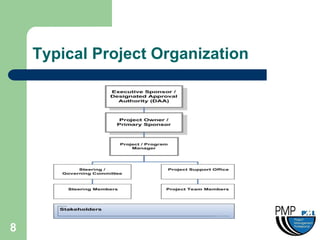
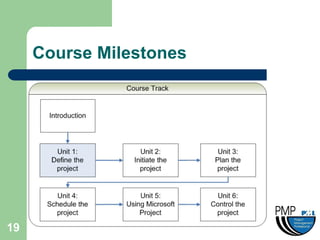
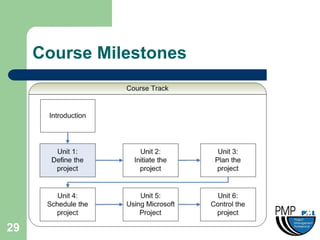
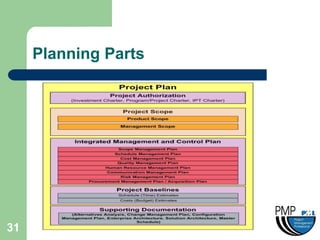
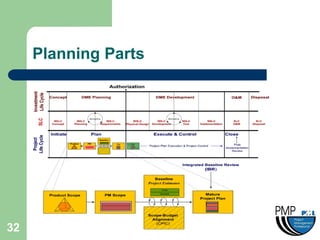
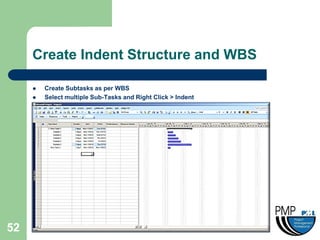
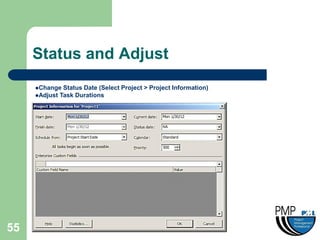
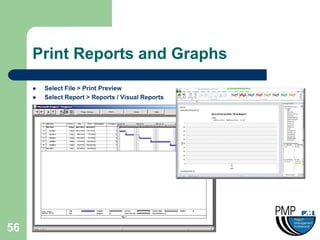
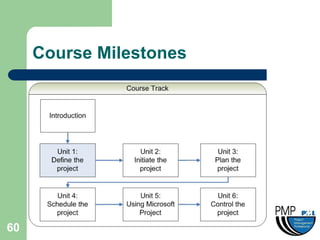
This document provides an overview of project management concepts and techniques. It outlines the objectives of a project management simulation course, which are to provide process knowledge and application of PMI principles and Microsoft Project. The document then covers various aspects of project management, including defining a project, initiating a project, planning, scheduling, controlling a project, and using Microsoft Project as a scheduling tool. Key topics like the project lifecycle, work breakdown structure, Gantt charts, resources, and change management are discussed at a high level.