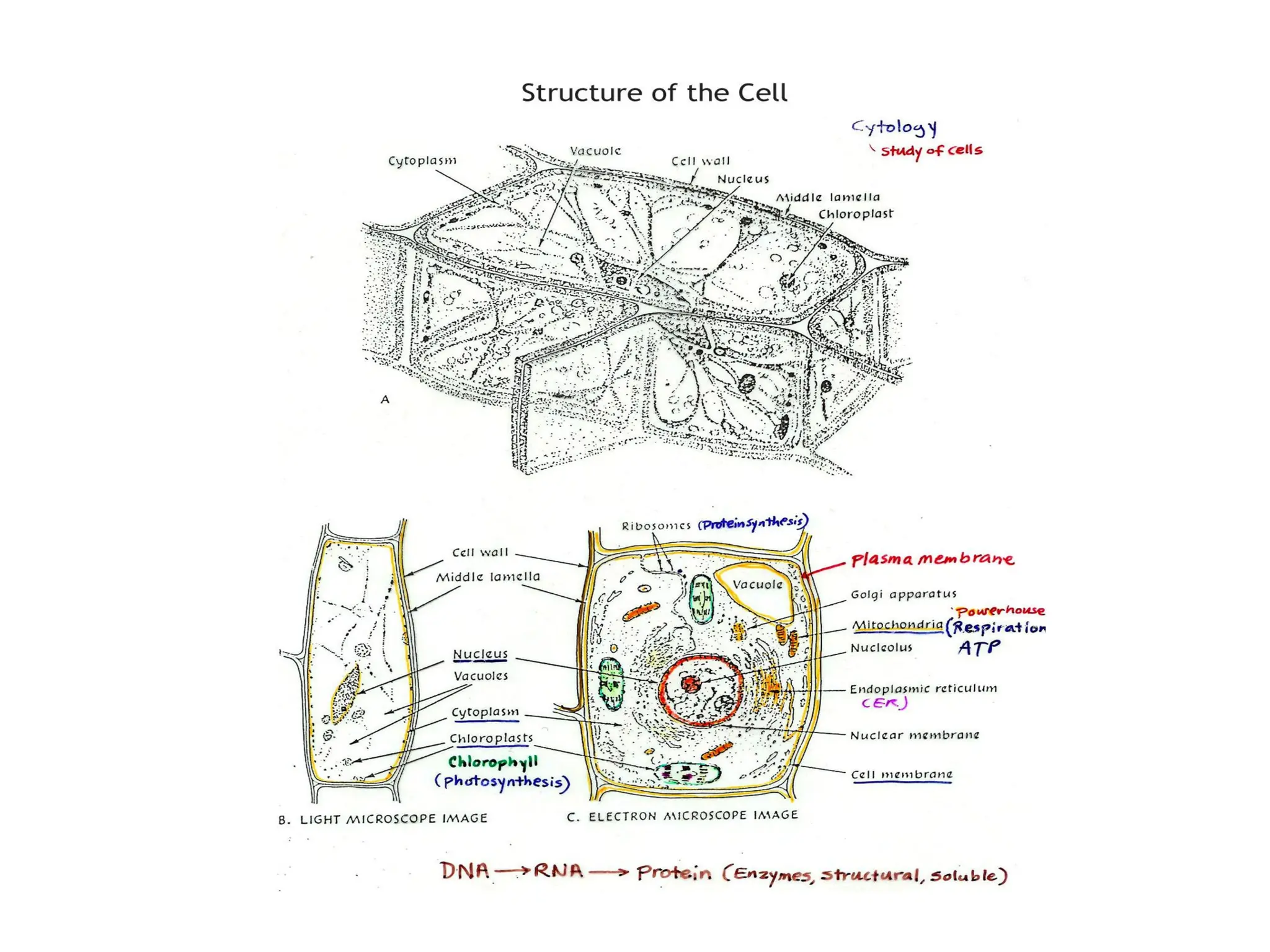
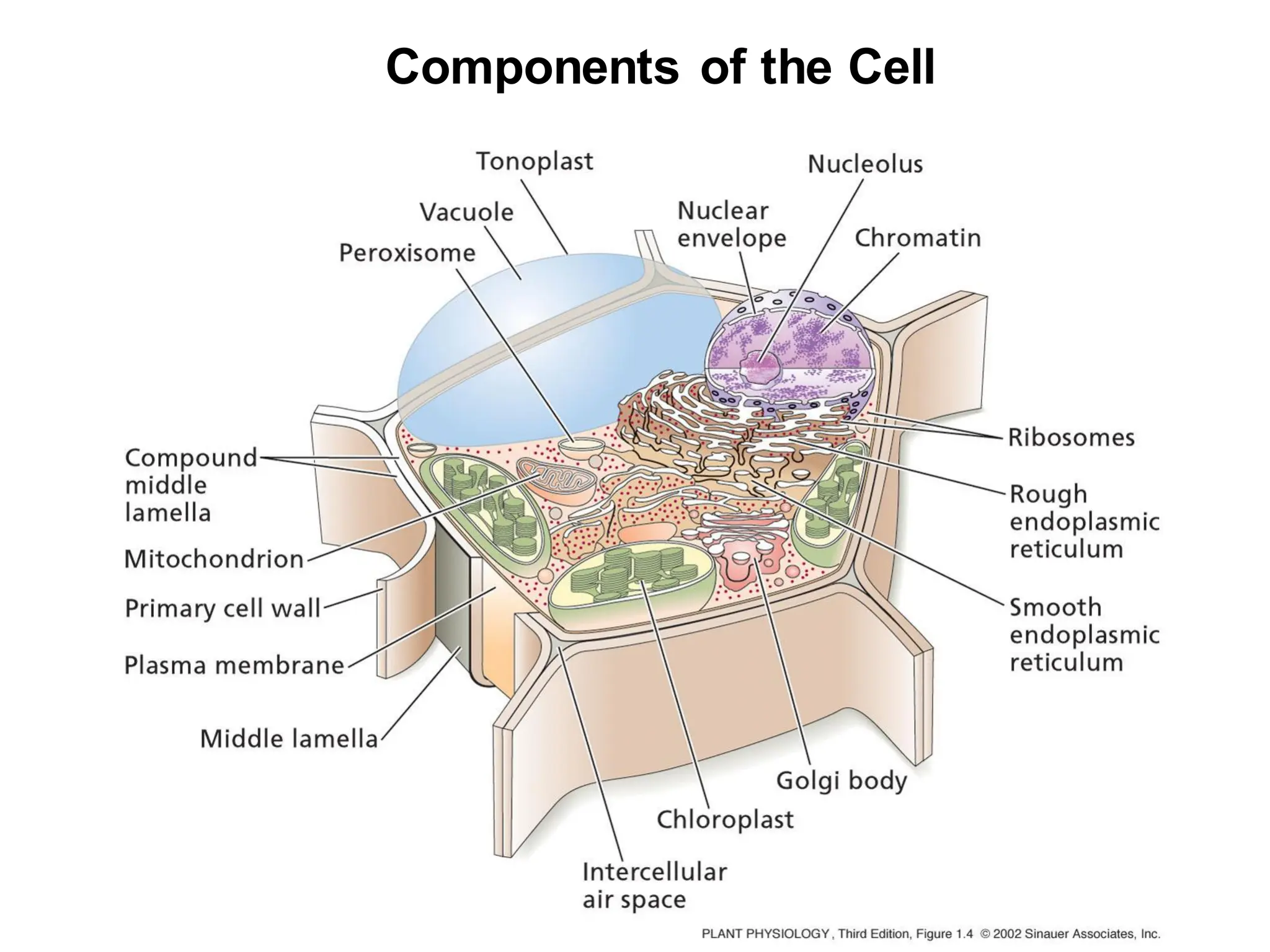
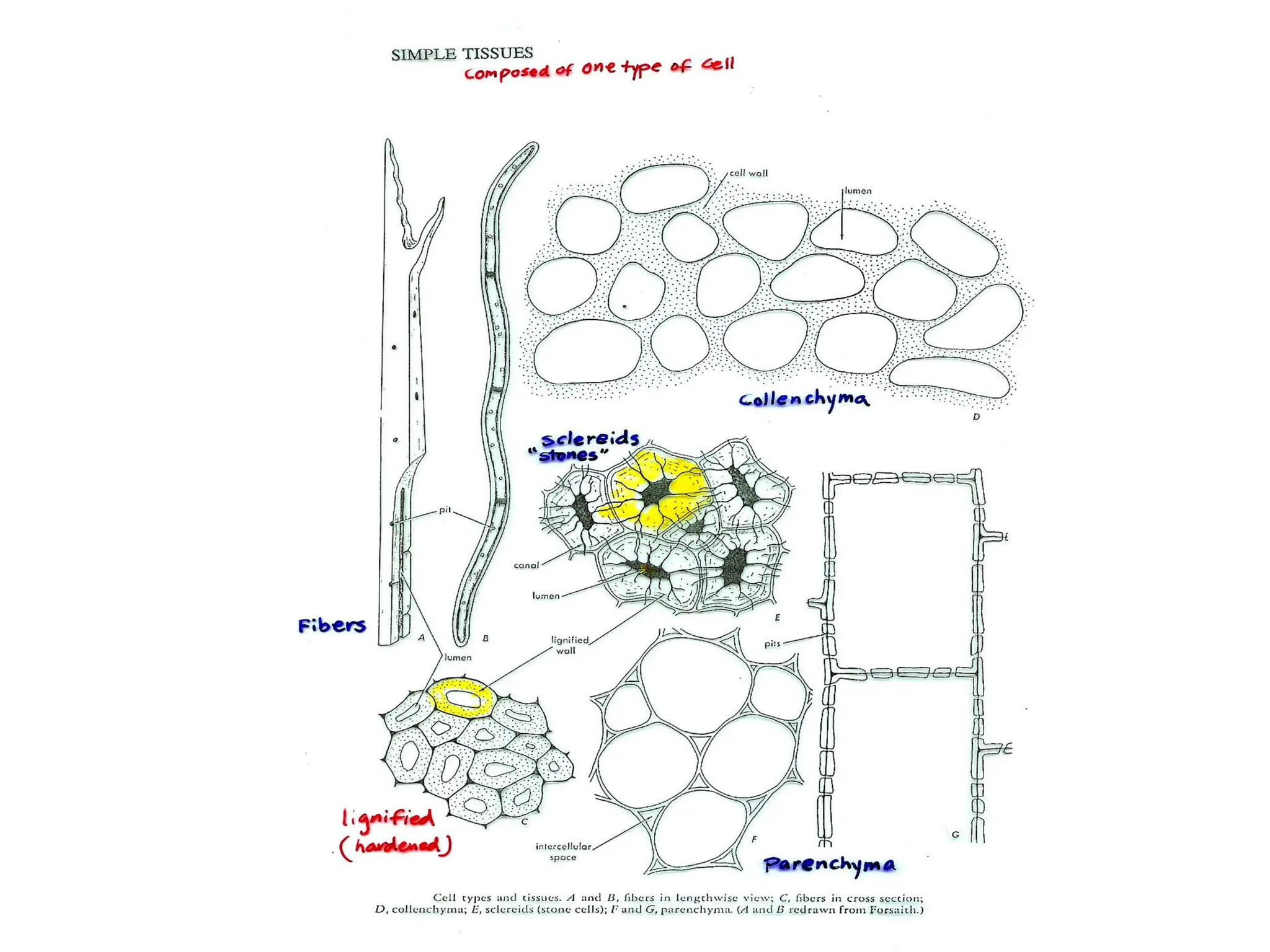
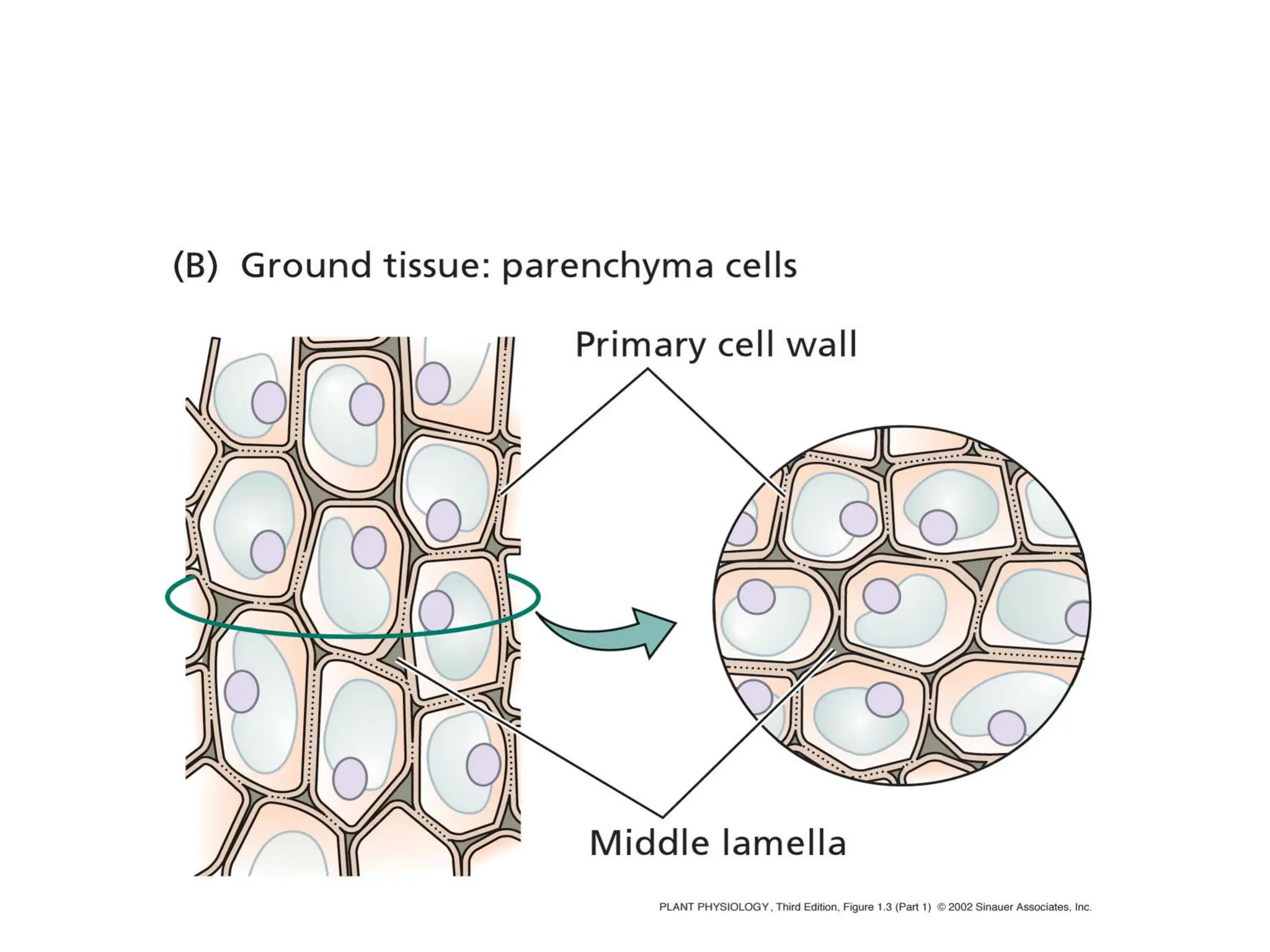
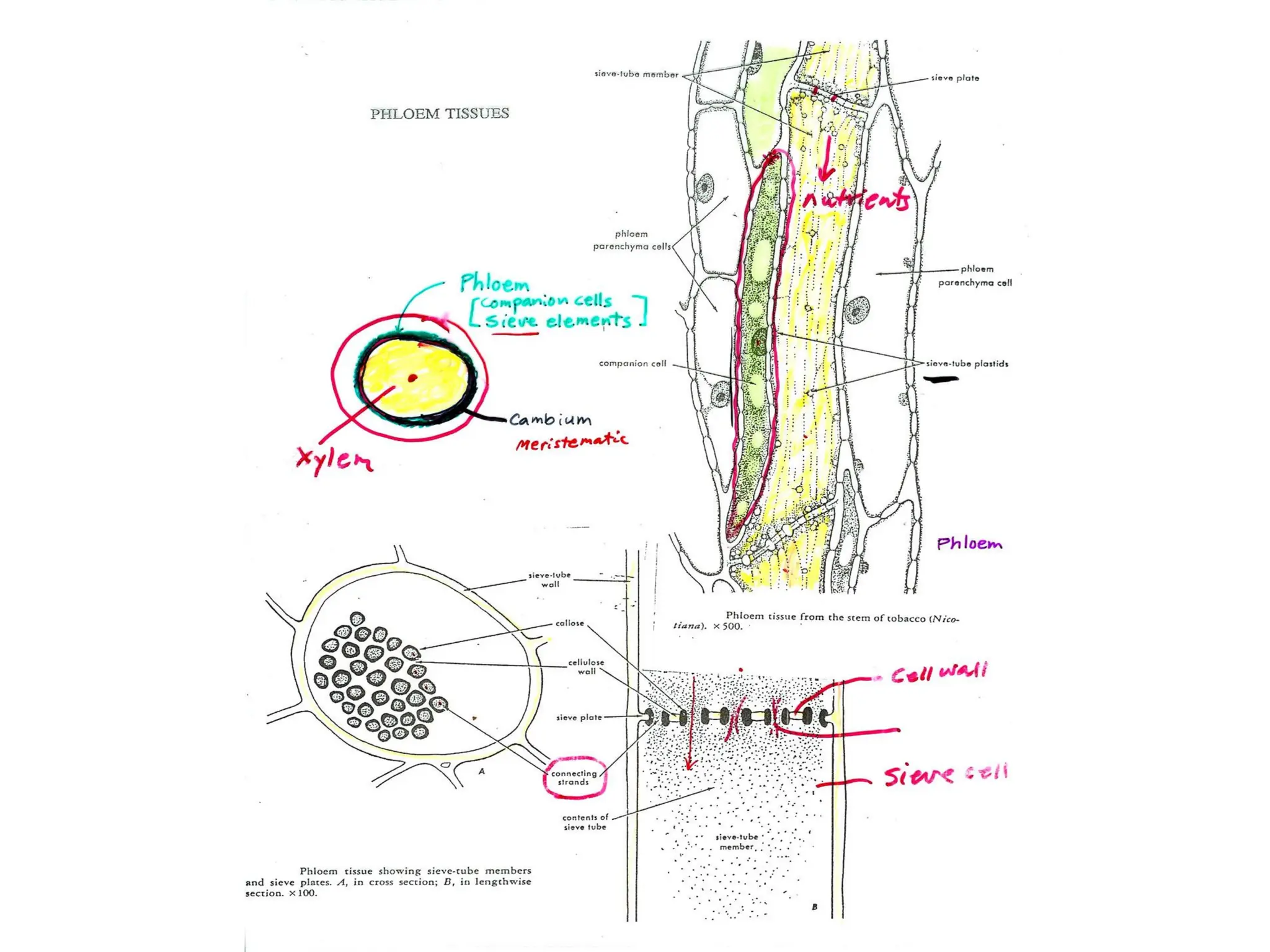
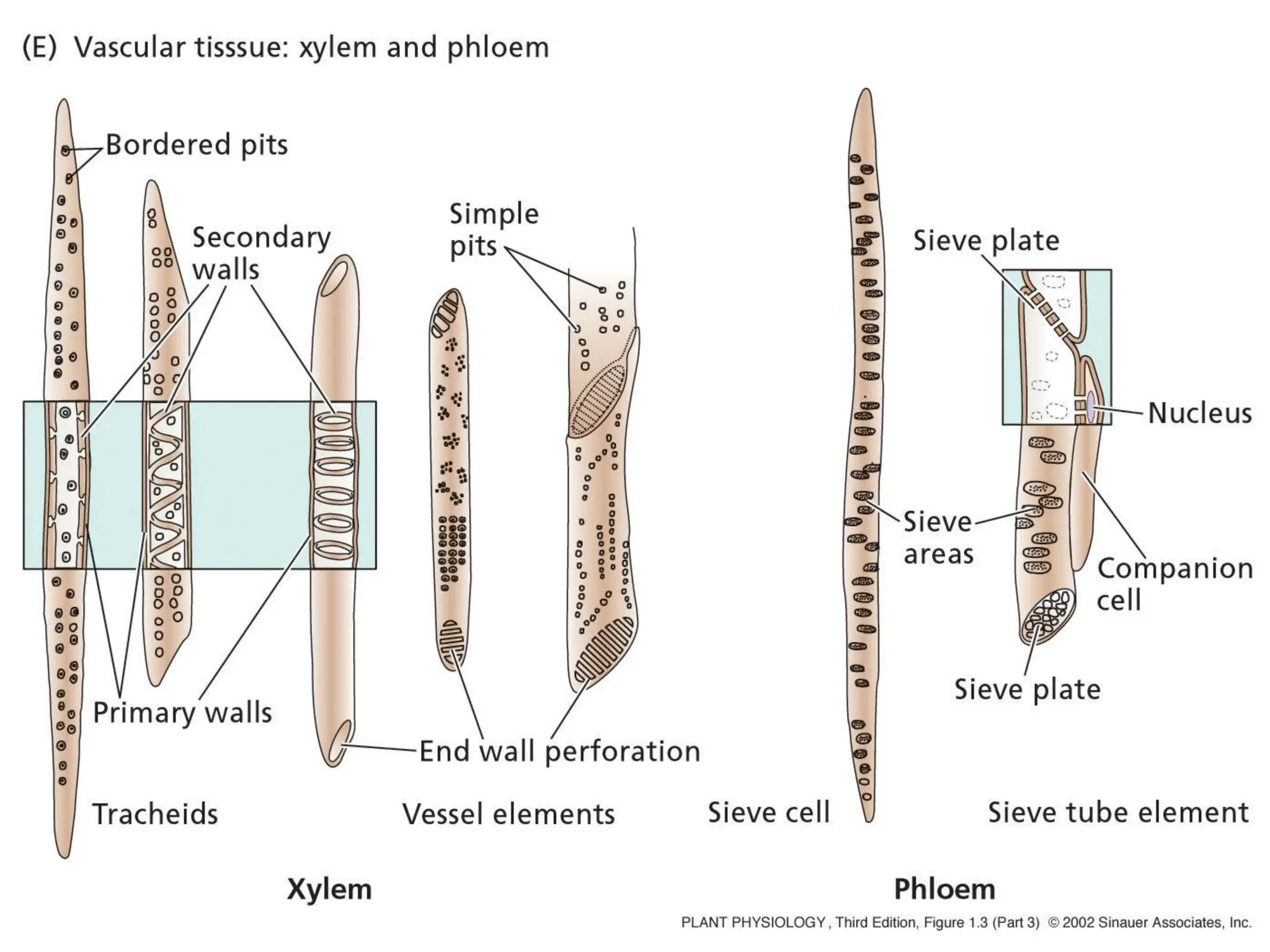
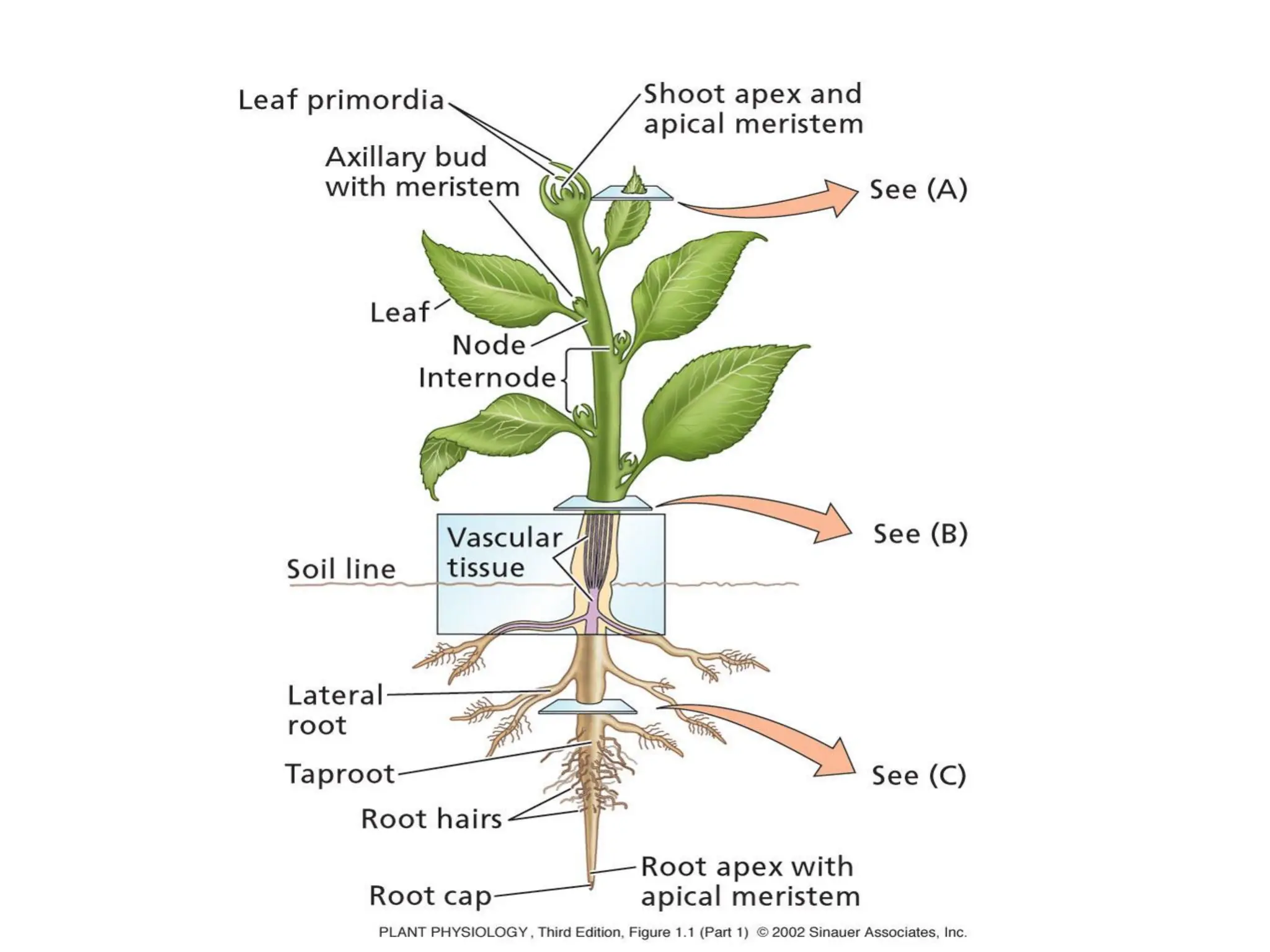
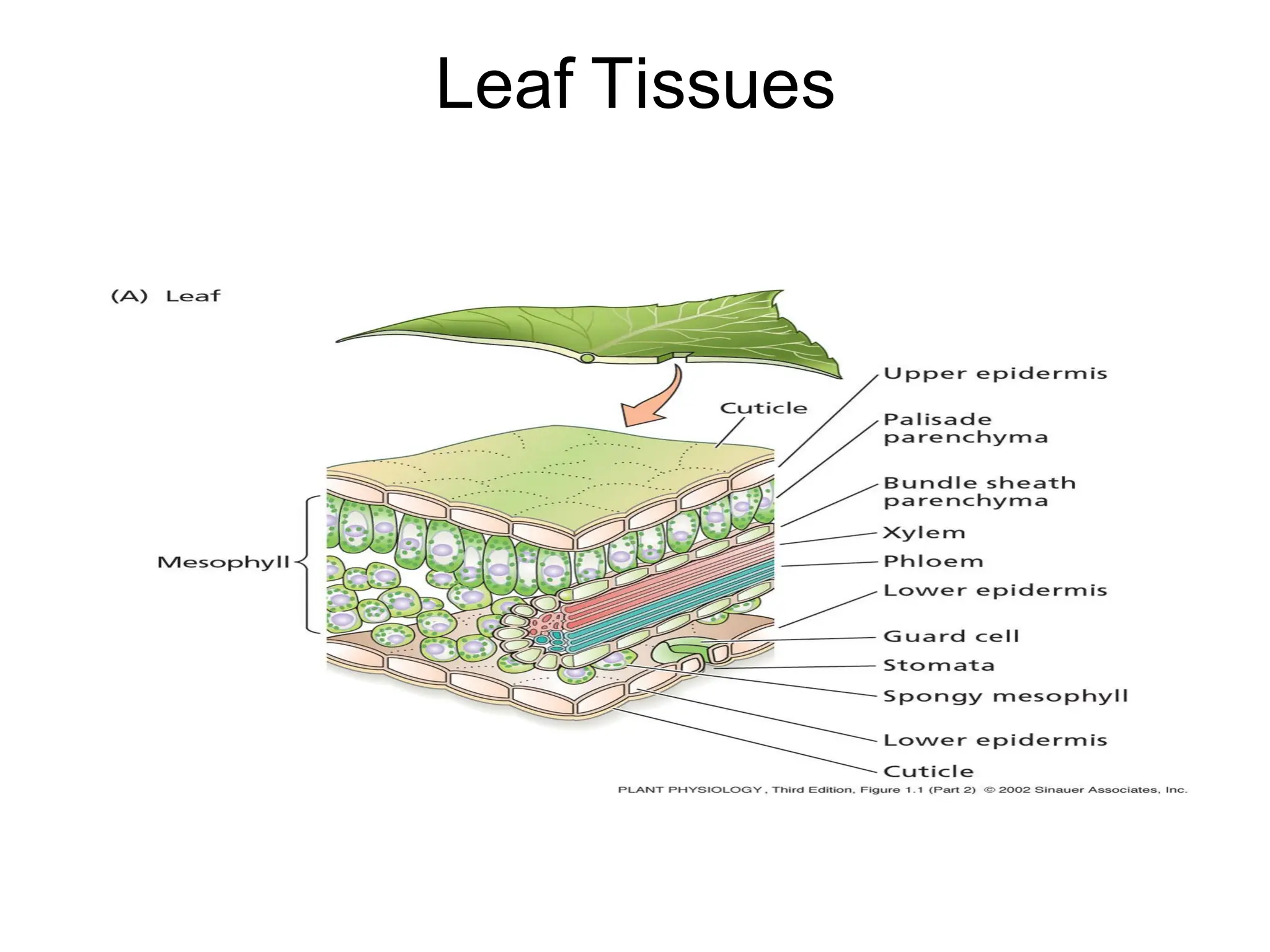
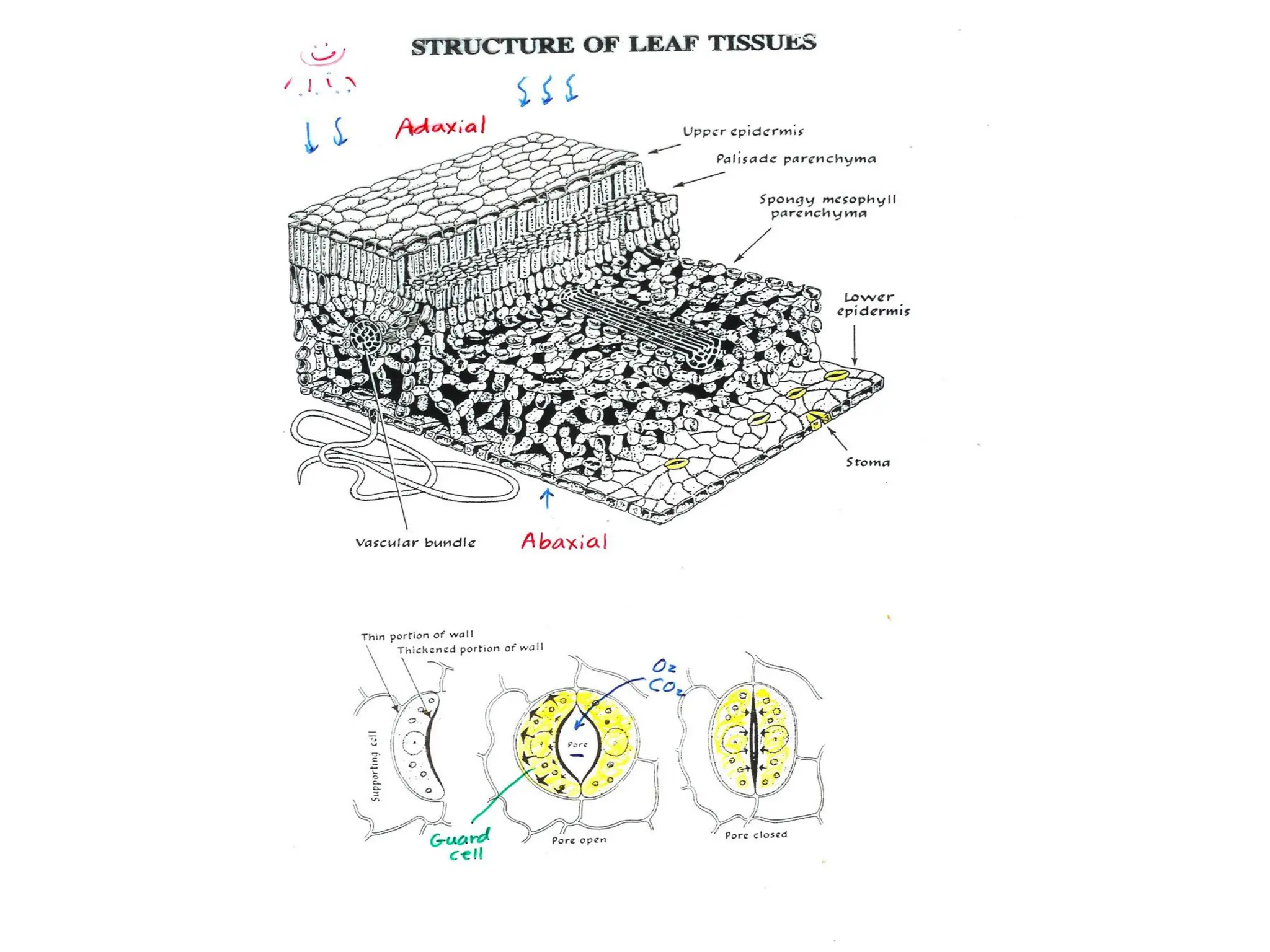
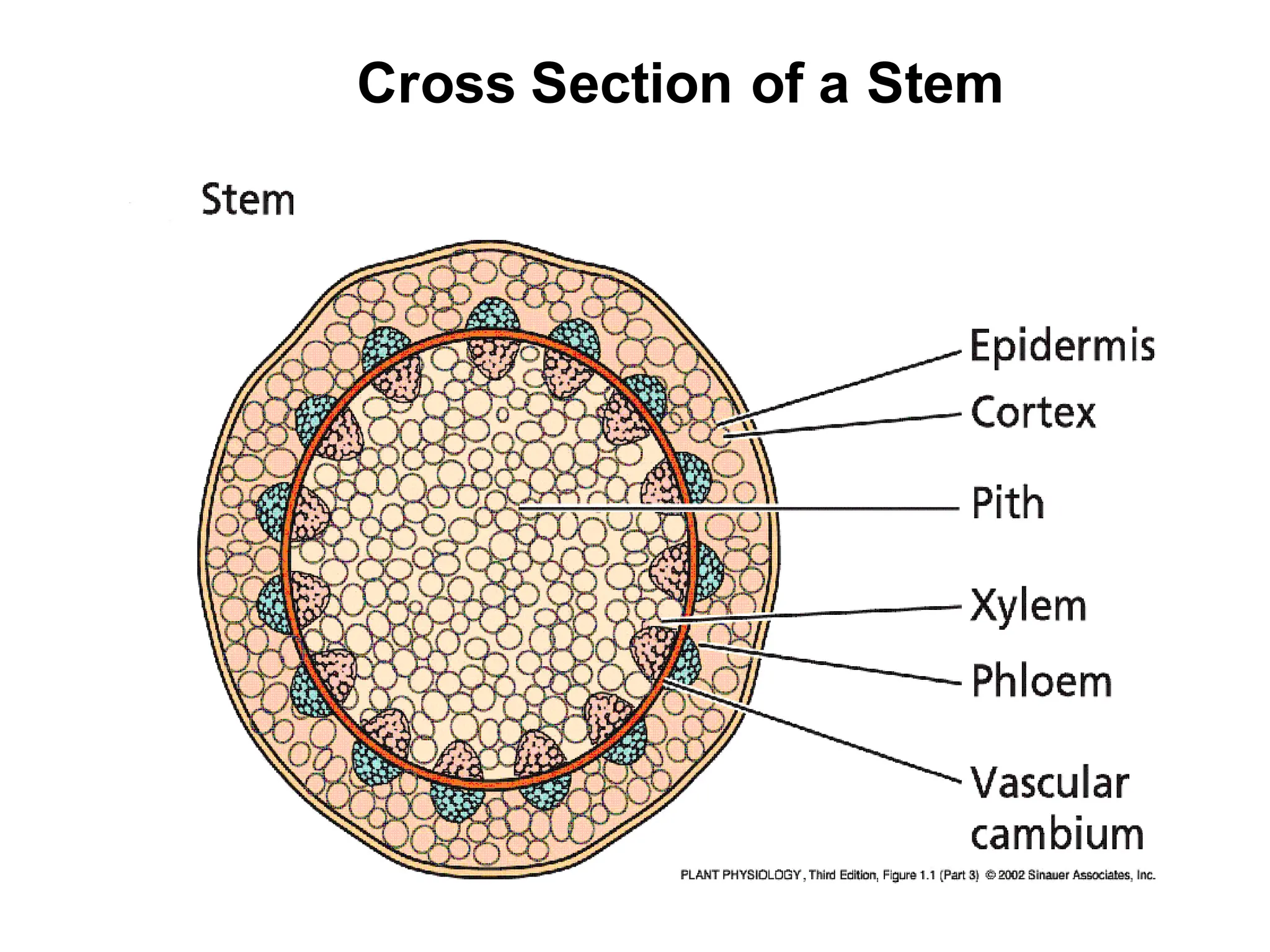
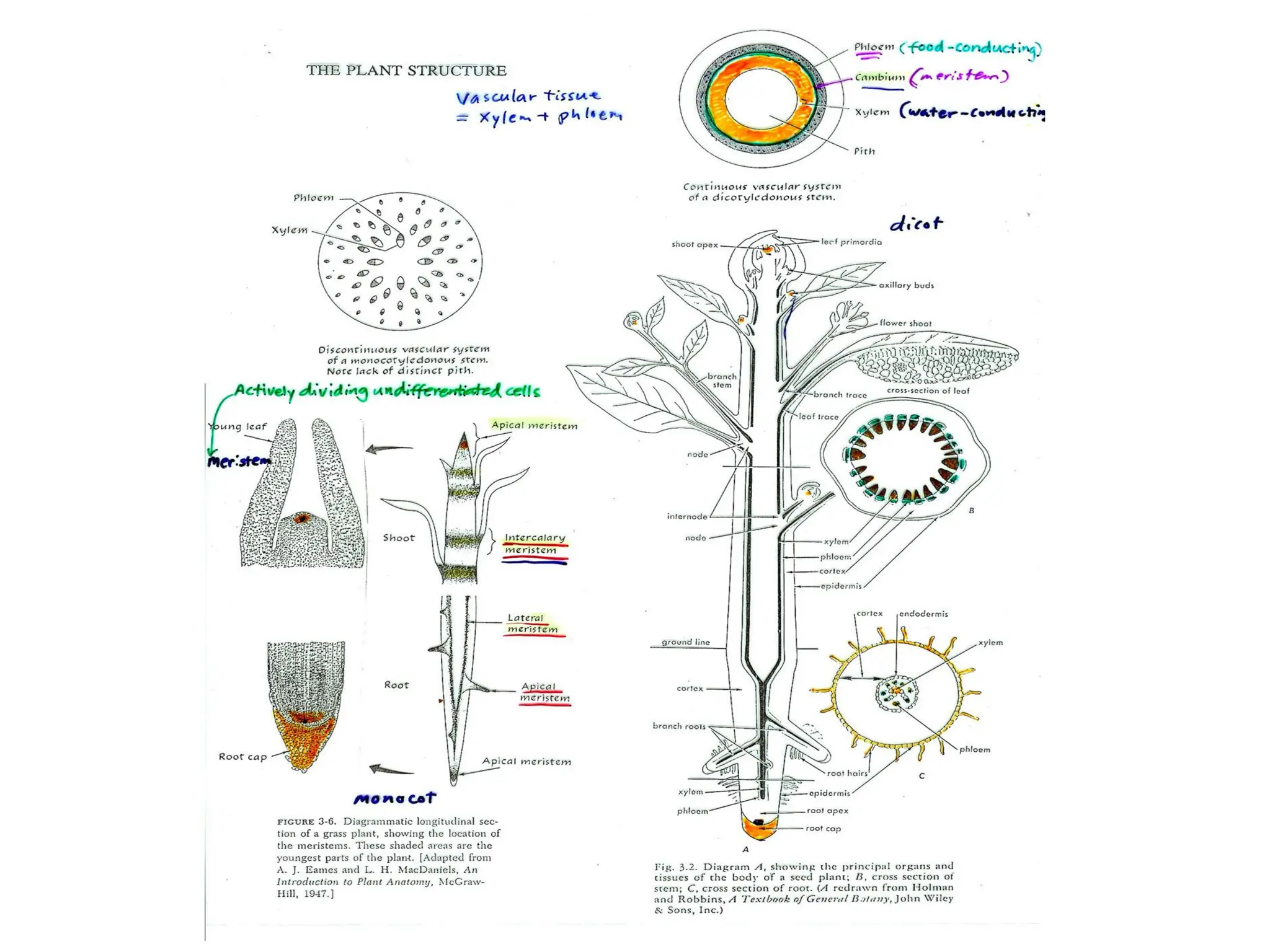
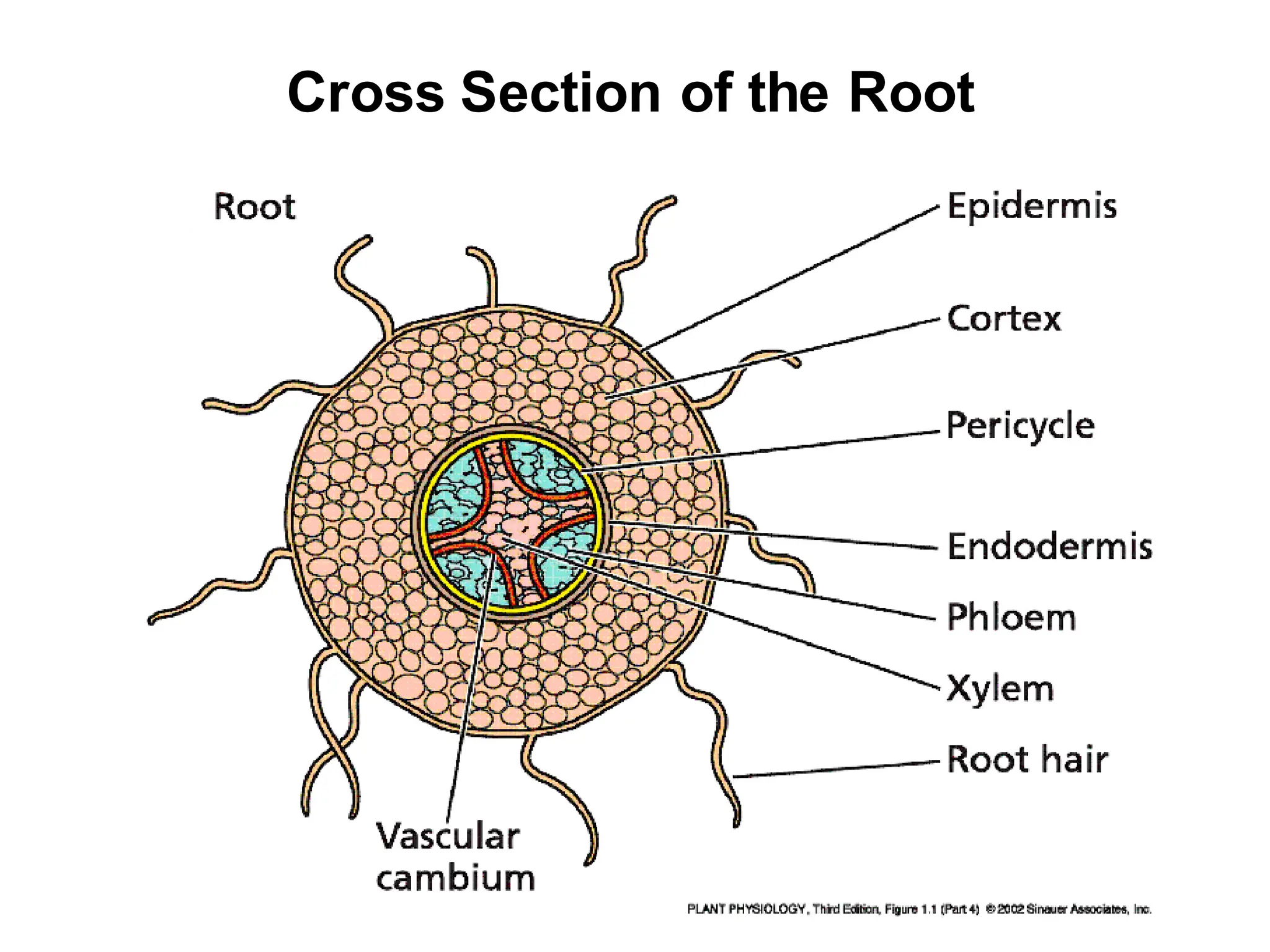
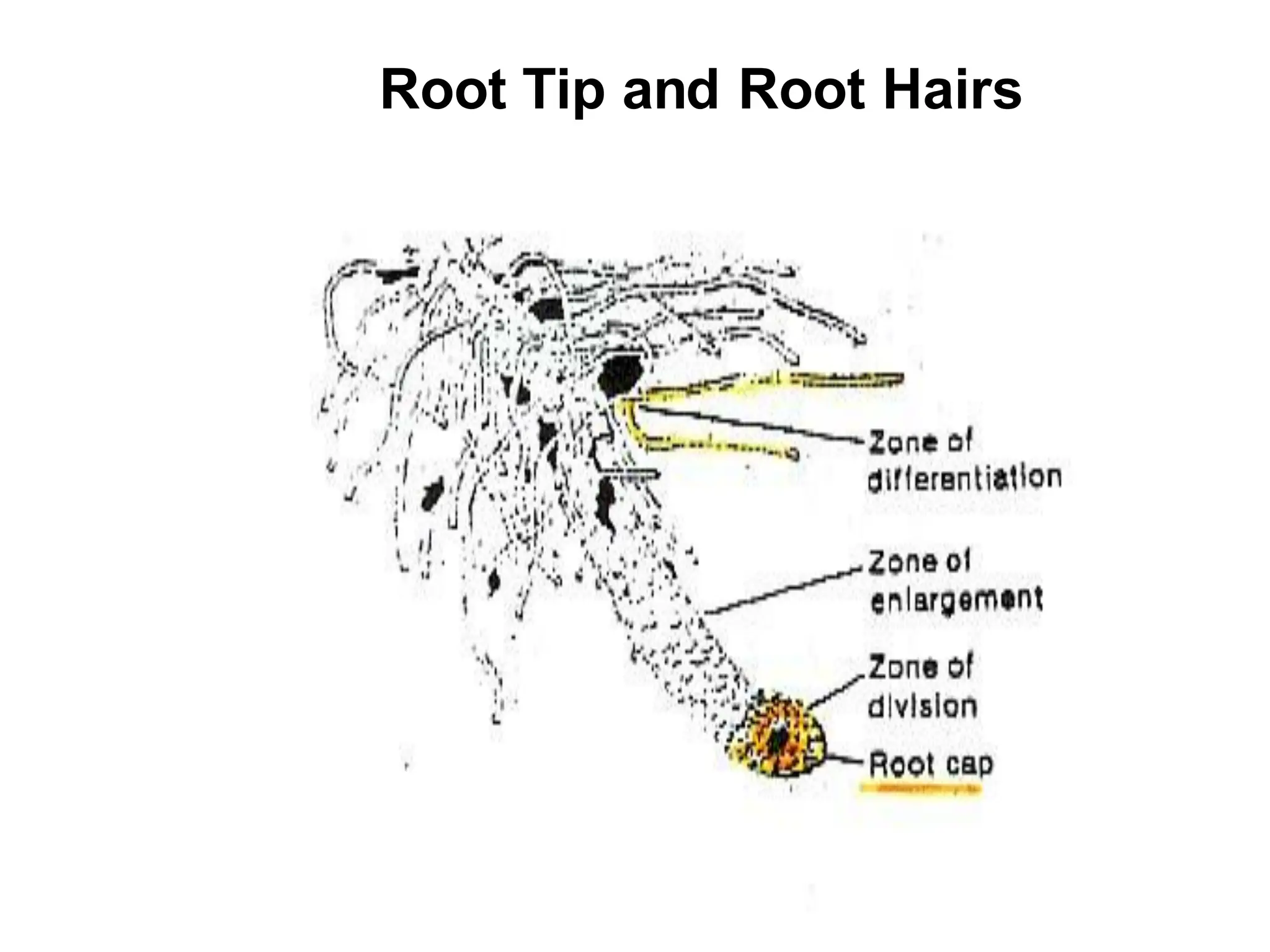
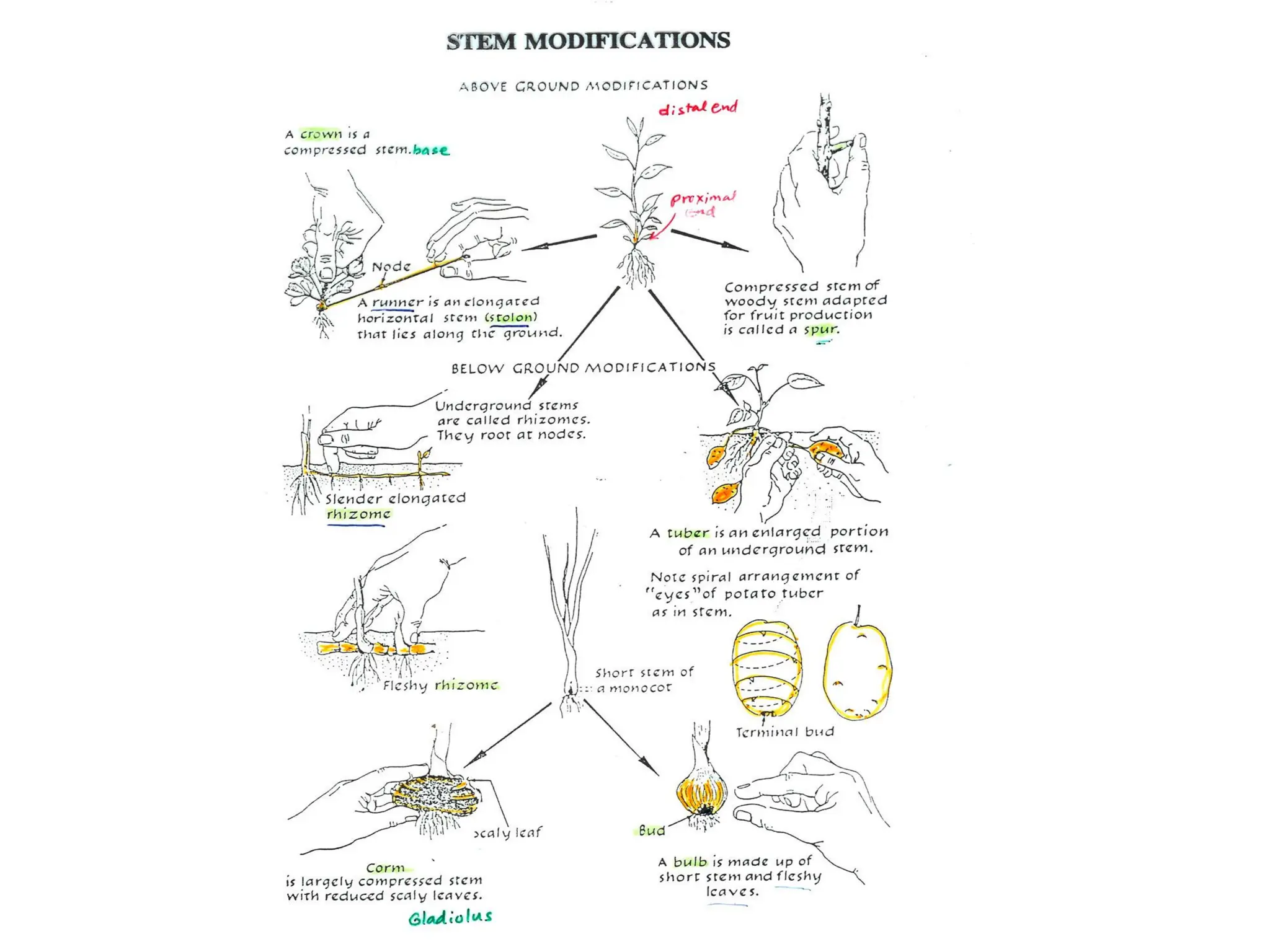
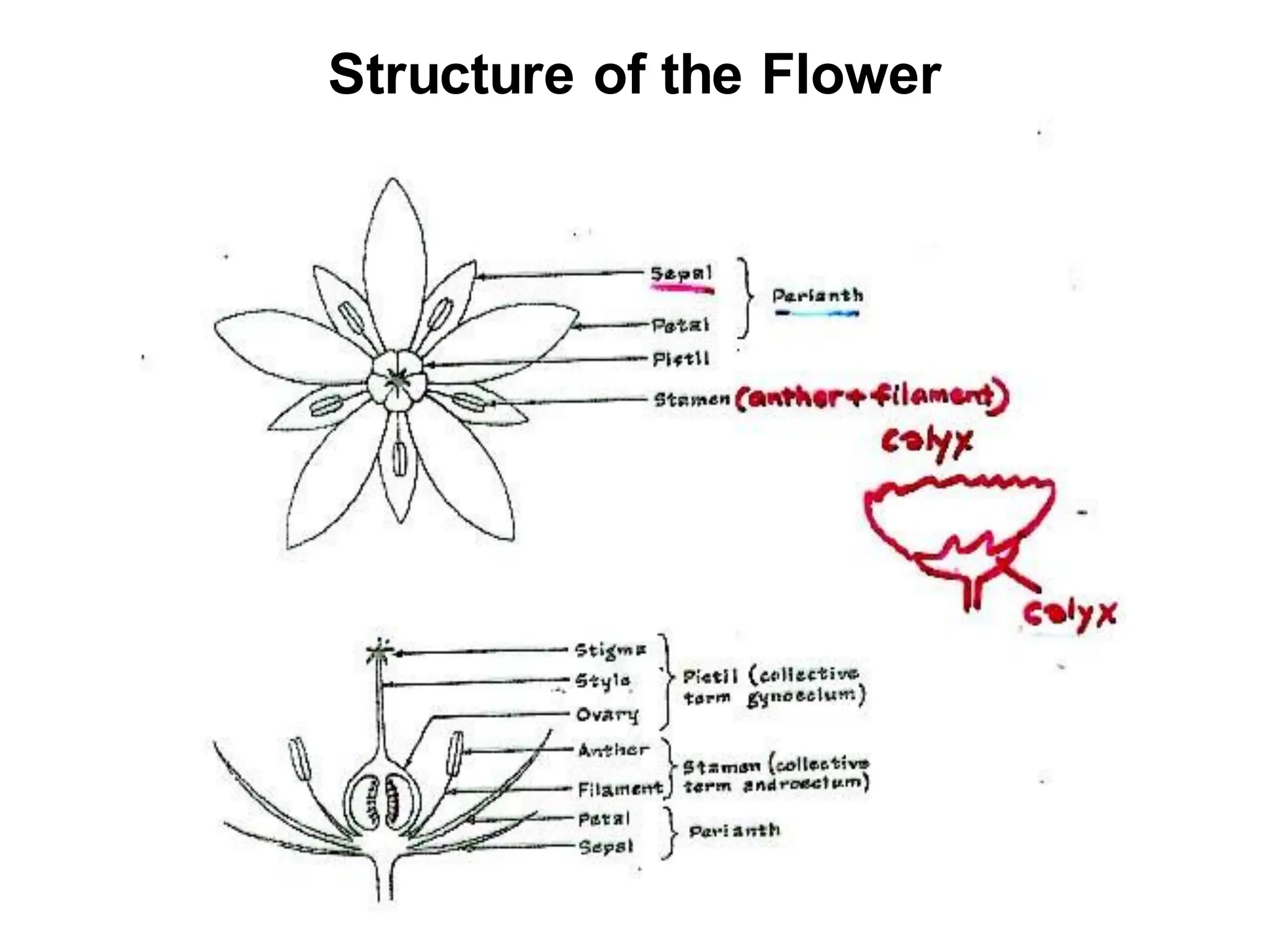
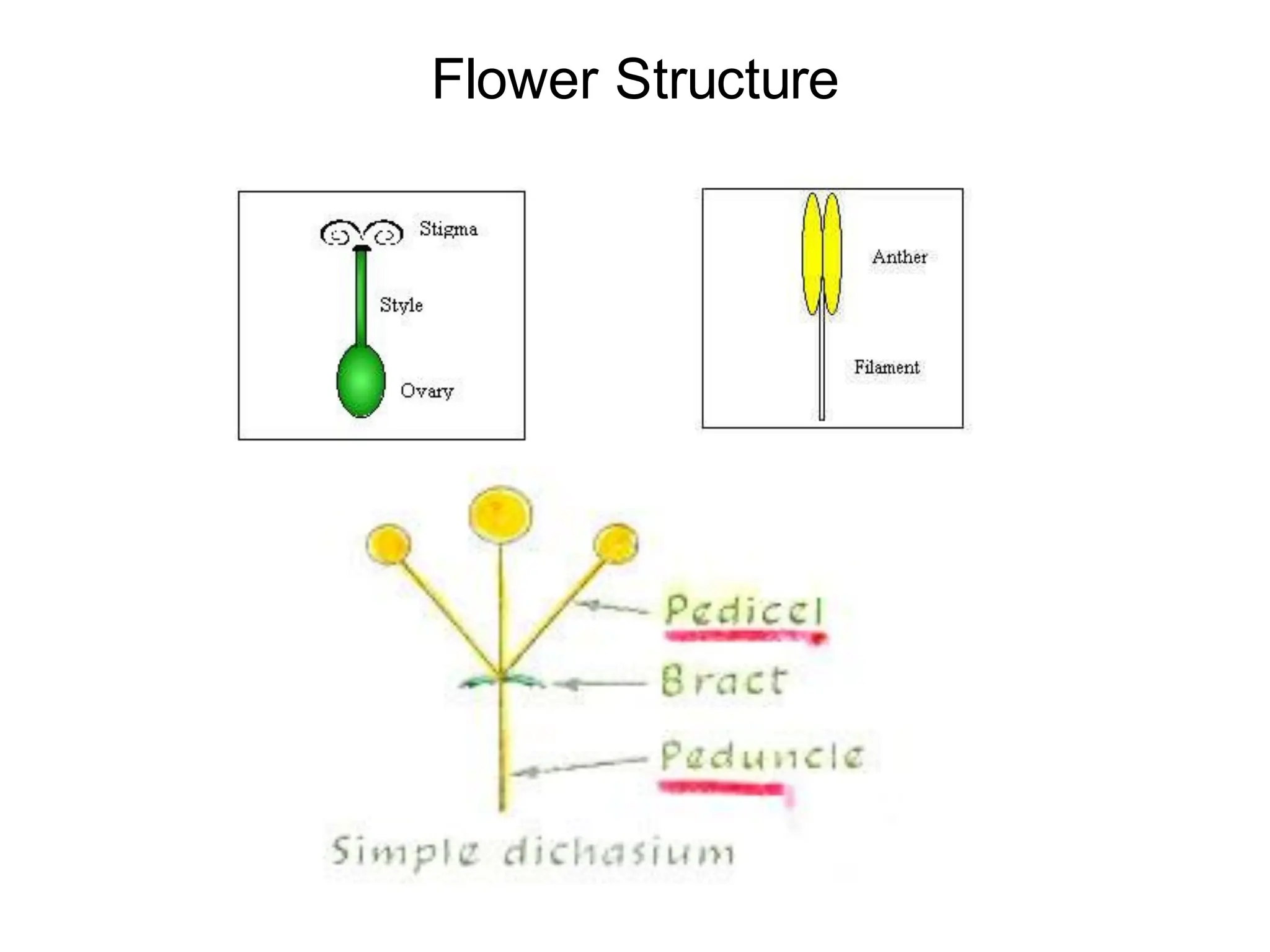
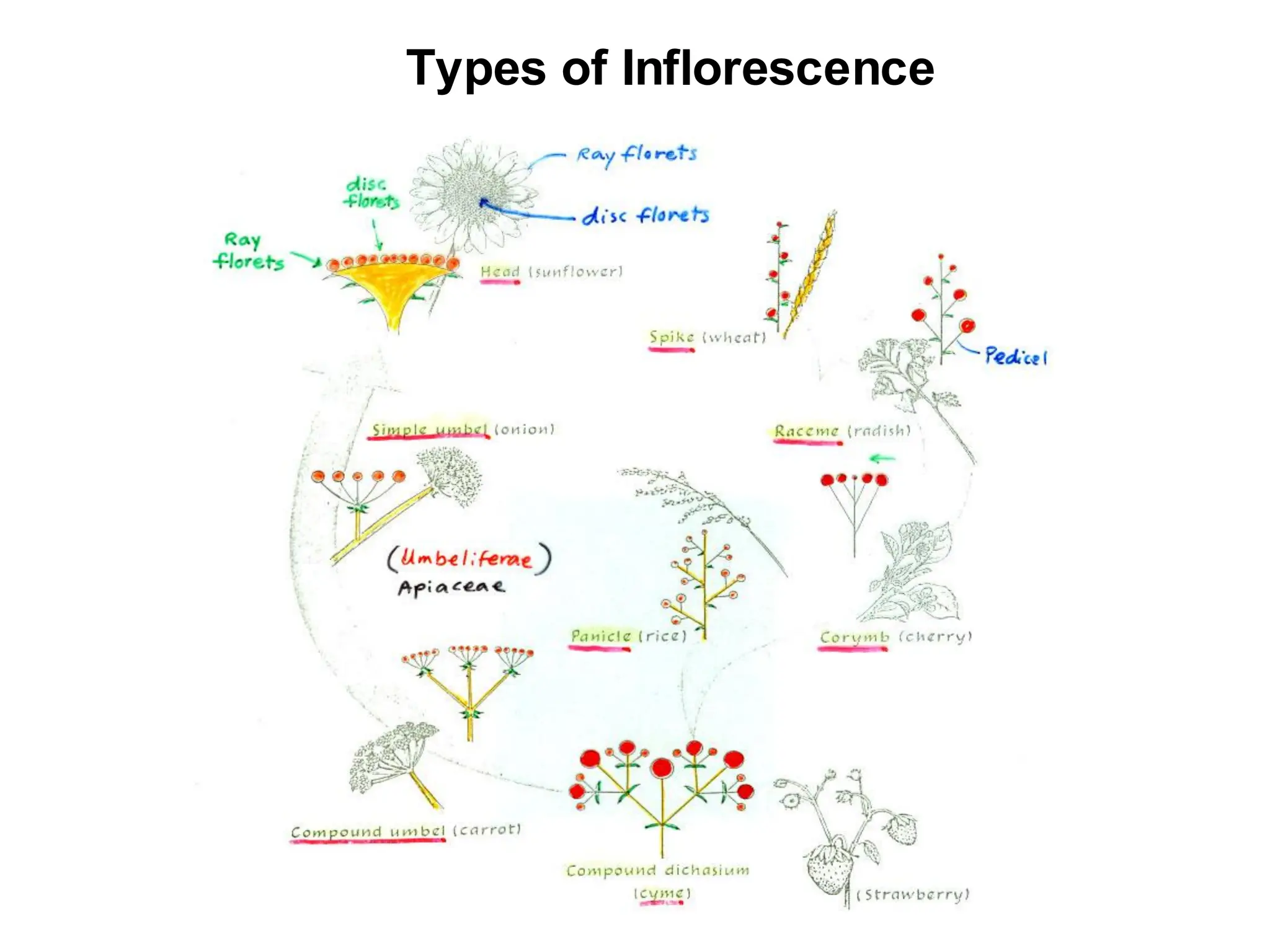
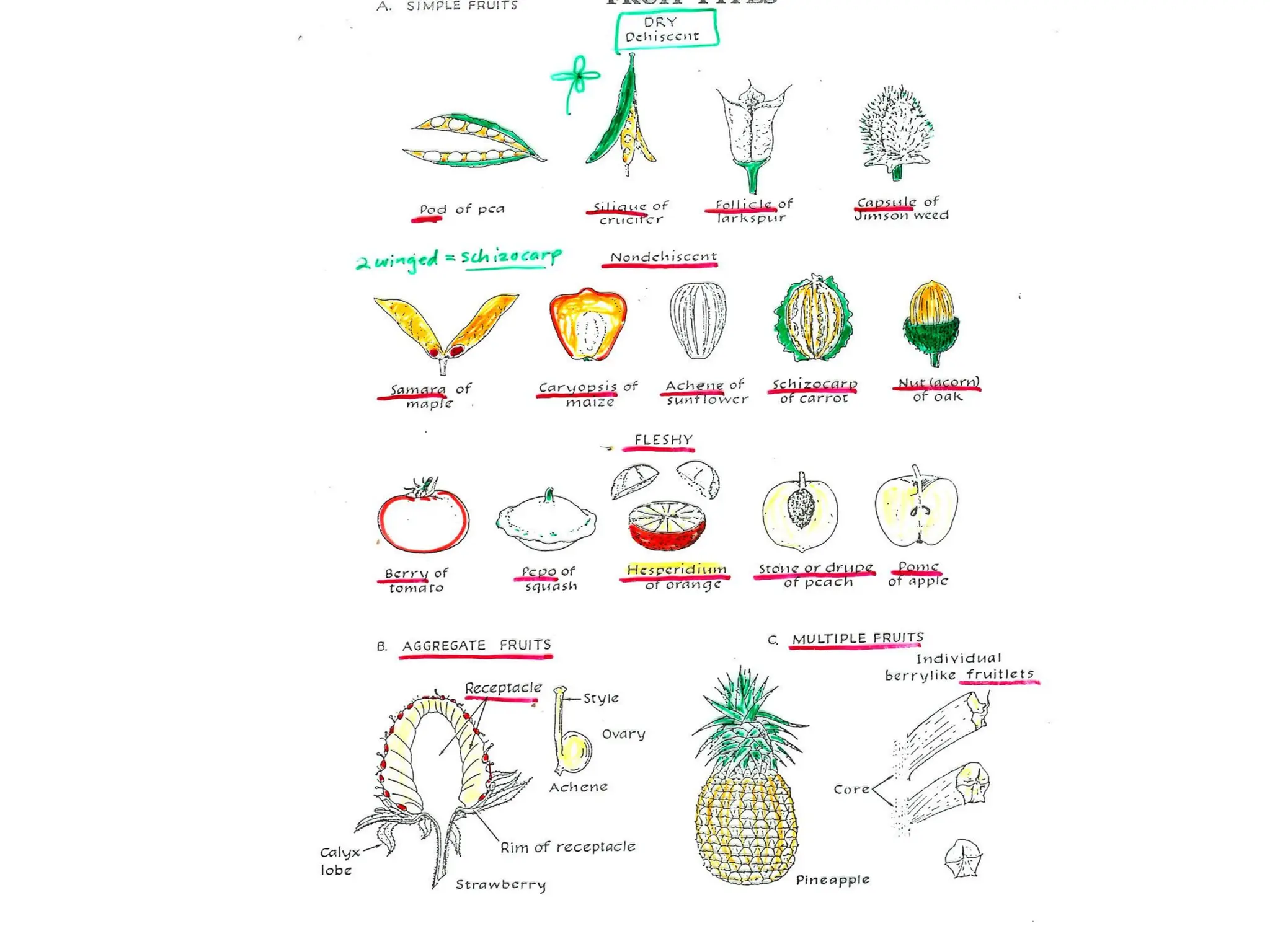
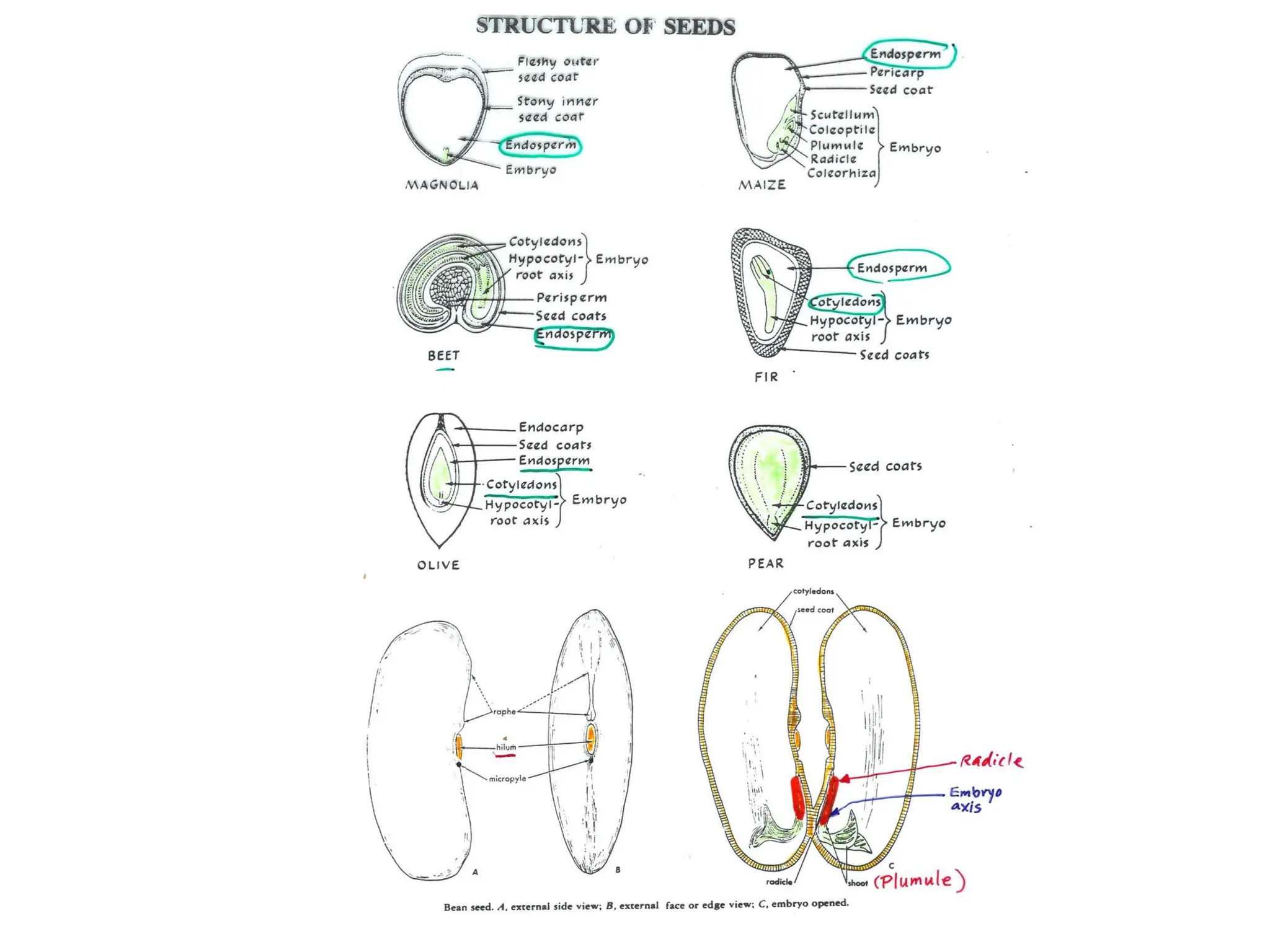
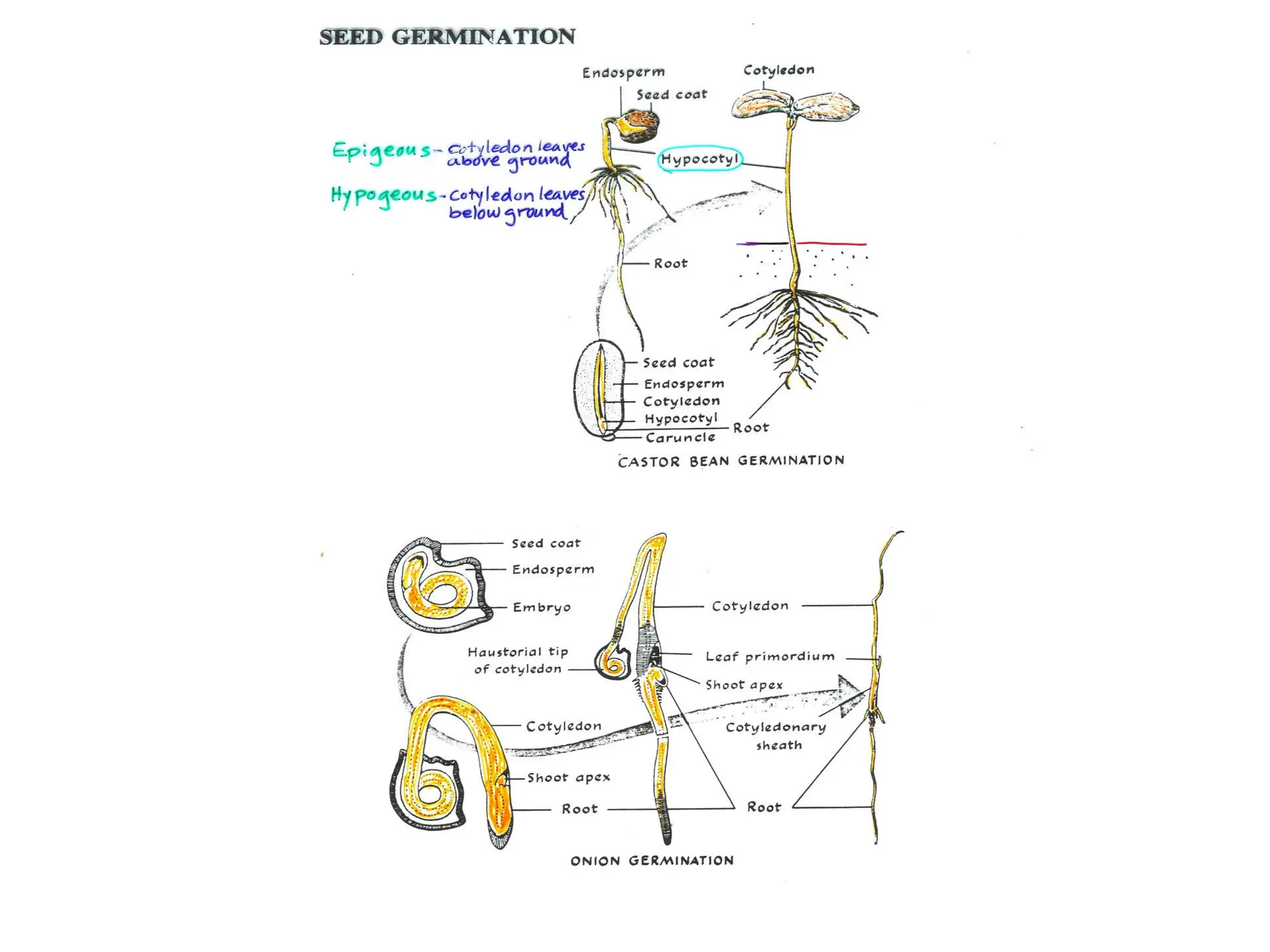
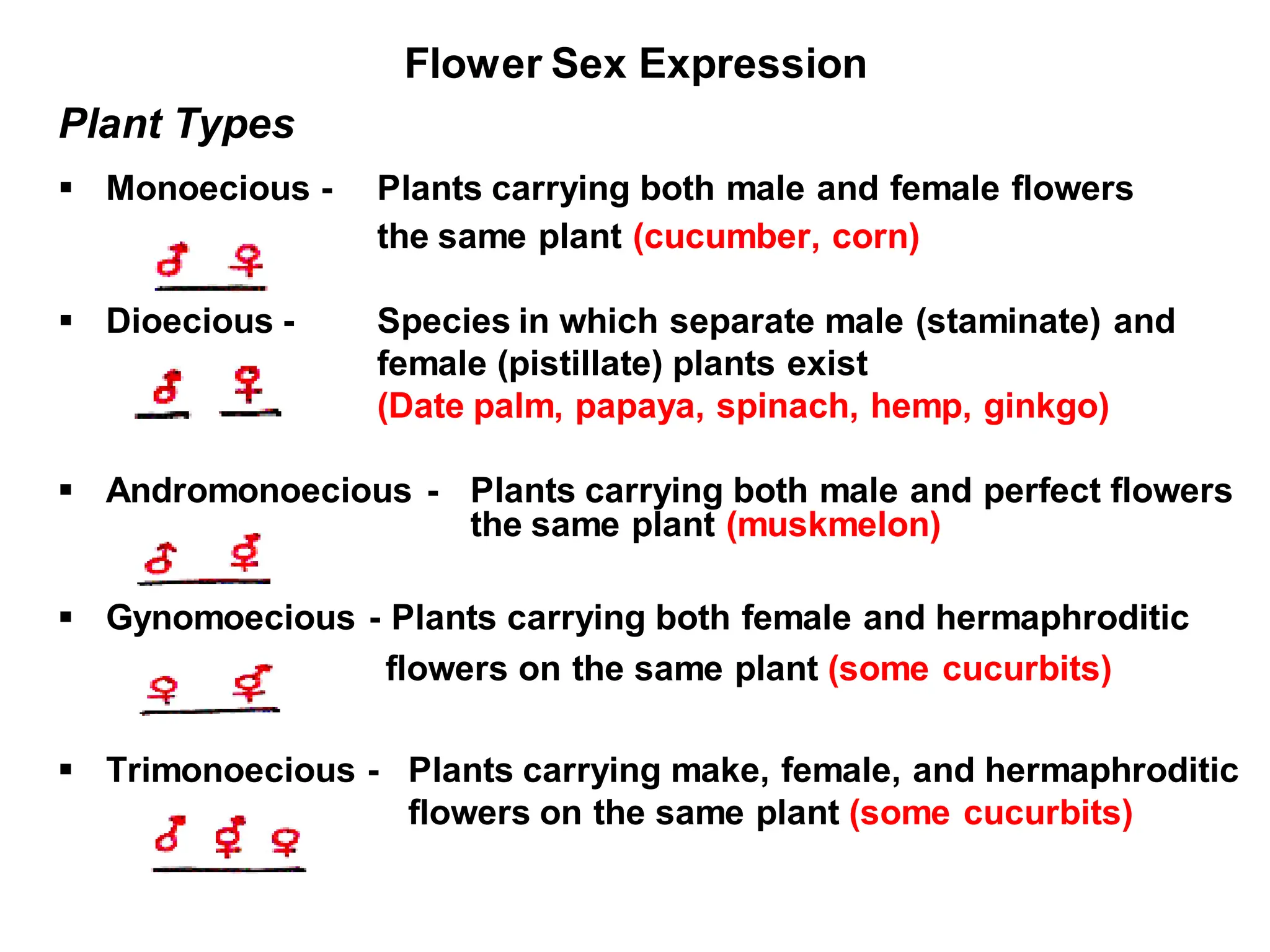
This chapter discusses plant structure and covers topics like plant cells and tissues, anatomical regions of plants, and morphological structures including roots, shoots, leaves, flowers, and seeds. It describes the structures of leaves, stems, roots, root tips, root hairs, and flowers. It also covers flower classification, inflorescence types, flower morphology, and flower sex expression in different plant types such as monoecious, dioecious, andromonoecious, gynomoecious, and trimonoecious plants.