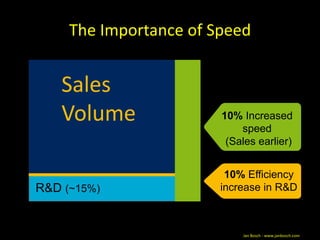
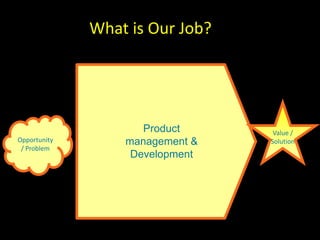
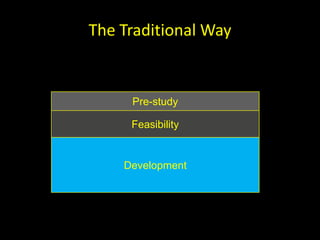
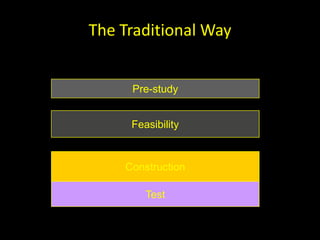
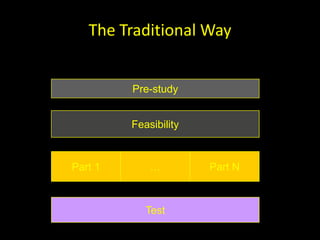
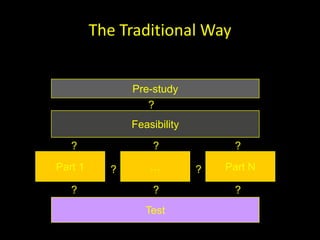
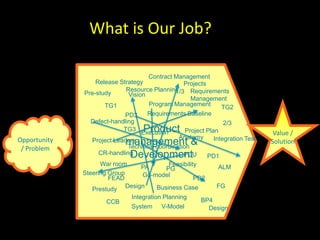
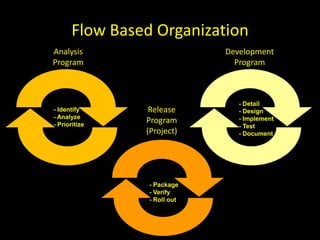
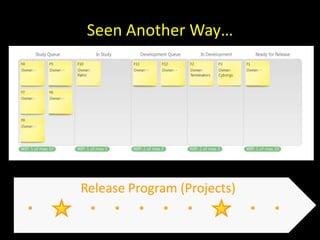
The document discusses success factors for agile development of large software products, emphasizing the importance of speed, product quality, and R&D efficiency. It highlights the need for a holistic view of product development, with self-organizing teams and continuous integration to enhance flow and reduce time to market. Challenges identified include fragmentation of work and communication issues, with a call for optimizing processes to improve overall outcomes.