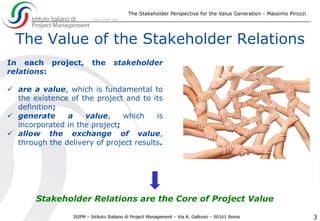
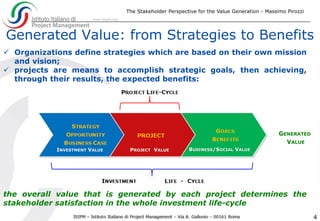
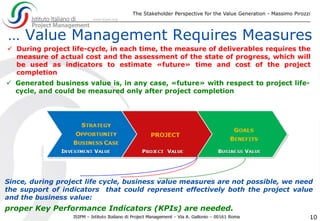
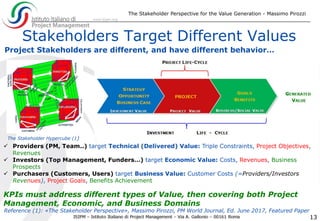
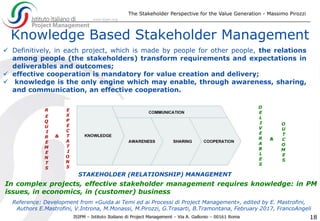
The document discusses the significance of effective stakeholder management in generating value for projects, emphasizing that stakeholders are both the executors and beneficiaries of project outcomes. It highlights the need for measuring stakeholder satisfaction through tailored Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to ensure project success, especially in complex projects where stakeholder expectations often diverge from initial requirements. Ultimately, it asserts that knowledge-based stakeholder management is essential for achieving desired project goals and value generation.