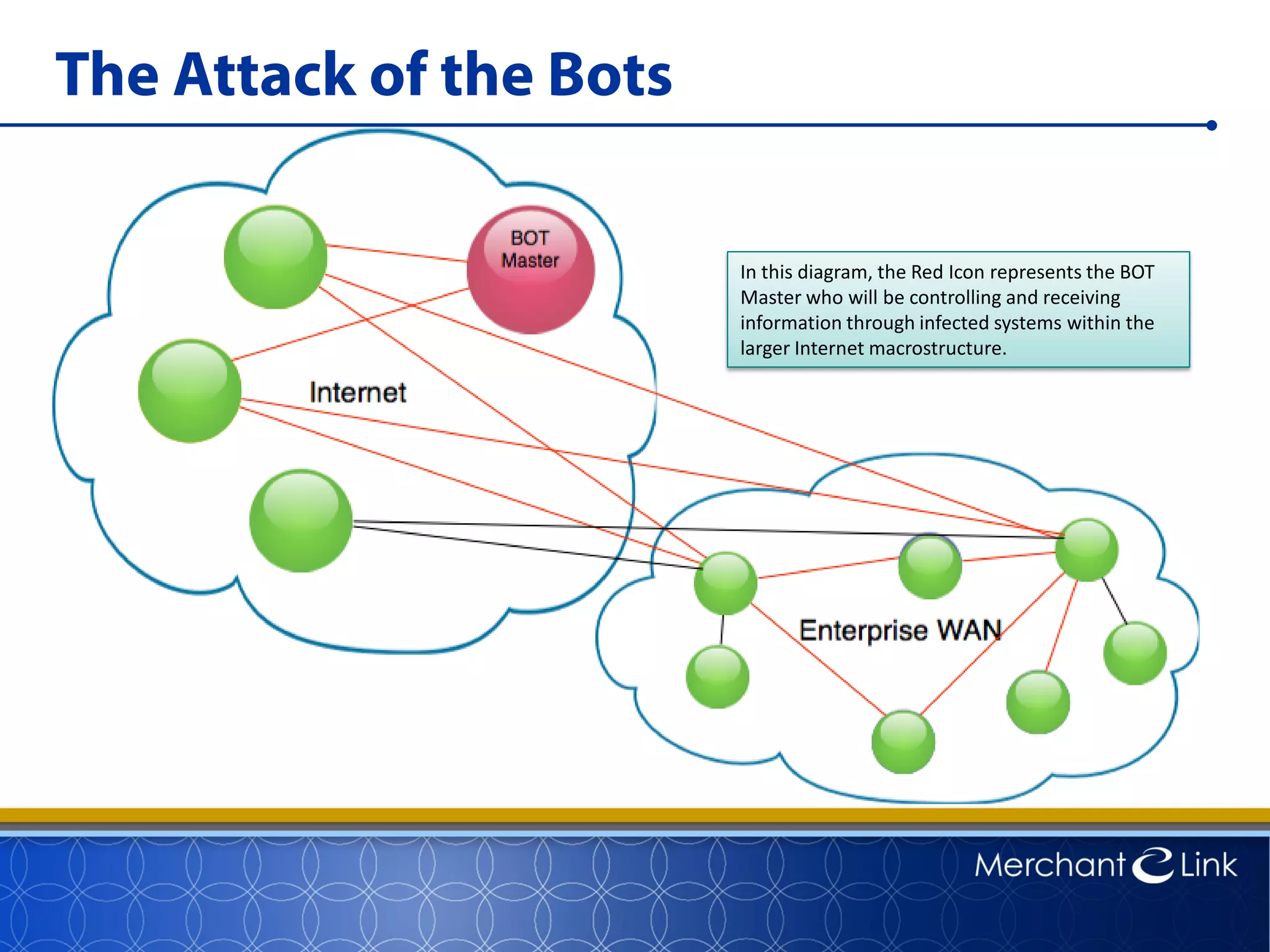
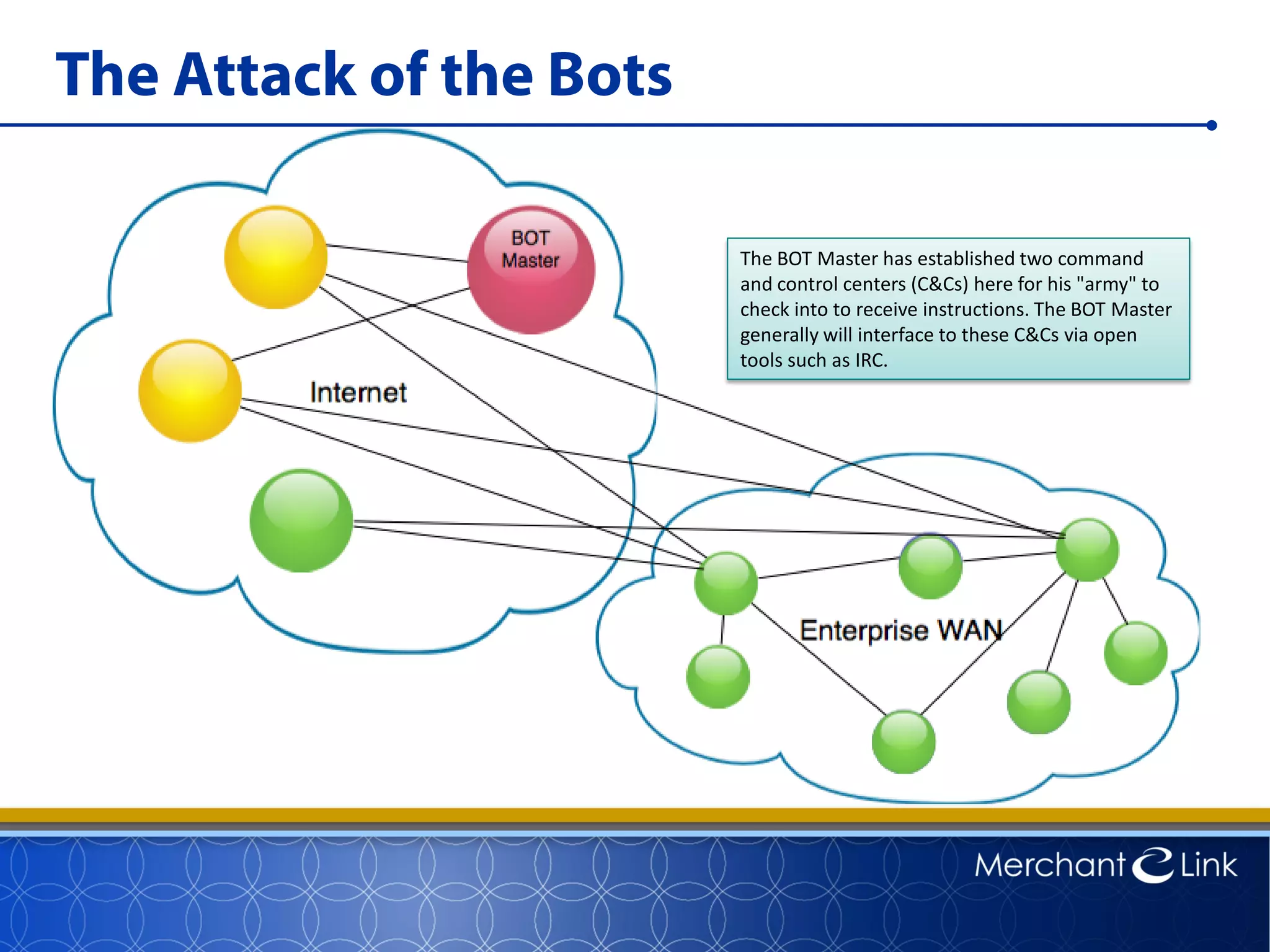
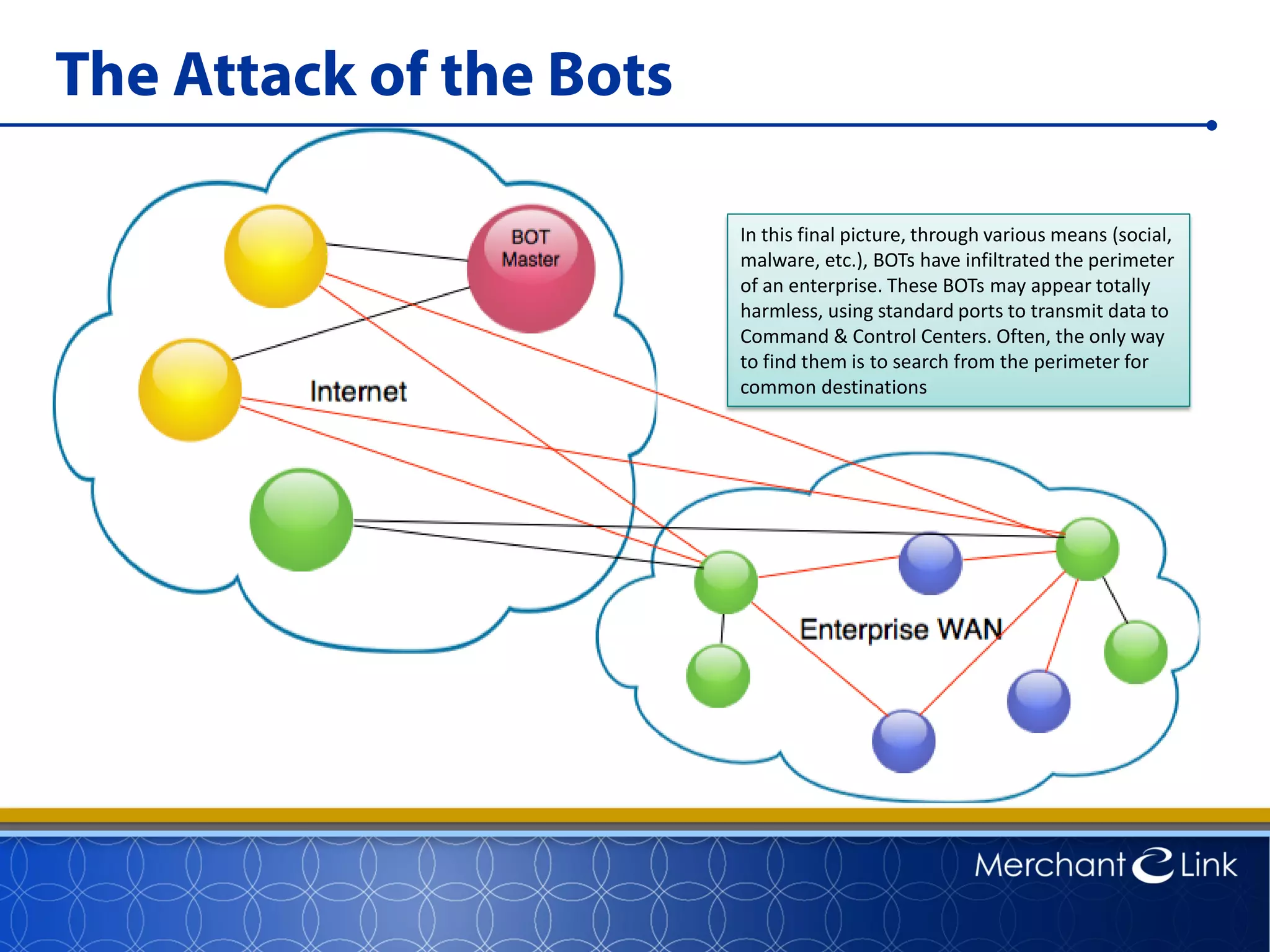
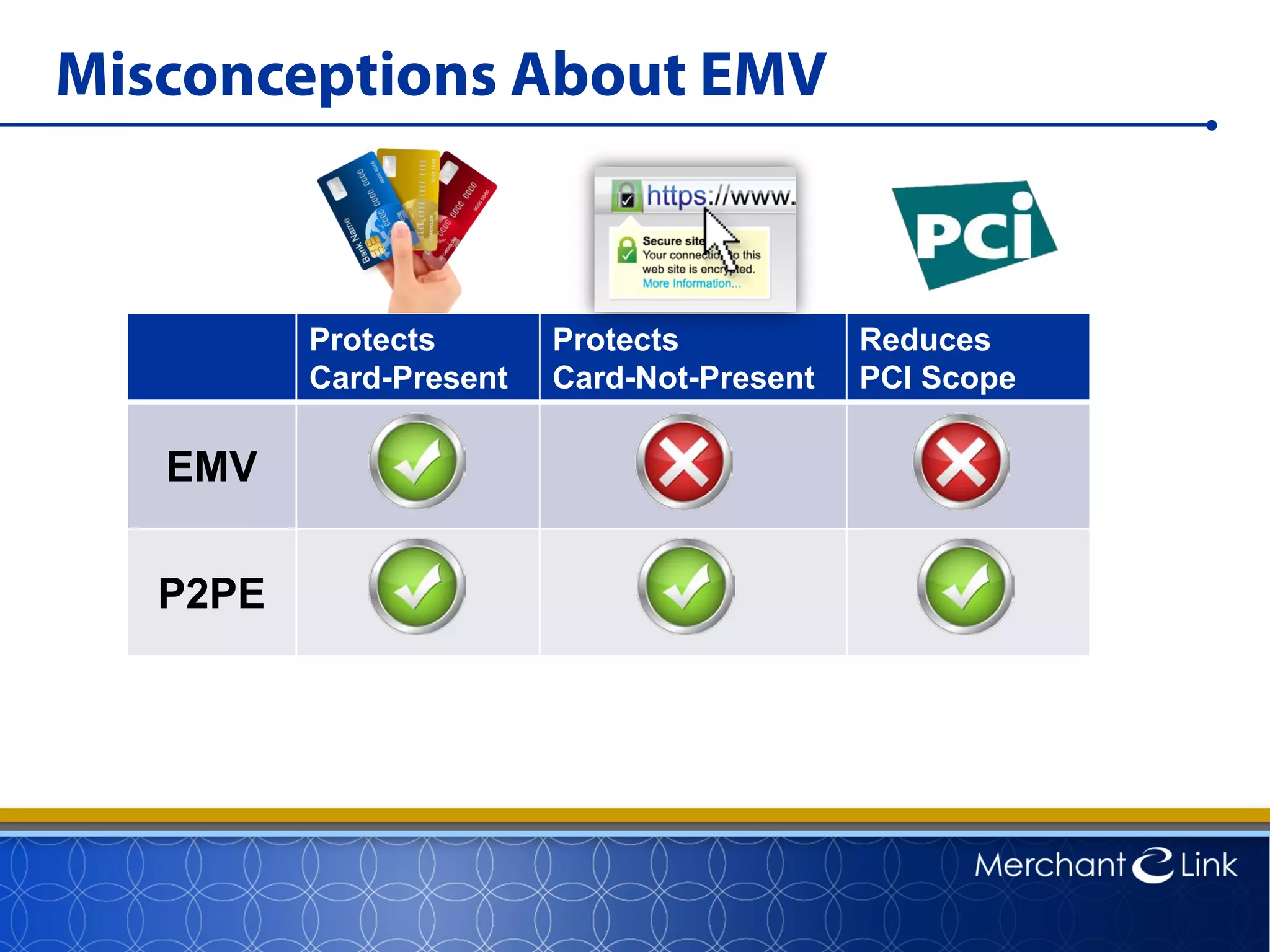
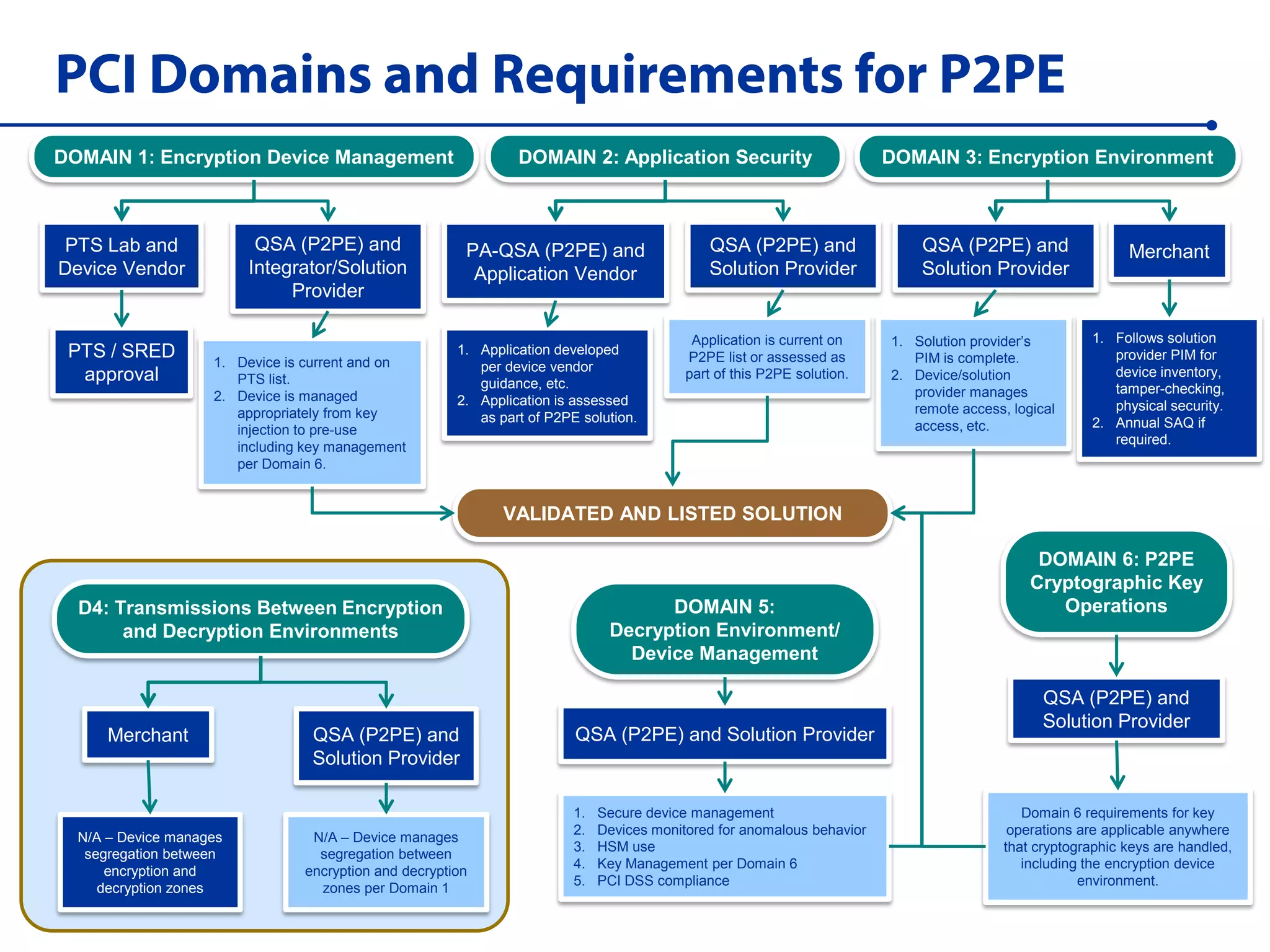
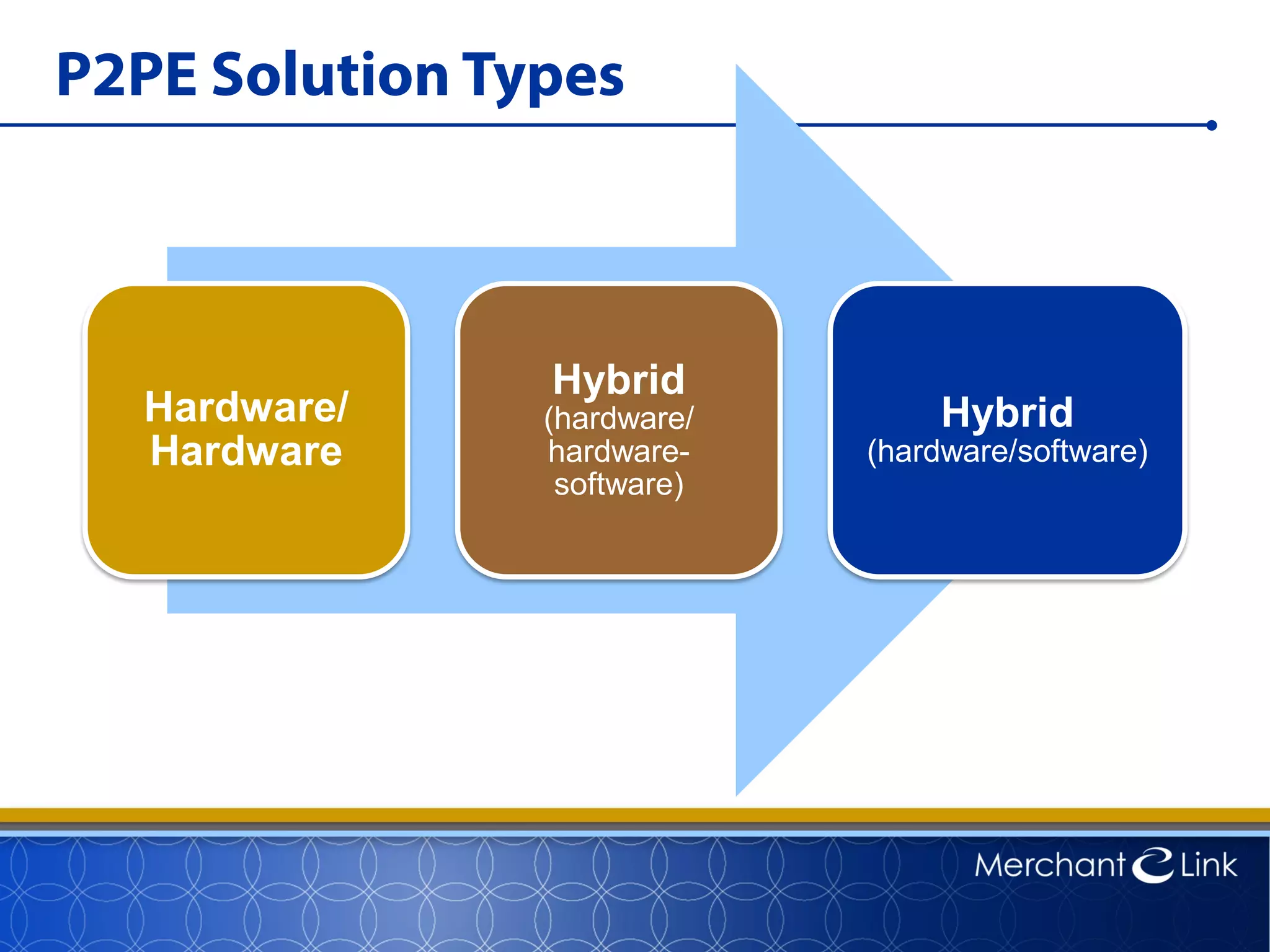
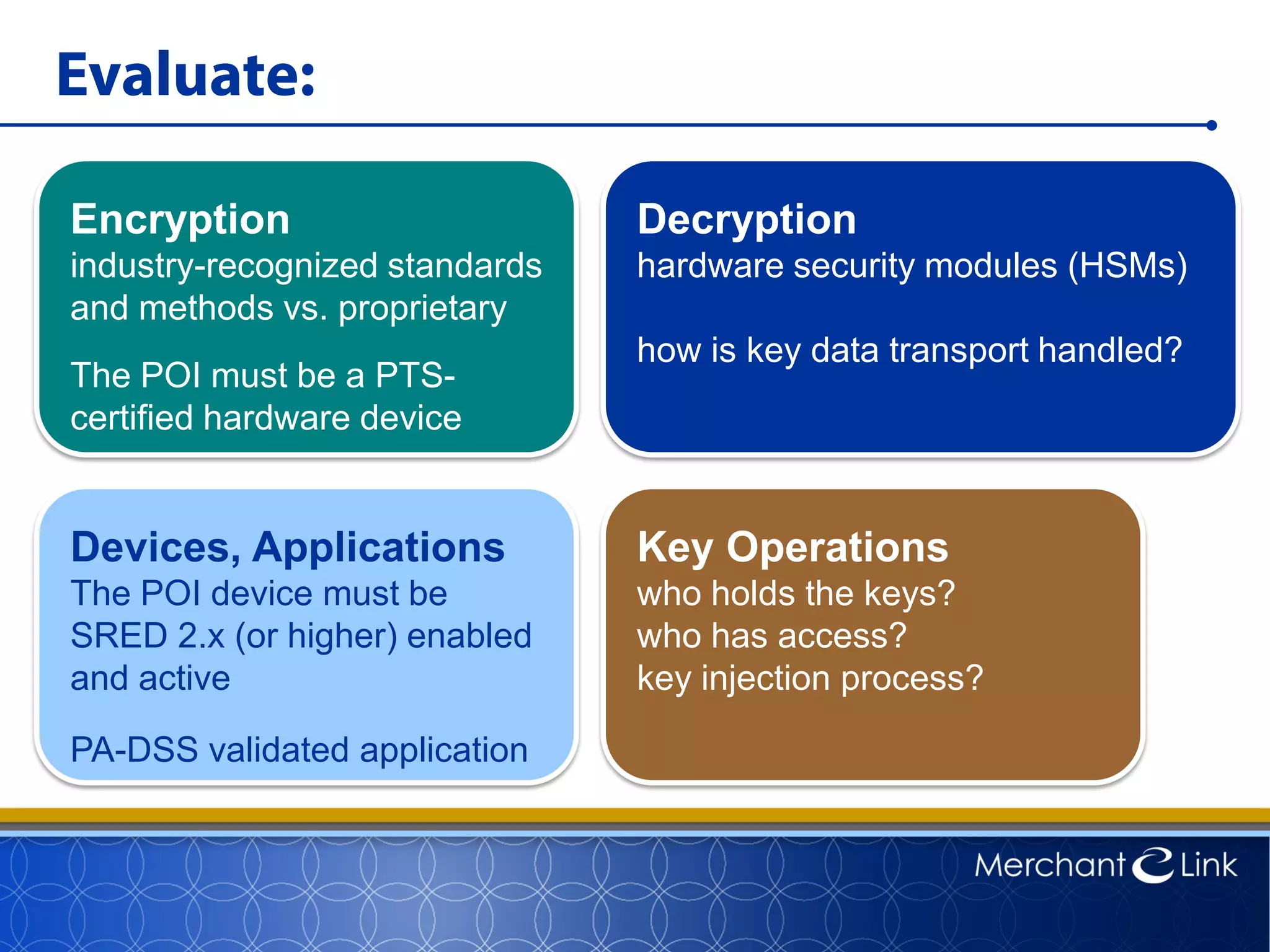
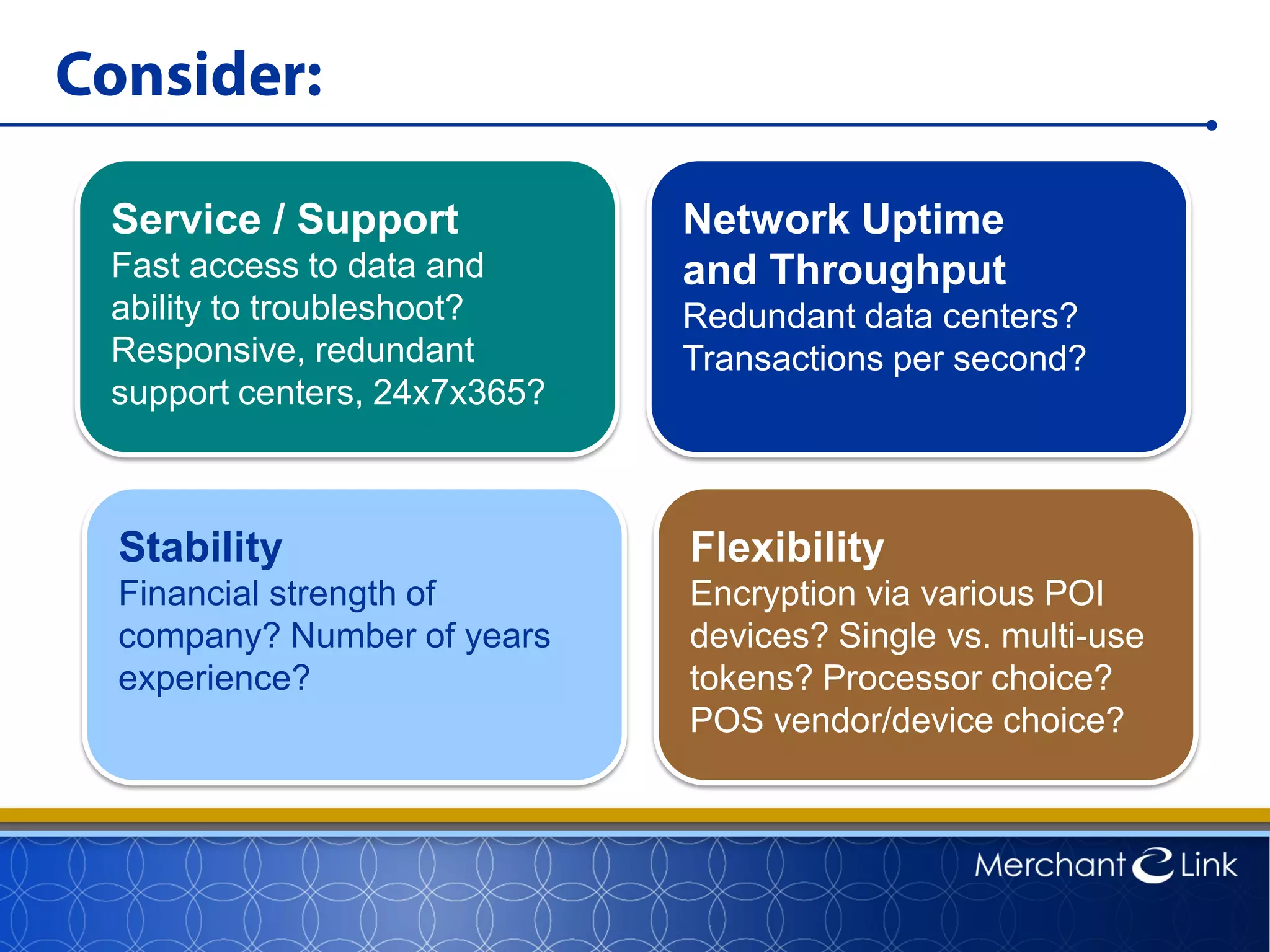
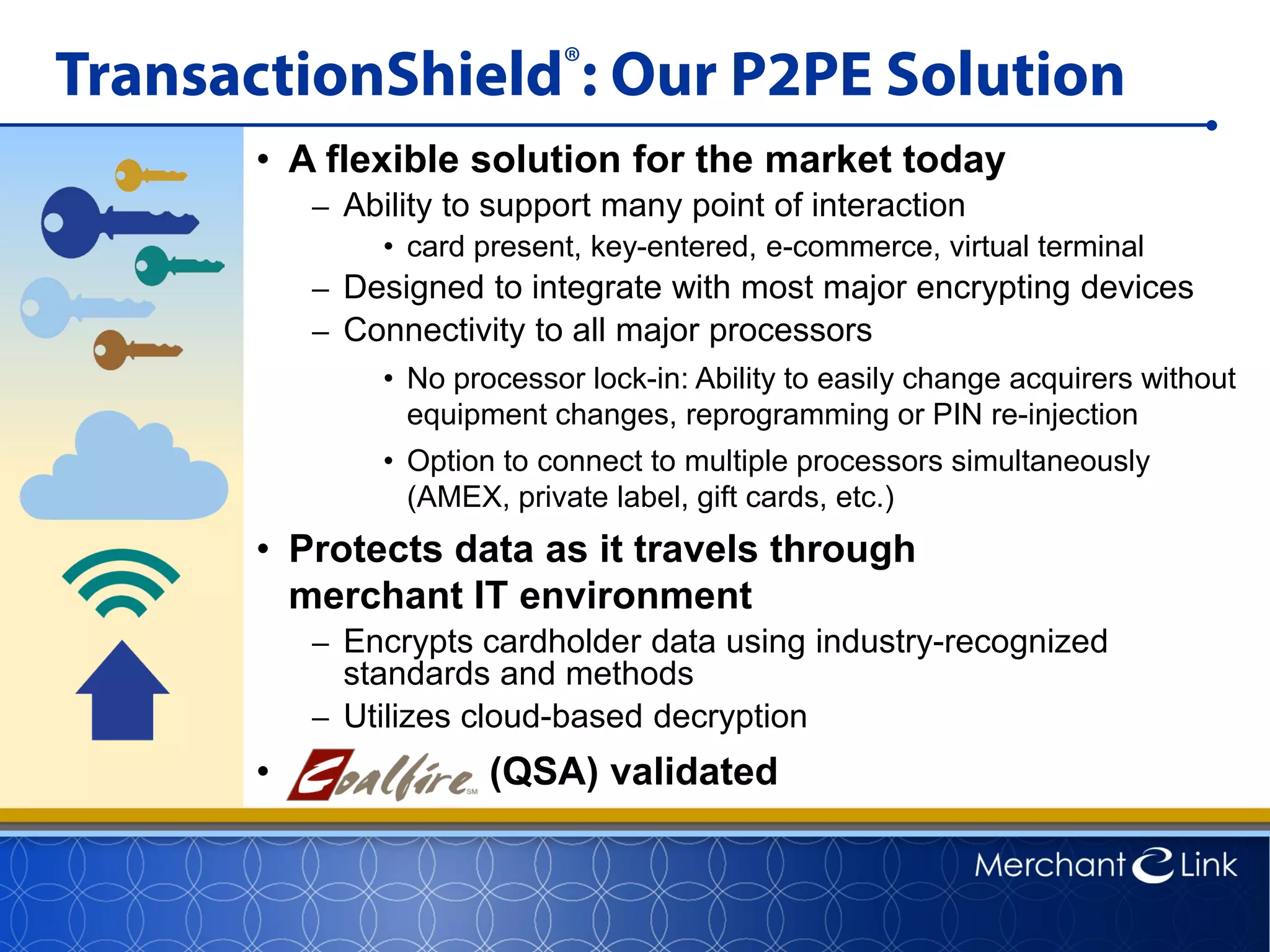
This document summarizes a live webinar about point-to-point encryption best practices and PCI compliance updates. The webinar covered current security threats to payment card data, industry responses like EMV and PCI P2PE requirements, and examples of point-to-point encryption solutions and their implementation best practices. It also discussed internal threats, botnet attacks, combating threats with PCI and EMV standards, misconceptions about EMV, PCI domains and requirements for P2PE, types of P2PE solutions, considerations for P2PE solutions, and Merchant Link's P2PE product.