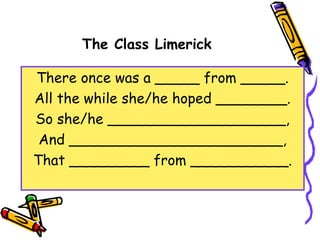
The document provides an overview of various poetry terms and techniques, such as alliteration, ballads, figurative language, and limericks. It includes definitions, examples, and descriptions of different poetic forms, emphasizing the role of rhythm and rhyme, particularly in humor and light-hearted poems. Additionally, it encourages the creation of original limericks by filling in given structures.